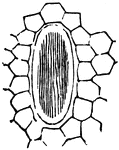
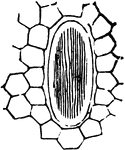
The Cellular Botany ClipArt gallery offers 293 illustrations of plant tissue at the cellular level, illustrations of cell division, and examples of individual pollen grains.
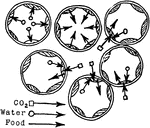
Palisade Cell Intake
"Diagram to show the intake of carbon dioxide by the palisade cells from the intercellular spaces, the…

Euphorbia Palisade Cells
"Starch grains from the palisade cells of a Euphorbia leaf." -Stevens, 1916
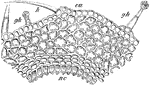
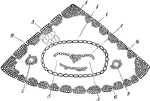
Cross Section Through Pelargonium Blossom Ovary
Pictured is the cross section of the pelargonium blossom ovary. (gh) represents the glandular hairs,…
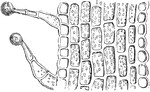
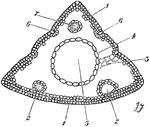
Vertical Section of Pelargonium Blossom Ovary
Pictured is the vertical section of the pelargonium blossom ovary. (gh) shows the glandular hairs.
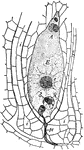
Cellular structure of peridia
"Under the power of about 90 diameters the general character of the peridia is seen. They are densely…
Lilium Philadelphicum
North American lily plant bearing orange, purple, and red flowers, and can grow up to 90 centimeters.

Photosynthesis
"Diagram to show the effect of different portions of the spectrum on photosynthesis. a to F, different…
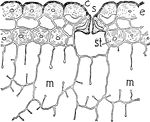
Pine Leaf
This image shows the cross-section of the outer cells of a leaf of pine. S, stoma; E, epidermis; C,…

Magnified Pine
"Diagrammatic representation of a block of pine wood highly magnified. a, Early growth; b, late growth;…
Transverse Section of Pinus Coulteri Leaf
Pictured are (1) strengthening cells, (2), internal ducts, (3) chlorophyll bearing cells, (4) bundle…
Transverse Section of Pinus Excelsa Leaf
Pinus is a genus of hardy, evergreen trees. Pictured are the strengthening cells (1), ducts surronded…

Pinus Sylvestris
"Radial longitudinal section of wood of Pinus Sylvestris. a, cambium; b, c, d, e, f, wood cells; f,…
Transverse Section of Pinus Sylvestris Leaf
Shown are the strengthening cells (1), ducts (2), wavy, chlorophyll bearing cells (3), bundle sheath…
Pit Development
"Different stages in the development of a bordered pit. b, The original, thin, primary wall; a, the…
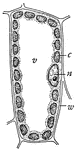
Plant Cell
Diagram of a mesophyll cell of a leaf: c, chloroplast; n, nucleus; v, vacuole; w, cell wall.
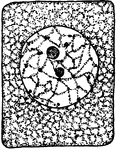
Plant Cell Division 1
First stage in plant cell division: Protophase 1; "Resting cell ready to begin division." -Stevens,…
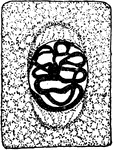
Plant Cell Division 2
Second stage in plant cell division: Protophase 2; "the nuclear reticulum is assuming the form of a…
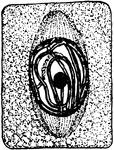
Plant Cell Division 3
Third stage in plant cell division: Protophase 3; "The nuclear thread has divided longitudinally throughout…

Plant Cell Division 4
Fourth stage in plant cell division: Protophase 4; "The nuclear membrane and the nucleolus have disappeared,…
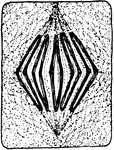
Plant Cell Division 5
Fifth stage in plant cell division: Metaphase; "The metaphase, where the longitudinal halves of the…

Plant Cell Division 6
Sixth stage in plant cell division: Anaphase; "The anaphase, or movement of the chromosomes toward the…
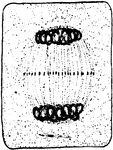
Plant Cell Division 7
Seventh stage in plant cell division: Telophase; "Telophase where the chromosomes have begun to spin…

Plant Cell Division 8
Eighth stage in plant cell division: "The connecting fibers have spread out and come into contact with…
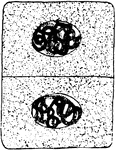
Plant Cell Division 9
Ninth and final stage in plant cell division: "A nuclear membrane has been formed about each daughter…
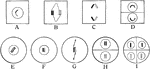
Plant Reproduction
"Showing method of association of paternal and maternal chromosomes, at A in all vegetative nuclei,…
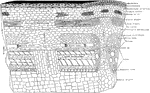
Plant Tissues
"Diagram to show the topography and character of the tissues that evolved from the primary meristems.…
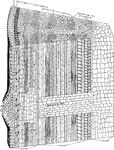
Plant Tissues
"Diagram showing additions to the primary tissues through the activity of the cambium and phellogen…
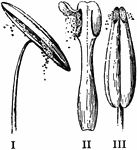
Pollen Discharge
"Modes of discharging pollen. I, by longitudinal slits in the anther-cells (amaryllis); II, by uplifted…
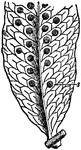
Common Polypody Leaf with Sori
"Polypodium widely distributed throughout the world, but specially developed in the tropics. The species…

Cross Section from Ovary of Primrose Flower
In the cross section from the ovary of the primrose flower the carpels are completely united. The carpels…

Raphides
This is an illustration of raphides, or acicular crystals, from the stalk of the Rhubarb: three of the…
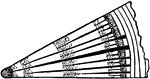
Medullary Rays
A characteristic found in woods. They are the radial ribbons extending vertically through the tree across…

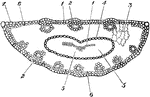
Cross Sections of Ovary or Red Campion
A shows five carpels joined in a central mass. B shows a half grown ovary with a central mass bearing…
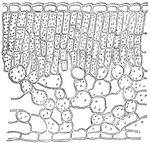
Rhododendron
This illustration shows a section of a leaf of Rhododendron. Note the compact palisade tissue which…
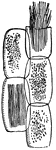
Rhubarb-plant
Some cells from stalk of Rhubarb-plant, three containing chlorophyll; two (one torn across) with rhaphides.
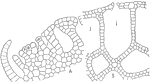
Ricciocarpus
This illustration shows the structure of the thallus of Ricciocarpus: A, section of the thallus, showing…
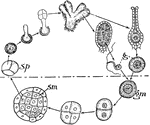
Ricciocarpus
This illustration shows a diagram of the life history of Ricciocarpus. The upper portion of the figure…
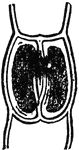
Sachs
"Splitting of partition wall between guard-cells to form the stoma (Sachs.)" — Encyclopedia Britanica,…
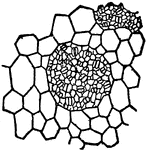
Saxifraga Sarmentosa
"Epidermis of leaf of Saxifraga Sarmentosa, showing clusters of stomata s, surrounded by large epidermal…

Silicles
"Silicles. 1. Of Shepherd's-purse (Bursa Bursa-pastoris). 2. Same, opened, to show the placentae, the…
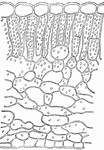
Spathyema
This illustration shows a section of the leaf of skunk cabbage, Spathyema. Note the poorly developed…
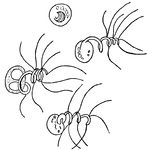
Spermatozooid of the Southern Maidenhair Fern and Venus Hair Fern
Spermatozooid, mature male germ cells, of Adiantum capillus-veneris. Also called spermatozoid.