Hollow Square
Military formation of the Romans, also agmen quadratum. Square formation with no troops in the middle.
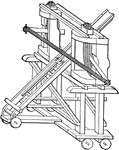
Ballista
The Ballista is a device for throwing large darts very accurately. The Roman Ballistas threw stones…

Parma
"A round shield, three feet in diameter, carried by the celites in the Roman army. Though small, compared…
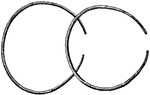
Gallic Torques
Gallic Torques were heavy necklaces of braided metal. Gauls carried their wealth in the form of Gold…

Periscelis
"An anklet or bangle, worn by the Orientals, the Greeks, and the Roman ladies also. It decorated the…

Persona
"A mask. Masks were worn by Greek and Roman actors in nearly all dramatic representations. This custom…

Persona
"A mask. Masks were worn by Greek and Roman actors in nearly all dramatic representations. This custom…
Pons Cestius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
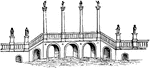
Pons Aelius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Ariminum
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Trajan
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
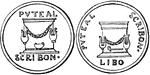
Puteal
"Puteal, properly means the enclosure surrounding the opening of a well, to protect persons from falling…
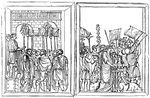
Signa Militaria
"Signa Militaria, military ensigns or standards. The most ancient standard employed by the Romans is…
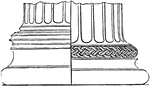
Spira
"Spira, the base of a column. in the Tuscan and the Roman Doric the base consisted of a single torus,…

Stadium
"A Greek measure of length, and the chief one used for itinerary distances. It was equal to 600 Greek…

Chrismatory
A receptacle for the chrism, or holy oil, used in the services or the Roman Catholic and Eastern Churches.

Roman augur
"Represents a Roman augur, with his litmus or divining staff, observing the signs in the heavens." —…
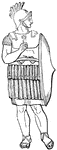
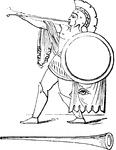
Roman Clypeus
"The following cut represents a Roman clypeus, from the column of Trajan. The projection in the centre…
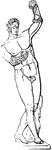
Boxer with cestus
"The cestus was used by boxers from the earliest times. It consisted of thongs of raw ox-hide, or of…

Syrinx
"Syrinx, the Pan's pipe, or Pandean pipe, was the appropriate musical instrument of the Arcadian and…
Roman trumpet
"There appears to have been no essential difference in form between Greek and Roman or Tyrrhenian trumpets.…

Ancilia
"According to the ancient authorities, it was made of bronze, and its form was oval, but with the two…

Tunica
"Tunica, an under-garment. Roman. The Tunica of the Romans, like the Greek chiton, was a woollen under…

Vestales
"Vestaes, the virgin priestesses of Vesta, who ministered in her temple and watched the eternal fire.…

Umbraculum
"Umbraculum, Umbella, a parasol, was used by Greek and Roman ladies as a protection against the sun.…
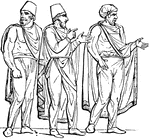
Sagum
"The sagum was open in the front, and usually fastened across the shoulders by a clasp. The form of…

Caesar in England
"All histories of England commence with the invasion of Julius Caesar, the earliest event in that quarter…

Guy Fawkes and his associates
"One of the most extraordinary events in the history of England is that commonly known by the name of…