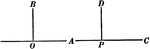This mathematics ClipArt gallery offers 127 images that can be used to demonstrate various geometric theorems and proofs.
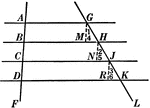
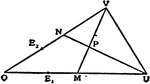
4 Parallel Lines Cut By 2 Transversals
Illustration used to prove the theorem "If three or more parallel lines intercept equal segments on…
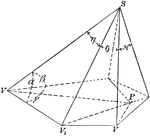
Face Angles of Convex Polyhedral Angle
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "The sum of the face angles of any convex polyhedral angle is less…
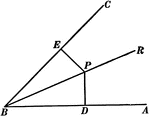
Perpendiculars To The Sides Of An Angle
Illustration used to show "The two perpendiculars to the sides of an angle from any point in its bisector…
Perpendiculars To The Sides Of An Angle
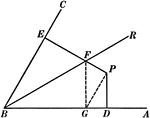
Illustration used to show "The two perpendiculars to the sides of an angle from any point not in its…
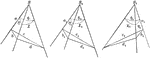
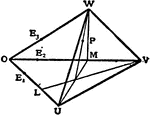
Symmetrical or Equal Trihedral Angles
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "Two trihedral angles, which have three face angles of the one equal…
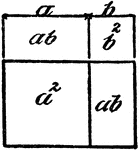
Squaring Binomial (a + b)
An illustration showing how to square binomial (a + b). (a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b².
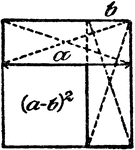
Squaring Binomial (a - b)
An illustration showing how to square binomial (a - b). (a - b)² = a² - 2ab + b².
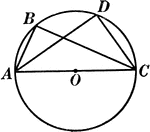
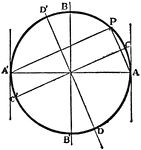
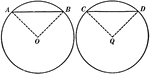
Angles Inscribed in the Same Segment Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle used to prove "All angles inscribed in the same segment are equal."
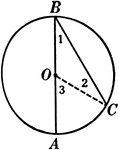
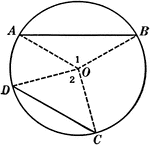
Inscribed Angle in a Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle with an inscribed angle that can be used to prove that "An inscribed angle…
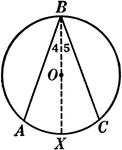
Inscribed Angle in a Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle with an inscribed angle that can be used to prove that "An inscribed angle…
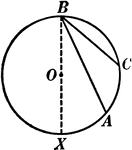
Inscribed Angle in a Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle with an inscribed angle that can be used to prove that "An inscribed angle…
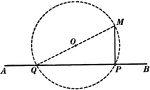
Obtuse Angles Inscribed in Circle Proof
Illustration of a circle used to prove "Any angle inscribed in a segment less than a semicircle is an…
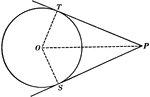
Equal Tangents to Circle Theorem
Illustration used to show that "If two tangents are drawn from any given point to a circle, those tangents…
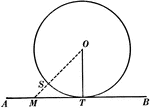
Tangent to Perpendicular Radius Circle Theorem
Illustration used to show that "A tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point…
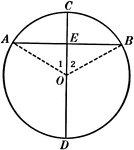
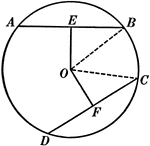
Diameter Perpendicular to a Chord in a Circle
Illustration used to show that "The diameter perpendicular to a chord bisects the chord and also its…
Equal Chords in Equal Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are equal, they…
Equal Chords in Equal Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are equal, they…
Unequal Chords in Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are unequal,…
Unequal Chords in Equal Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are unequal,…
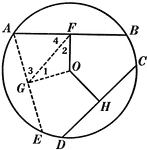
Unequal Chords in Equal Circles Theorem
Illustration used to show that "In equal circles, or in the same circle, if two chords are unequal,…
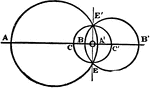
Circumferences of 2 Circles
Illustration used to prove "If two circumferences meet at a point which is not on their line of centers,…
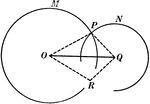
Circular Involution
Every elliptical involution has the property that there are two definite points in the plane from which…
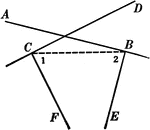
Intersecting Lines Corollary
Illustration used to prove the corollary that "Two lines perpendicular respectively to two intersecting…
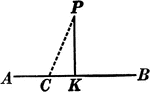
Perpendicular to Line Corollary
Illustration used to prove the corollary that "From a point outside a line there exists only one perpendicular…
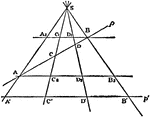
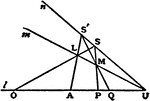
Cross-Ratio Four Points
The cross-ratio of four points in a line is equal to the cross-ratio of their projections on any other…
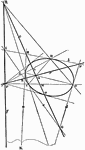
Second Order Curve Tangents
Any four-point on a curve of the second order and the four-side formed by the tangents at these points…
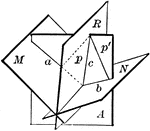
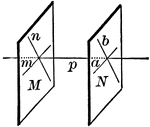
Plane Bisecting Dihedral Angle
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "Every point in a plane which bisects a dihedral angle is equidistant…
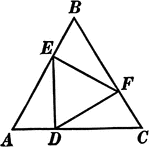
Equilateral Triangle Inscribed In An Equilateral Triangle
Illustration used to prove that triangle EFD is equilateral given that triangle ABC is equilateral and…
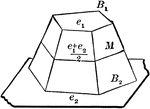
Volume of Frustum of a Pyramid
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "The volume of the frustum of a pyramid (cone) is equal to the sum…
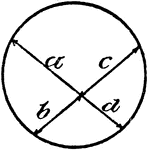
Model Of Geometric Proportions In A Circle
An illustration showing a model of a circle with intersecting chords that illustrates the following…
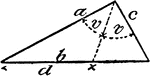
Model Of Geometric Proportions In A Triangle
An illustration showing a model of a triangle that illustrates the following relationship: a:c = d:(b…
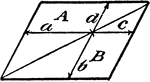
Model Of Geometric Proportions
An illustration showing a quadrilateral model that illustrates the following relationships: a:b = c:d,…
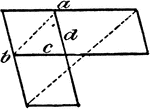
Model Of Geometric Proportions
An illustration showing a model that illustrates the following relationships: a:b = c:d, ad = bc. Product…
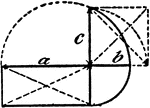
Model Of Geometric Proportions
An illustration showing a model that illustrates the following relationships: a:b = c:b, ab = c²,…
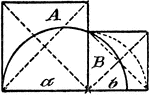
Model Of Geometric Proportions
An illustration showing a model that illustrates the following relationship: A:B = a:b.
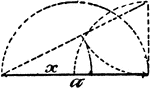
Model Of Geometric Proportions
An illustration showing a model that illustrates the following relationships: a:x = x:a - x, x = √(a²…
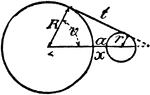
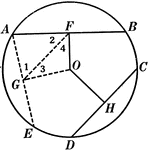
Model Of Geometric Relationships In 2 Circles
An illustration showing a model of 2 circles with tangent lines, diameters, and radii that illustrates…
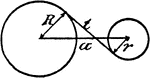
Model Of Geometric Relationships In 2 Circles
An illustration showing a model of 2 circles with tangent lines, diameters, and radii that illustrates…
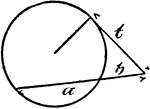
Model Of Geometric Relationships In A Circle
An illustration showing a model of a circle with an exterior angle formed between a tangent and a secant…
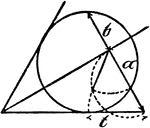
Model Of Geometric Relationships In A Circle
An illustration showing a model of a circle with angles formed between tangents and secants that illustrates…
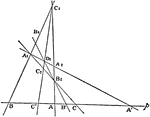
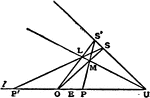
Involution
The three points in which any line cuts the sides of a triangle and the projections, from any point…
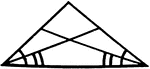
Angle Bisectors In An Isosceles Triangle
Illustration showing that if two angles of a triangle are equal, the bisectors of these angles are equal.
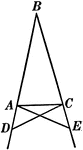
Base Angles In An Isosceles Triangle
Illustration showing that can be used to prove that the base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal.
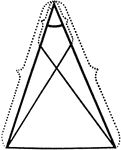
Equal Segments In An Isosceles Triangle
Illustration showing that if equal segments measured from the vertex are laid off on the arms of an…
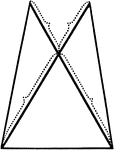
Equal Segments In An Isosceles Triangle
Illustration showing that if equal segments prolonged through the vertex are laid off on the arms of…
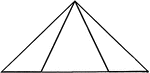
Equal Segments In An Isosceles Triangle
Illustration showing that if equal segments measured from the end of the base are laid off on the base…
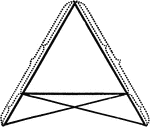
Equal Segments In An Isosceles Triangle
Illustration showing that if equal segments measured from the end of the base prolonged are laid off…
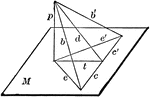
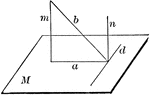
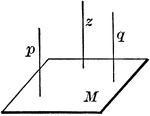
Perpendicular To Line In Plane
"If from the foot of a perpendicular to a plane a straight line is drawn at right angles to any line…
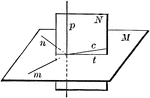
Plane Perpendicular To Line
"All the perpendiculars to a straight line at the same point lie in a plane perpendicular to the line."
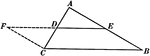
Line Joining Midpoints on a Triangle
Illustration used to prove "The line joining the mid-points of two sides of a triangle is parallel to…
2 Equal Parallelograms
Illustration used to prove the theorem "Two parallelograms are equal if two sides and the included angle…