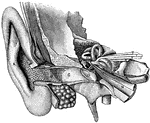
General view of organ of hearing
"A, pinna; B, cavity of the concha, showing the openings of a great number of sebaceous…
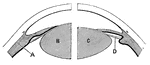
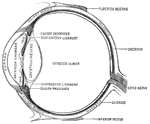
Lens of the eye
"Diagram showing the Change in the Lens during Accomadation. On the right the lens is arranged for distant…
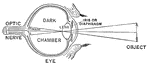
Diagram of the Eye
"Diagram illustrating the Manner in which the Image of an Object is inverted on the Retina." — Blaisedell,…
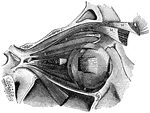
Muscles of the eyeball
"A, attachment of tendon connected with the four recti muscles; B, external rectus,…
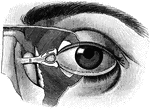
Eyeball
"The Relative Position of the Lachrymal Apparatus, the Eyeball, and the Eyelids. A, lachrymal canals,…

Attachment of the recti
"Showing the attachment of the recti, or straight muscles to the eyeball, also the distribution of arteries…
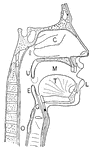
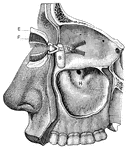
Nasal and throat passageways
"Diagram of a Sectional View of Nasal and Throat Passageways. C, nasal cavities; T,…
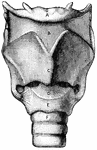
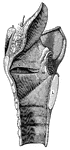
Front view of the larynx
"Cartilages and Ligaments of the Larynx. (Front view.) A, hyoid bone; B, membrane…
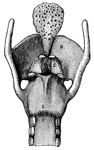
Posterior view of the larynx
"Cartilages and Ligaments of the Larynx. (Front view.) A, epiglottis; B, thyroid cartilage;…
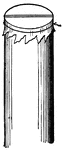
Air Passage
"To illustrate roughly the passage of air through the glottis, force air through such a tube by blowing…

Hand seat
"Showing how the Improvised Three-Handed Seat may be used to carry an Injured Person. The picture also…
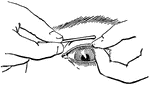
Everted eyelid
"Showing how the upper eyelid may be everted with a pencil or penholder." — Blaisedell, 1904
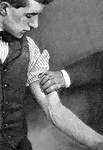
Branchial artery
"Showing how firm pressure may be made with the fingers to compress the branchial artery of the left…
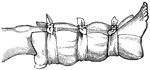
Temporary splint
"Showing how a pillow, an inside coat, a "sweater", or a blanket may be used as a temporary splint on…

Hair with ringworm
"A Piece of Hair from the Scalp infested with a Mold which produces Ringworm. Ringworm may occur anywhere…

Compound microscope
"A Compound Microscope. The appearance of the various structures and tissues of the human body as revealed…
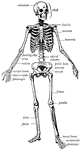
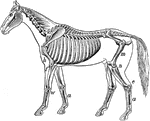
Human skeleton
"The human body, like a great building, has a framework which gives the body its shape and provides…
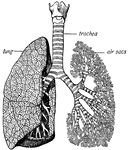
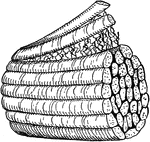
Trachea and lungs
"The trachea has in its walls stiff rings of cartilage that hold it open so that the air can…
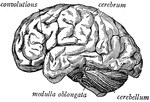
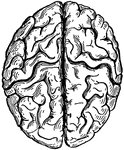
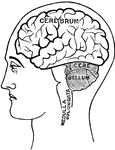
Side view of the brain
"The brain seen from the side, showing the three principal divisions." — Ritchie, 1918
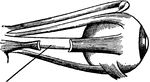
Muscles of the Eyes
"The eye is moved about by six muscles. The back ends of these muscles are attached to the eye sockets.…
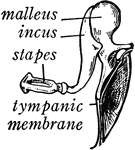
Bones of the Ear
"Across the middle ear a chain of three small bones stretches from the tympanic membrane to the inner…
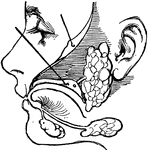
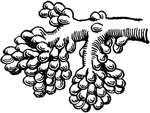
Salivary glands
"There are three pairs of salivary glands. One pair lies under the tongue; one pair is found under the…
Spine
"The spine, sawn in two lengthwise, showing the spinal canal and the holes between the vertebrae, where…
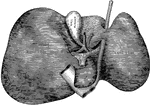
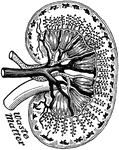
Pancreas
"The pancreas, partly cut away, so as to show the duct, which collects the pancreatic juice, and empties…
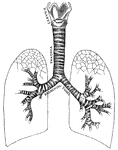
Respiratory system
"Larynx, trachea, and bronchi, showing the manner of division, and the rings of cartilage." —…
Pulmonary lobule
"Section of a pulmonary lobule, showing its division into pulmonary vesicles." — Tracy, 1888
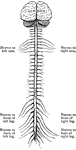
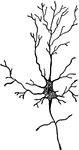
Central Nervous System
"Brain and spinal cord, with the thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves." — Tracy, 1888
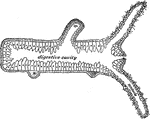
Section of a hydra
"Longitudinal section of a Hydra; b, bud which will form a young one; ba, base by…
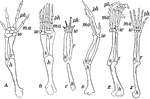
Forearms of vertebrates
"Fore limbs of vertebrates showing similarity of structure. A, salamander; B, turtle;…
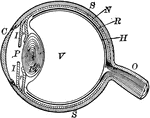
Eyeball
"The most essential parts of human vision are contained in the eyeball, a nearly spherical body, about…
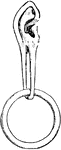
Dyak's ear
"Many of both sexes wear enormous ear plugs and earrings, some of which are as big around as a napkin.…
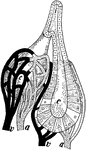
Gland
"Diagram to show the working parts of a gland. v and a are blood tubes with thin-walled branches around…
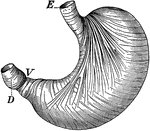
Stomach
"The stomach is a half-gallon sac, with an outer wall of muscle lined within by mucous membrane, made…
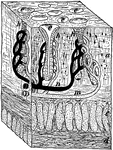
Cross-Section of Stomach Wall
"A tiny block out of the stomach wall. a, the mucous membrane; c and d, the muscles; h, gastric glands;…
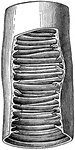
Piece of small intestine
"Piece of small intestine cut open to show wrinkling of inner coat bearing villi." —Davison, 1910
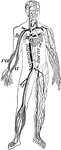
Veins and arteries
"Chief veins and arteries of the body. a, place of the heart; the veins are in black. On the right side…
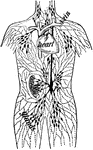
Lymph Vessels
"The lymph vessels of the body. rc, the thoracic duct; lac, the lacteals taking the lymph and fatty…
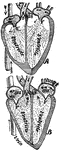
Beating heart
"Diagram of the rush of blood when the heart beats. The valves v open above are closed below while the…
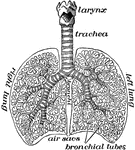
The lungs
"The lungs fill up most of the cavity of the chest. One lies on either side of the heart which is in…
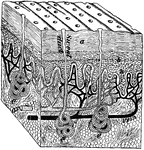
Section of skin
"A block out of the skin. a, dead part and d live part of the epidermis; e, sweat glands; n, nerve endings."…
Muscles of the forearm
"The extensor muscles on the back of the forearm. Note the tendons at the wrist." —Davison, 1910
Muscles of the Arm
"Muscles on the front of the arm. Note the while cords, the tendons at the wrist." —Davison, 1910