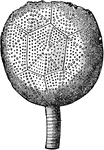
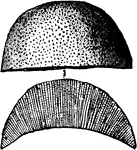
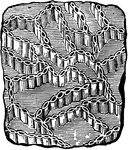
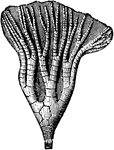
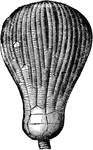
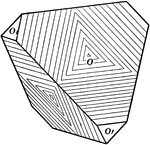
Actinocrinus Radiate
An ancient radiate from the Carboniferous Age, the Actinocrinus proboscidialis.

Rain Prints
"The impressions of the large rain-drops of a short shower made on a half-dry mud, have often been preserved…
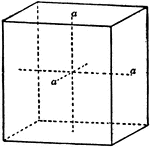
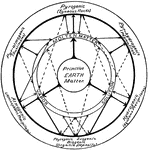
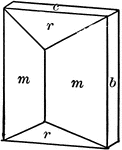
Symmetry of Rhombohedral Class
"The vertical crystallographic axis is one of trigonal symmetry, and the three horizontal crystallographic…
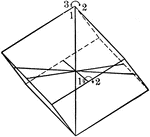
Negative rhombohedron
"The rhombohedron is a form consists of six rhombic-shaped faces, which correspond in their position…
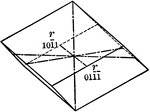
Positive rhombohedron
"The rhombohedron is a form consists of six rhombic-shaped faces, which correspond in their position…

Rhynchotreta Mollusk
A mollusk radiate from the Paleozoic time, Rhynchotreta cuneata from the United States and Great Britain.

Rill Marks
Marks made by water spreading over shells of stones that are lodged in the sand, in this image in Silurian…
Rock Layers Showing Geological Periods
"Diagrammatic structure section of the Wasatch Range in Ogden Canyon." -Lee, 1915

Rock Layers Showing Types of Rock
"Cross section of Marsh Creek valley at McCammon, Idaho." -Lee, 1915

Basaltic Rock
Basaltic rock is a common extrusive volcanic rock. Fingal's Cave is a sea cave composed of basaltic…
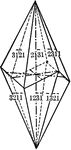
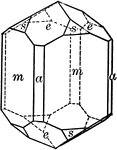
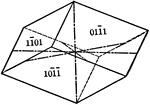
Scalenohedron
"This form consists of twelve scalene triangular faces. These faces correspond in their position to…
Scapolite
"A crystal of scapolite, upon which the faces of the third-order pyramid are shown." — Ford, 1912
Scheelite
"Tetragonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually simple pyramids of first order. Closely resemble isometric…
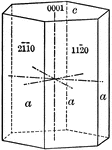
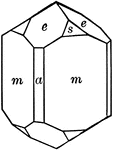
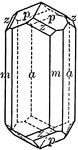
Prism of the second order
"This is a form consisting of six rectangular vertical faces, each of which intersects two of the horizontal…
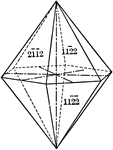
Pyramid of the second order
"This is a form composed of twelve isoceles triangular faces, each of which intersects two of the horizontal…

Shore Erosion and Distribution of Sediments
The floor of the sea was first formed or rocks that had cooled from a state of fusion. The few islands…
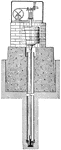
Pendulum Seismograph
"inverted Vertical Pendulum Seismograph. Marvin System. A stiff vertical tube, pivoted at its bottom…
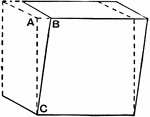
Shear
"Shear is a particular form of strain produced by causing plane layers of a material to slide parallel…
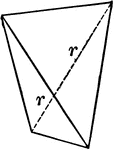
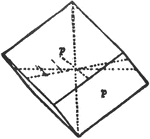
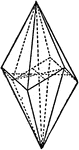
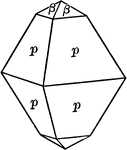
Sphenoid
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…
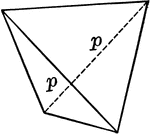
Sphenoid
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…
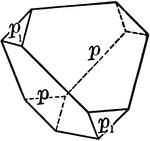
Sphenoid, positive and negative
"It consists of four isoceles triangular faces which intersect all three of the crystallographic axes,…
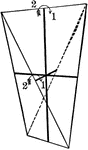
Symmetry of Sphenoidal class
"The Sphenoidal Class corresponds in the Tetragonal system to the Tetrahedral class in the Isometric…
Springs
Two cases of springs: "In one, the water descends through the porous bed e to the layer d, which is…
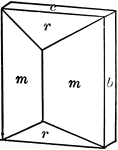
Staurolite
"Orthohombic. Habit prismatic, showing usually a combination of prism with large angle, brachypinacoid,…
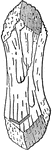
Stilbite
"Monoclinic. Uniform in cruciform twins. Commonly tabular parallel to clinopinacoid. Crystals usually…
Uncomformable strata
"In some places a series of strata A, having a certain dip, rest directly upon the eroded surface of…
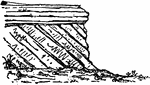
Unconformable Strata
"Unconformability between horizontal and inclined strata. Inferior Oolite (a b) resting on Carboniferous…