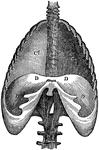
The Diaphragm
The diaphragm, which is the principal muscle that act sin breathing. Here you have the cavity of the…
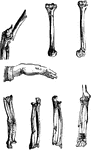
Thigh Bone and Arm Bone
Here you see the thigh bone on the left and the arm bone on the right. In both, the shaft is hollow,…
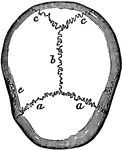
Cranial Sutures
The bones of the top of the head are fastened together by what are called sutures which are locked together…
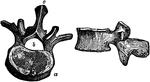
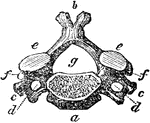
Two Views of a Vertebra
Two views of vertebra. 24 vertebrae make up the spinal column. On the left figure, a is the…
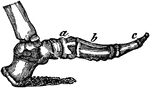
Side View of the Bone of the Foot
Bones of the foot, side view. In this figure the bones of the tarsus extend from the heel to a;…
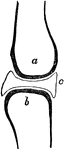
Joint
A joint between two bones (a and b). The ends of all bones are tipped with cartilage so that they may…

Heel Muscle
The lower part of the large muscle that raises the heel during walking. P, the muscle, makes up most…
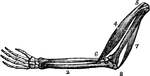
Arm Muscles
Two of the principal muscles f the arm (4 and 7). Between these is the bone of the arm (1) and the bones…
Tendons of a Finger
The arrangement of the tendons of a finger. At a b c are the 3 bones of the finger. At f…
Bisection of the Humerus
The humerus bisected lengthwise. Labels: a, marrow-cavity; b, hard bone; c, spongy bone; d, articular…
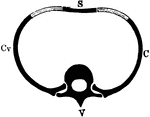
Segment of the Axial Skeleton
Diagrammatic representation of a segment of the axial skeleton V, a vertebra; C, Cv, ribs articulating…
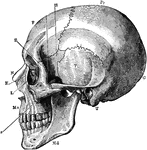
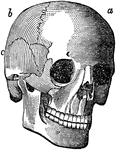
Side View of the Skull
A side view of the skull. Labels: O, occipital bone; T, temporal; Pr, parietal; F, frontal; S, sphenoid;…
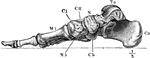
Bones of the Foot
The bones of the foot. Labels: Ca, calcaneum, or os calcis; Ta, articular surface for tibia on the astragalus;…
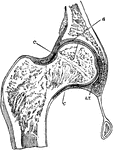
Hip Joint Section
Section through the hip-joint. Labels: a and b, articular cartilages; c, capsular ligament.
Thigh Bone
The thigh bone cut through the middle. Labels: b, hard bone; h, d, spongy bone; ma, marrow.
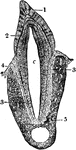
Premolar Tooth
Section through a premolar tooth of a cat still embedded in its socket. Labels: 1, enamel; 2, dentine;…
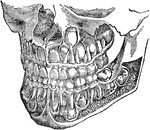
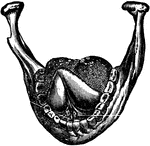
The Deciduous and Permanent Teeth
The deciduous and permanent teeth, shown as they are placed in the jaw with portions of bone removed…
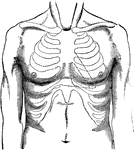
Breast Surface
Surface of the breast in a normal condition; contours or cardial torpor to the left of the breast bone.…
Upper Surface of the Tongue
Front view of the upper surface of the tongue; as also of the arch of the bone of the palate.
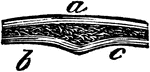
Bone Structure
If we divide any of the long bones longitudinally, we find two kinds of structure, the hard or compact,…
Thigh Bone Section
The above cut represents a section of the thigh bone. The extremities (a, w) having a shell or thin…

Membranous Portion of Bone
Membranous, or gelatinous portion of bone; the earthy portion being so completely removed (by immersion…

Earthy Portion of Bone
Earthy portion of bone, resulting from exposure to a strong heat. The resulting bone is very brittle,…
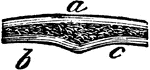
Bone Structure
Bone structure. Labels: a, the external, b,c, the internal table; the intermediate cellular texture,…
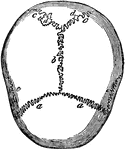
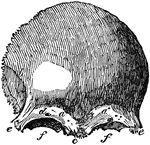
Skull Sutures
Sutures of the skull. Labels: a,a, the coronal suture, from the Latin corona, crown, so called from…
Frontal Bone
A front view of the frontal bone; a,a, frontal sinuses; b, the temporal arch, beneath which lies the…
Vertebra of the Neck
A vertebra of the neck. Labels: a, body of the bone; b, the spinal process; c, d, the transverse processes…

Fourth Rib
Fourth rib. Labels: a, vertebral extremity, called the head, which is connected with the bodies of the…
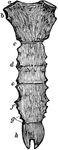
Sternum
The sternum in this cut consists of two bones. The first is broad and thick above, and contracts as…
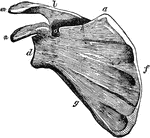
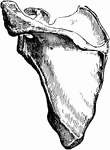
Scapula
Scapula. Labels: a, superior angle; d, the glenoid cavity, or socket for the round head of the arm bone;…
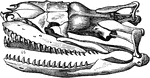
Boa Constrictor Skull
"Skull of Boa constrictor. a, quadrate bone; b, b, halves of lower jaw." -Cooper, 1887
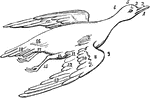
Bird Parts
"1. Lower mandible. 2. Upper mandible. 3. Forehead. 4. Loral space. 5. Crown of the head. 6. Hind part…
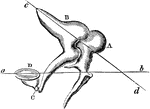
Bones of the Ear
A, the malleus, or mallet, with its long handle running down, to touch with its delicate extremity the…

Splints and Sling
"Fracture of the arm: Apply two splints, one in front, the other behind, if the lower part of the bone…
Splint
"Fracture of the thigh: Apply a long splint, reaching from the armpit to beyond the foot on the outside,…
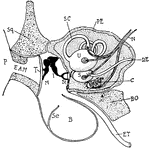
Cat Ear
"Diagram showing the ear and related parts in a young cat. P., Pinna; Sq., squamosal: E.A.M., external…
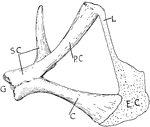
Turtle Pectoral Girdle
"Pectoral girdle of a Chelonian. G., Glenoid cavity; SC., scapula; P.C., procoracoid fused to the scapula;…
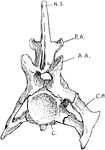
Crocodile Vertebra
"Cervical vertebra of crocodile. N.S., Neural spine; P.A., posterior articular process; A.A., anterior…
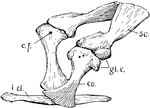
Crocodile Pectoral Girdle
"Pectoral girdle of crocodile. sc., Scapula; glc., glenoid cavity; co., coracoid; c.f., coracoid foramen;…
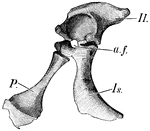
Crocodile Pelvic Girdle
"Half of the pelvic girdle of a young crocodile. Il., Ilium; a.f., acetabulum; Is., ischium; P., pubis…
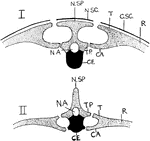
Mammal and Chelonian Backbones
"Vertical section through backbone and ribs of Chelonian (I.) and Mammal (II.). N.SP., neural spine;…
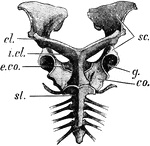
Echidna Pectoral Girdle
"Pectoral girdle of Echidna. sc., Scapula; cl., clavicle; i.cl., prosternum or "interclavicle"; co.,…
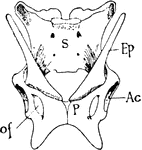
Echidna Pelvis
"Pelvis of Echidna. S., Sacrum; Ep., epipubic bones; Ac., acetabulum; o.f., obturator foramen between…
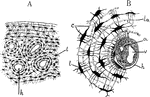
Bony Tissue
"Bony Tissue. A, portion of cross-section of a bone, the upper portion of the figure representing the…
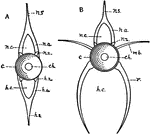
Fish Vertebrae
"Diagram of vertebrae of a bony fish. A, caudal; B, trunk. c, centrum or body of the vertebra; ch.,…
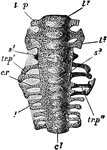
Rock Pigeon Sacrum
"Columba livia. Sacrum of a nestling (about fourteen days old), ventral aspect. c1, centrum of first…
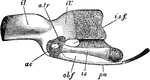
Rock Pigeon Innominate
"Columba livia. Left innominate of a nestling. The cartilage is dotted. ac, acetabulum; a. tr, anti-trochanter;…