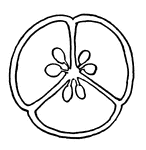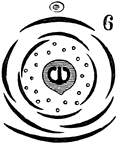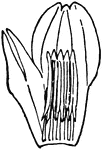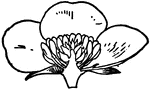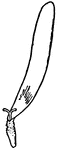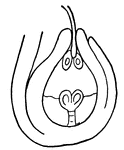
Fertilization (Flower)
This illustration shows the fertilization of a flower, by means of a pollen tube entering a micropyle,…
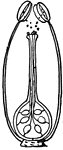
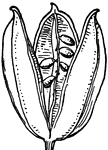
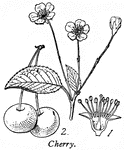
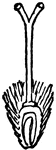
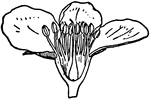
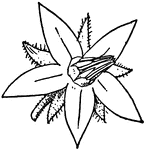
Fertilization (Flower)
This illustration shows fertilization of a flower, by means of pollen falling from stamens (male organ)…
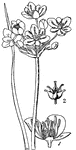
Flowering Rush
A European plant which grows in stagnant or nearly stagnant water. It has long, sword-shaped leaves,…

Frankincense
Frankincense (Olibanum) is a gum resin obtained from Boswellia Carterii, of the order Burseraceae, and…
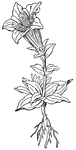
Gentian
A genus of hardy plants, Gentians belong to the order Gentianaceae. They have a bitter taste, and one…

Geum Urbanum
Geum urbanum is a member of the genus Geum, a genus of hardy plants (Rosaceae). Not usually used decoratively,…

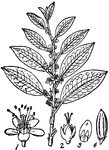
Glaux Maritima
Also known as Sea Milkwort, Glaux Maritima is a hardy perennial seashore plant belonging to the order…
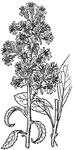
British Golden-rod
British Golden-rod is a member of the large composite genus Solidago, which is chiefly North American.…
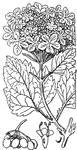
Guelder Rose
Also known as the Snowball Tree, the Guelder Rose is a cultivated form of the genus Viburnum, especially…

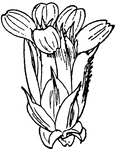
Juncus Effusus
Known as the soft rush, Juncus effusus is nearly as common as the most common species, J. conglomeratus.…
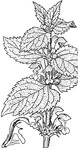
Lamium Album
Lamium album (also known as the white dead-nettle, or archangel) is a member of the Lamium, a genus…
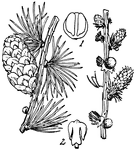
Larch, Cone and Flowers (male and female)
Larch, or Larix, is a genus of hardy, deciduous, coniferous trees of very graceful habit. They bear…
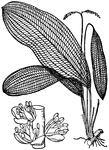
Lattice Leaf
Lattice Leaf is the popular name of a water plant, 'Aponogeton jenestralis', belonging to the order…

Colored Leaves of 'Cornus florida'
This illustration shows the colored leaves of 'Cornus florida', surrounding the small flowers and rendering…

Coconut Tree
Coconut palm. A, section of fruit; a, husk; b, shell; c, albumin; d, cavity; e, embryo; f, aperture…
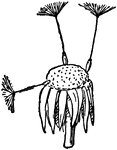
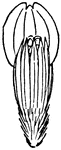
Fruit Receptacle
Composite, or compound flowers, form the largest of all botanical orders. 3, receptacle with fruit adhering.
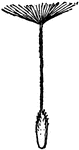
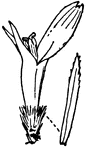
Single Fruit
Composite, or compound flower, from one of the largest botanical orders. 4, single fruit.