Clipart tagged: ‘hearing’
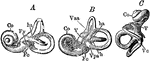
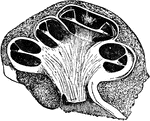
The Bony Labyrinth of the Ear
Casts of the bony labyrinth of the ear. Labels: A, left labyrinth see from the outer side; B, right…
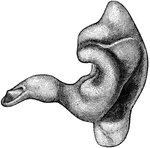
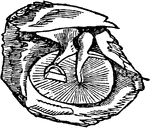
External auditory canal
"A Cast of the External Auditory Canal. The auditory canal is a passage in the solid potion of the temporal…
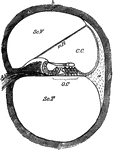
Cochlea
Diagram of a section of a coil of the cochlea of the ear. Labels: C.C, canal of the cochlea; mR, its…
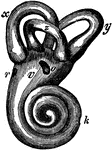
The Cochlea and Passages of the Ear
In this figure are shown the winding passages of the ear (the labyrinth of the ear). The middle part…
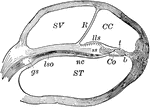
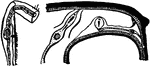
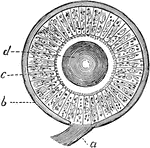
Cochlea, Section of
Section of one coil of the cochlea, magnified. Labels: SV, scala vestibuli; R, membrane of Reissner;…

Ear Trumpet
"The Ear Trumpet is an instrument designed for the collection and conduction of sounds. By increasing…
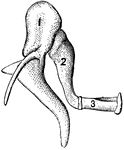
Bones of the Ear
"1, malleus, or hammer; 2, incus, or anvil; 3, stapes, or stirrup." — Blaisedell, 1904
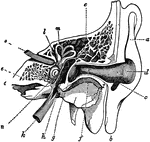
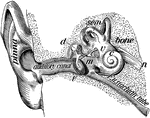
A Cross-Section of the Ear
Cross-section of the external and internal ear. a, b, and c: External ear. d: Entrance…
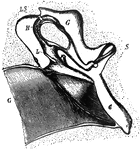
Middle Ear
The middle ear and its bones, considerably magnified. Labels: G, the inner end of the external auditory…
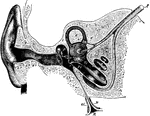
Section of the Ear
Semidiagrammatic section through the right ear. Labels: M, concha; G, external auditory meatus; T, tympanic…
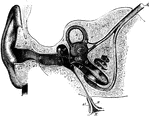
Section Through the Right Ear
Semi-diagrammatic section through the right ear. Labels: M, concha; G, external auditory meatus; T,…
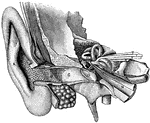
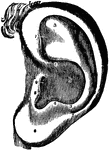
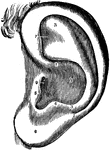
General view of organ of hearing
"A, pinna; B, cavity of the concha, showing the openings of a great number of sebaceous…
Sense of Hearing
Hearing is the perception of certain vibrations of bodies. These vibrations give rise to sound waves.…
Sense of Hearing
Hearing is the perception of certain vibrations of bodies. These vibrations give rise to sound waves.…

Sense of Hearing
Hearing is the perception of certain vibrations of bodies. These vibrations give rise to sound waves.…

Sense of Hearing
Hearing is the perception of certain vibrations of bodies. These vibrations give rise to sound waves.…

None so Deaf as Those That Won't Hear
"A poor man here is asking for relief, / The full-fed, portly man appears quite deaf; / He's humbly…
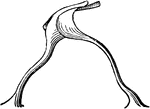
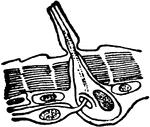
The Rods of Corti
The rods of Corti of the ear showing a pair of rods separated from the rest. Labels: i, inner, and e,…
The Rods of Corti
The rods of Corti of the ear. Shown hear is a bit of the basilar membrane with several rods on it, showing…

Sonometer
A sonometer is an apparatus by which the transverse vibrations of strings can be studied. It is also…

Tone
An example of how to produce a tone. This illustration shows one end of a string fixed to a hook and…

Tone
"A glass bell is fixed to stand, and beside it is a stand carrying a small ivory ball. This is so arranged…

Tone
"If a light strip of steel is firmly gripped at one end in a vice and the other end plucked aside, it…