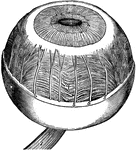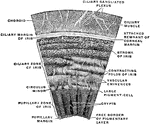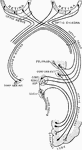
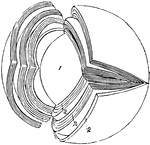
Vascular Coat of the Eye
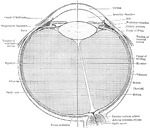
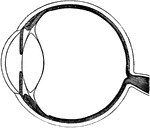
The middle or vascular coat of the eyeball exposed from without. Left eye, seen obliquely from above…

Eye-splice
"For making an eye splice, the end of the rope is unlaid and the strands are bent upon the body of the…
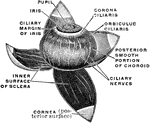
Eyeball
"The Relative Position of the Lachrymal Apparatus, the Eyeball, and the Eyelids. A, lachrymal canals,…
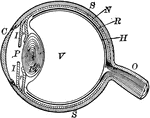
Eyeball
"The most essential parts of human vision are contained in the eyeball, a nearly spherical body, about…
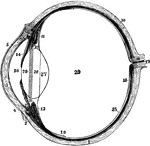
Left Eyeball in Horizontal Section
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
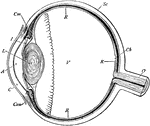
Section of the Eyeball
Section of the eyeball. Labels: Con, conjunctiva; C, cornea; A, aqueous humor; I, iris; L, crystalline…
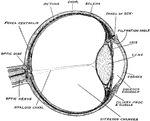
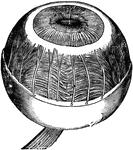
Eyeball
Horizontal section of the eyeball, showing the suspensory ligament of the lens, the aqueous and vitreous…
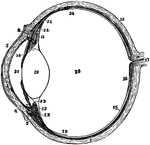
The Eyeball in Horizontal Section
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
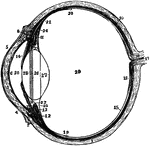
Section of Left Eyeball
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
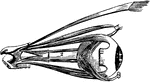
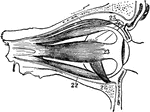
The Eyeball with its Muscle
The eyeball with its muscles attached. The upper muscle not attached to the ball belongs to the upper…
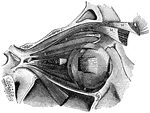
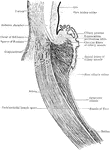
Muscles of the eyeball
"A, attachment of tendon connected with the four recti muscles; B, external rectus,…
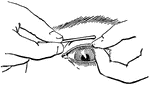
Everted eyelid
"Showing how the upper eyelid may be everted with a pencil or penholder." — Blaisedell, 1904
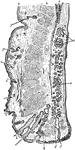
Vertical Section Through Eyelid
Vertical section through the upper eyelid. Labels: a, Skin; b, Orbicularis palpebrarum; b', Marginal…
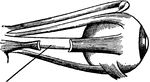
Muscles of the Eyes
"The eye is moved about by six muscles. The back ends of these muscles are attached to the eye sockets.…
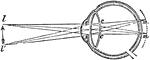
Flattened Eye
"A representation of the manner in which the image is formed in the eye, when the cornea or crystalline…
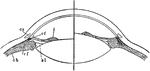
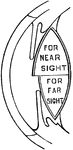
Focusing of the Eye
Diagram to illustrate the mechanism of accommodation (focusing); on the right half of the figure for…

Formation of an Image on the Eyeball
Suppose a person was looking at a church with a tree standing at its side, he would have in each eye…
Galeodes
"Galeodes sp., one of the solifugae. Dorsal view. I to VI, Bases of the prosomatic appendages. o, Eyes.…
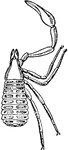
Garypus Litoralis
"Garypus litoralis, one of the Pseudoscorpiones. Dorsal view. I to VI, The prosomatic appendages. o,…
Garypus Litoralis
"Garypus litoralis, one of the Pseudoscopions. Lateral view. I to VI, Basal segments of the six prosomatic…
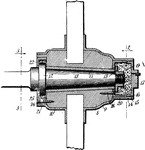
Wheel Hub
The central part of a car wheel (or fan or propeller etc) through which the shaft or axle passes
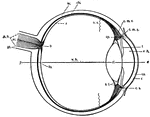
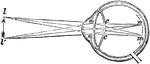
Human Eye
This diagram shows a side view of the right eye of man. a.c., central artery; a.h., aqueous humor; b.,…
Indistinct Vision
"...where we suppose that the object a, is brought within an inch or two of the eye, and that the rays…
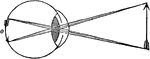
Inversion of Objects by the Eye
"The actual position of the vertical object a, as painted on the retina, is therefore such as is represented…
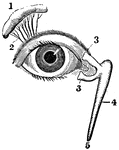
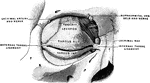
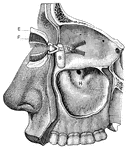
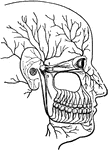
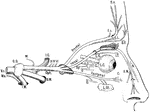
View of the Lachrymal Gland and Nasal Duct
View of the lachrymal gland and nasal duct. Labels: 1, The lachrymal gland. 2, Ducts leading from the…
Lens of a Rabbit
Meridional section through the lens of a rabbit. Labels: 1, Lens capsule; 2, epithelium of lens; 3,…
Crystalline Lens
Laminated structure of the crystalline lens. The laminae are split up after hardening in alcohol. Labels:…
Section Through Lens
Section through the equator of the lens. Showing gradual transition of the epithelium into lens fibers.
The Use of the Crystalline Lens
A convex lens, bends the ray of light which pass through it, so that they meet at a point called a focus.…
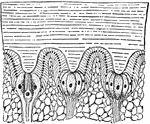
Limulus
"Section through a portion of the lateral eye of Limulus, showing three ommatidia—A, B and C.…

Manatee Face
"Front view of head of American Manatee, showing the eyes, nostrils, and mouth with the lobes of the…

Manatee Face
"Front view of head of American Manatee, showing the eyes, nostrils, and mouth with the lip contracted."…
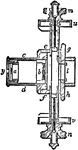
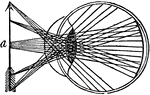
Micrometer
"The horizontal section in the direction of the axis of the telescope. The eye-piece ab consists of…
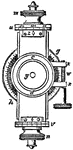
Micrometer
"The vertical section in the direction of the axis of the telescope. The eye-piece ab consists of two…

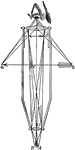
Micrometer
"The original Merz micrometer of the Cape Observatory, made on Fraunhofer's model. S is the head of…
Microscope
"A microscope consists of a lens or a combination of lenses used to observe small objects, often so…
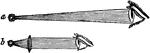
Single Microscope
"Let a be the distance at which an object can be see distinctly, and b, the distance at which the same…
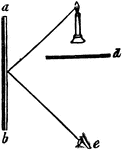
Plane Mirror
"Suppose the mirror, a b, to be placed on the side of a room, and a lamp to be set in antoher room,…
Near-sighted
"A representation of the manner in which the image is formed in the eye of a near-sighted person. The…
Ophthalmic Nerve
Scheme of the distribution of the ophthalmic nerve. Labels: Vs, trigeminal nerve, afferent root; Mo,…

Optic Nerve
The terminal portion of the optic nerve and its entrance into the eyeball, in horizontal section.
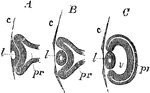
Development of the Primary Optic Vesicle in a Chick
Longitudinal section of the primary optic vesicle in the chick. Labels: A, from an embryo of 65 hours;…
Position and Size of Image for Eye Optics
An illustration of the position and the size of the image viewed by the eye. The eye approximates the…
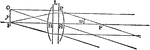
Optical Position and Size of Image Through Magnifying Glasses
"If y be the object the image appears to a normal eye situated behind the system L with passive accommodation…
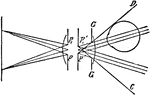
Optical Position of Diaphragms using Lens
"The intersection of the principal rays in this case lies in the middle of the entrance pupil or of…
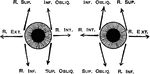
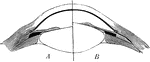
Diagram to Show the Action of the Orbital Muscle
Diagram to show the action of the orbital muscle. The arrows show the direction of the action of each…