Cistercian Monk
The Order of Cistercians, sometimes called the White Monks, is a Roman Catholic religious order of enclosed…

Costume of a Bishop (12th Century)
The pontifical vestments, also referred to as episcopal vestments or pontificals, are the liturgical…

John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe (mid-1320s – 31 December 1384) was an English theologian, translator and reformist.…

Norman Doorway
The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the…

Early English Door
The most significant and characteristic development of the Early English period was the pointed arch…

Decorated Doorway
The most significant and characteristic development of the Early English period was the pointed arch…

Decorated Arch and Piscina
A piscina or sacrarium is a shallow basin placed near the altar of a church, used for washing the communion…
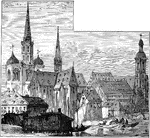
Constance Cathedral
The Cathedral of Constance (Konstanzer Münster in German) served as the central church of the diocese…

Beauchamp Chantry, St. Mary's, Warwick
The church foundations date back nearly nine hundred years, being created by Roger de Beaumont, 2nd…

King's College Chapel, Cambridge
Henry VI planned a university counterpart to Eton College, the chapel being the only portion that was…

The Alamo
The Alamo, originally known as Mission San Antonio de Valero, is a former Roman Catholic mission and…

Hidalgo Castello
Hidalgo Castello was a Mexican Roman Catholic priest and revolutionary rebel leader. He is regarded…

John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe (mid-1320s – 31 December 1384) was an English theologian, translator and reformist.…

Mary I of England
Mary I (18 February 1516 - 17 November 1558), was Queen of England and Queen of Ireland from 19 July…

St. Paul's Cathedral, London (Interior)
St Paul's Cathedral, is the Anglican cathedral on Ludgate Hill, in the City of London, and the seat…

Thomas Cardinal Wolsey
Thomas Cardinal Wolsey (c.1470~1471 – November 28 or November 29, 1530), who was born in Ipswich,…

Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X, born Giovanni de' Medici (December 11, 1475 – December 1, 1521) was Pope from 1513…

Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II (5 December 1443 – 21 February 1513), born Giuliano della Rovere, was Pope from…

John Cardinal Fisher
John Cardinal Fisher (c.1469 – 22 June 1535), from 1935 Saint John Fisher, was an English Catholic…

A Carthusian
The Carthusian Order, also called the Order of St. Bruno, is a Roman Catholic religious order of enclosed…

Pope Paul III
Pope Paul III (February 29, 1468 – November 10, 1549), born Alessandro Farnese, was Pope of the…

Bishop Hugh Latimer
Hugh Latimer (c. 1485-October 16, 1555) was the bishop of Worcester, and by his death he became a famous…

St. Mary's Church, Cambridge
In addition to being a parish church in the Diocese of Ely, it is the University Church for the University…

Queen Mary Tudor
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), was Queen of England and Queen of Ireland from 19…

Josip Juraj Strossmayer
Josip Juraj Strossmayer (February 4, 1815 – May 8, 1905) was a Roman Catholic bishop, benefactor and…

Pope Sixtus V
Pope Sixtus V (December 13, 1521 – August 27, 1590), born Felice Peretti di Montalto, was Pope…

Archbishop Edmund Grindal
Edmund Grindal (c. 1519 – 6 July 1583) was an English church leader who successively held the…

Archbishop John Whitgift
John Whitgift (c. 1530 – February 29, 1604) was Archbishop of Canterbury from 1583 to his death. Noted…

Frederick II of Prussia
An illustration of Frederick II of Prussia attempting to find lodging for the evening. Frederick II…

Mary, Queen of Scots
Mary I (popularly known in the English-speaking world as Mary, Queen of Scots and, in France, as Marie…

A Puritan Soldier
A Puritan of 16th and 17th century England was an associate of any number of religious groups advocating…

Prince Rupert of the Rhine
Rupert, Count Palatine of the Rhine, Duke of Bavaria, commonly called Prince Rupert of the Rhine, (17…
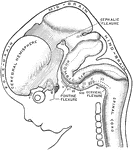
Brain of Embryo
Profile view of brain of a human embryo of ten weeks. The various cranial nerves are indicated by numerals.…

Charles I of England
Charles I, (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland and Ireland from…

Hereford Cathedral
In the war between King and Parliament (the English Civil War) the city of Hereford fell into the hands…

Church of All Saints, Wilden, Worcestershire
All Saints Church in Wilden, Worcestershire about one mile to the north east of Stourport. It was designed…

Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London, a major conflagration that swept through the central parts of London from…

Archbishop William Sancroft
William Sancroft (30 January 1617 – 24 November 1693), was the 79th archbishop of Canterbury. He became…

King George I of Great Britain
George I (28 May 1660 – 11 June 1727) was King of Great Britain and Ireland from 1 August 1714…

Frederick II of Prussia on Horseback
An illustration of Frederick II of Prussia on horseback. Frederick II (January 24, 1712 – August 17,…

Frederick II of Prussia and Judges
An illustration of Frederick II of Prussia and the unjust judges. Frederick II (January 24, 1712 –…

Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (April 27, 1737 - January 16, 1794) was an English historian and Member of Parliament.…

James Cardinal Gibbon
James Cardinal Gibbons (23 July 1834 - 24 March 1921) was an American prelate, the Roman Catholic Archbishop…

Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classical scholar,…
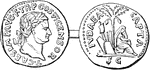
Roman Coins (Denarius)
An illustration of a roman coin (denarius). The left side represents the laurel-crowned head of Titus.…

Julius Caesar (profile)
An illustration of Caesar. A politician of the populares tradition, he formed an unofficial triumvirate…

Man and Woman in Roman Clothing
An illustration of a man and woman standing in typical Roman clothing. Clothing in ancient Rome generally…

Isabella of Castille
Isabella I (April 22, 1451 – November 26, 1504) was Queen of Castile and León. She and…

Frederick II of Prussia
Frederick II (January 24, 1712 – August 17, 1786) was a King of Prussia (1740–1786) from…

Lesbia
Lesbia was the pseudonym of the lover to whom the Roman poet Gaius Valerius Catullus (84-54BC) dedicates…
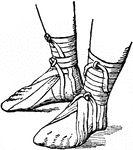
Roman Sandal
A sandal worn in Ancient Rome. This sandal is different from Greek sandals because it has a vamp, or…

Cardinal McCloskey
John Cardinal McCloskey, (March 10, 1810 - October 10, 1885) was an American cardinal, the fifth bishop…

Martha Washington's Bridal Watch
Watch belonging to Martha Custis Washington (June 2, 1731 – May 22, 1802), the wife of George…

Washington Resigning His Commission
At Fraunces Tavern on December 4, Washington formally bade his officers farewell and on December 23,…
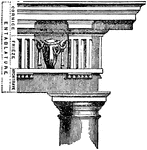
Entablanture
An entablature refers to the superstructure of moldings and bands which lie horizontally above columns,…