Myxine
"The body is long and eel-like, and the skeleton is reduced to a mere cartilaginous tube. It ours out…
Cuttlefish
"It has no shell, and no skeleton, but has two conical pieces of horny substance imbedded in the back,…
!["The Pen-Fish or Common Calamary, <em>L. vulgaris</em>, is the best-known species of the genus; the body is somewhat pellucid, of a greenish hue, changeable to dirty brown; the eyes are large and lustrous, of an emerald green, phosphoric, and fiery in a high degree. It is common in the european seas, and was known to the ancient Greeks and Romans. [Shown with a quill pen]" — Goodrich, 1859](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/14000/14004/cmncalamari_14004_mth.gif)
Common calamari
"The Pen-Fish or Common Calamary, L. vulgaris, is the best-known species of the genus; the…
Loligo brevipinna
"A small species, the body three to four inches long, beak prominent and horny; the long arms slender,…

Bonelli's Cheiroteuthis
"Has the body eight inches long, and the longest tentacles nearly three feet." — Goodrich, 1859

Abdomen
"The belly; that part of the body of a mammal which lies between the thorax and the pelvis; In entomology,…
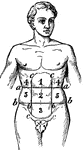
Abdominal
"In human anatomy, certain regions into which the abdomen is arbitrarily divided for the purpose of…
Eolis papillosa
"In these animals, which generally appear like small slugs, the branchiæ are arranged along on…
Leach's bursatella
"The descriptions of it are very obscure; it appears to be destitute of shell, the body globular, the…
Sagitta
"These are little fish-like animals furnished with one or two fin-like organs on the body and a broad…

Carinaria
"The Carinaria has an elongated transparent body, dotted with elevated points, and furnished toward…

Washington Medal Front
"Silver medal awarded to Washington. The following are the device and inscriptions on the front: An…

Woodhull's Grave
"Woodhull's Grave. Nathaniel Woodhull was born at Mastic, Long Island, December 30, 1722. Agriculture…

mummy
"Mummy. Another striking religious custom was the embalming of the dead. It was thought that the soul…

Martin Luther
"Martin Luther was born at Eisleben in 1483. He was the son of a poor miner, had entered the Augustinian…
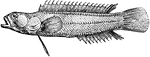
Acanthoclinus
"(A fish that) had a compressed claviform body, posterior dorsal fins nearly opposite to the anus, prolonged…

Napoleon
"France under Napoleon. The consulate was the form of government established after the overthrow of…

Agrilus
"Agrilus ruficollis. a, anal end of body of larva; b, larva; c, beetle. (The vertical lines show natural…

Ailette
"A plate of iron worn over the mail to protect the shoulders of a man-at-arms, before the introduction…

John Brown
In 1859, John Brown collected a small body of men, white and black, in the mountains of Maryland. He…

Tiger Beetle Larve
"The common European species, Cincindela campestris, may be found flying and running around…

Tiger Beetle and Larvae
"The common European species, Cincindela campestris, may be found flying and running around…
!["The Inquisitor Carabus, <em>C. inquisitor</em>, has the same form and manner as the [Sycophant Carabus]: the body is an inch long, and of a blackish-green color." — Goodrich, 1859](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/14600/14649/inquiscarabs_14649_mth.gif)
Inquisitor Carabus
"The Inquisitor Carabus, C. inquisitor, has the same form and manner as the [Sycophant Carabus]:…

Blue Carabus
"The Blue Carabus, C. cyaneus, is an inch and a quarter long, the body oval, flat, and above…

Bombadier Beetle
"The bombadier beetle has a large oval abdomen, which secretes a caustic fluid. They live in societies,…
Amphisile scutata
"The body is much compressed, and is armed with bony plates connate with the vertebrae and spinous processes.The…

Four-Spotted Beetle
"Smallish insects, generally of a black color, with the elytra rather shorter than the body, which is…

Giant Buprestis
"The Giant Buprestis, B. gigantea of guiana, is two inches long, and its body is of a green…

Capricorn Beetle
"The insects of this tribe, called Capricorn Beetles and distributed throughout most parts…

Drone Bee
"The working bee, for collecting wax, enters a flower, the stamens of which are loaded with pollen.…

Working Bees
""The working bee, for collecting wax, enters a flower, the stamens of which are loaded with pollen.…

Death's Head Moth
"The most remarkable species is the Death's Head Moth, Acherontia Atropos, a large kind,…

Walking Leaf
"The Phasmina includes some curious insects, one species of which is the Walking-leaf, Phyllium…
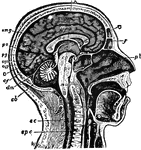
Human Brain
"The Brain is the encephalon, or center of the nervous system and the seat of consciousness and volition…
!["[The paguridae] includes the Hermit or Soldier Crab, <em>Pagurus Bernardus</em>, the abdominal portion of whose body is quite soft, forming a sort of cylindrical fleshy mass behind the shelly cephalothorax. As the comfort of the animal would be materially interfered with were this soft, worm-like appendage exposed to be grabbed at by every passing fish who might take a fancy to it, he usually seeks some shelter for its tail, and the habitation selected is generally the empty shell of some univalve mollusk." — Goodrich, 1859](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/14900/14983/hermit-crab_14983_mth.gif)
Hermit-crab
"[The paguridae] includes the Hermit or Soldier Crab, Pagurus Bernardus, the abdominal portion…

King crab
"It is among the largest of crustaceous animals, sometimes measuring as much as two feet in length.…

Calymene
"The trilobite's general form is shown in the annexed figure of the Calymene Blumenbachii;…

Lob-worm
"Errantia means wandering, and is applied to numerous species, of which the Lob-worm or Lug-worm,…

Earth-worms
"The bodies of these animals are of a cylindrical form, somewhat pointed at the anterior extremity,…
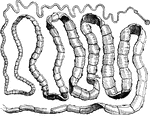
Tape-worm
"The body is composed of numerous joints or segments, each one resembling the others; these are often…
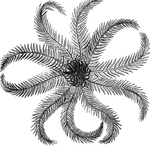
Rosy feather-star
"The body is flattened and covered with several cacareous plates; the lower, or entral surface, bears…

Cathedral of St. John the Divine
"A Cathedral is the principal church of a diocese, and the Cathedral city is the seat of the bishop…

Giant Centipede
"A Centipede is a worm having a long slender, depressed body, protected by coriaceous plates, 21 pairs…

Chinchilla
"Chinchilla is a genus of South American herbivorous rodents very closely allied to the rabbit, which…

Collie
"Collie is a breed of the dog of obscure origin, which is highly valued. Many anecdotes are told of…

Eclipse
"An Eclipse is an interception or obscuration of the light of the sun, moon, or other heavenly body…
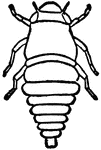
Larval Frog Hopper
"Frog Hoppers are ranked under the homopterous sub-order of insects. The name of frog hopper refers…
Frog Hopper on Leaf
"Frog Hoppers are ranked under the homopterous sub-order of insects. The name of frog hopper refers…
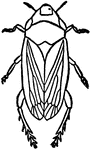
Adult Frog Hopper
"Frog Hoppers are ranked under the homopterous sub-order of insects. The name of frog hopper refers…

Wild Goose
"Goose is the name of a well-known family of natatorial birds. The domestic goose is believed to have…

Female Gorilla
"The Gorilla is a celebrated anthropoid ape, generally belived to come nearer than any known one to…
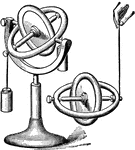
Gyroscope
"The Gyroscope is an instrument constructed by M. Foucault to make the rotation of the earth visible.…

Hedgehog
"Hedgehog is a quadruped distinguished by having the body covered with spines instead of hair. The skin…

Heron
"Heron is the common name of birds of the genus Ardea. The herons are distinguished by having a long…

Tomato Plant
"Tomato, or Love Apple, is a plant of the natural order Solanaceæ. It is one of a genus of several…

Tomato
"Tomato, or Love Apple, is a plant of the natural order Solanaceæ. It is one of a genus of several…

Tomato
"Tomato, or Love Apple, is a plant of the natural order Solanaceæ. It is one of a genus of several…
!["A Tooth is one of the hard bodies of the mouth, attached to the skeleton, but not forming part of it and developed from the dermis or true skin. True teeth consist of one, two, or more tissues differing in their chemical composition and in their microscopical appearances. Dentine, which forms the body of the tooth, and 'cement,' which forms its outer crust, are always present, the third tissue, the 'enamel,' when present, being situated between the dentine and cement. The incisors, or cutting teeth, are situated in front. In men there are two of these incisors in each side of each jaw. The permanent incisors, molars, and premolars are preceded by a set of deciduous or milk teeth, which are lost before maturity, and replaced by the permanent ones. The canines come next to the incisors. In man there is one canine tooth in each half-jaw. The premolars (known also as bicuspids and false molars) come next in order to the canines. In man there are two premolars in each half-jaw. The true molars (or multicuspids) are placed most posteriorly. In man there are three molars in each half-jaw, the posterior one being termed the wisdom tooth. The figures [in the illustration] refer to months after birth."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15200/15256/teeth1_15256_mth.gif)
First Teeth
"A Tooth is one of the hard bodies of the mouth, attached to the skeleton, but not forming part of it…