The Cellular Botany ClipArt gallery offers 293 illustrations of plant tissue at the cellular level, illustrations of cell division, and examples of individual pollen grains.
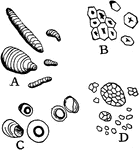
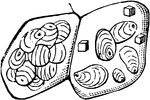
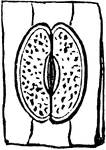
Starch
"Starch from different sources. A, curcuma starch; B, corn starch; C, tapioca starch; D, rice starch,…
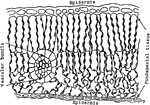
P. Galapageium Stem Tissue
The cross section of the stem of Pisdium Galapageium, which carries very little water.
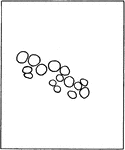
Water Cress Stem Tissue
The cross section of the stem of water cress, which carries very little water.
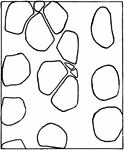
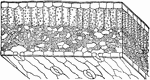
Yellow Poplar Stem Tissue
The cross section of the stem of yellow poplar, which carries large amounts of water.
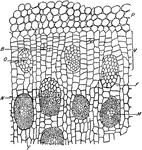
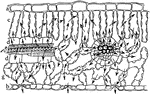
D. Marginata Stem
"Portion of a cross section throughout the stem of Dracaena marginata. P, parenchyma of cortex. V, meristematic…
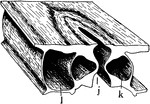
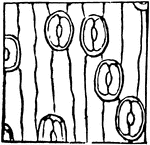
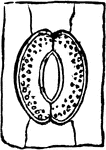
Stoma
"A typical stoma in cross section and surface view combined. k, guard cell; j, the gap or stoma between…
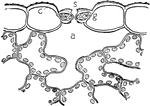
Stoma
This illustration shows a section across a stoma. The stoma is the tiny opening or pore, found mostly…
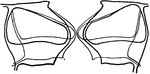
Stoma Guard Cells
"A, diagram showing relative position of the guard cells in cross section in the open and closed positions;…
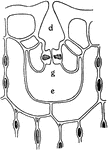
Depressed Stoma
"B, depressed stoma of Hakea suaveolens. g stands beneath the guard cells; d, outer, and e inner, cavities."…
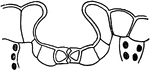
Depressed Stoma
"A, depressed stoma of the under side of a leaf of Amherstia nobilis." -Stevens, 1916
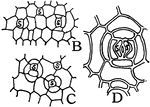
Stomata Formation
"B and C, early stages in the formation of stomata; at s, mother cells of guard cells are shown. D,…

Stone Cells 1
First developmental stage of stone cells: "1, in the primary meristem condition." -Stevens, 1916
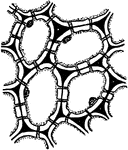
Stone Cells 2
Second developmental stage of stone cells: "2, the cells have enlarged and the walls have begun to thicken…
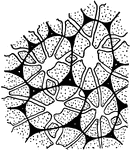
Stone Cells 3
Third and final developmental stage of stone cells: "3, The walls are completed. The primary wall is…

I. Balsamina Storage Tissues
"Storage tissues of the cotyledon of Impatiens Balsamina. A, from the resting seed, and B, from a germinating…

Stored Food
"Diagram to show path of stored food upward through the tracheal tubes, and through the phloem portion…
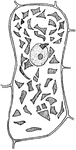
T. Majus Cell
"A, cell from the epidermis of the upper side of the calyx of Tropaeolum majus with crystalline chromoplasts."…
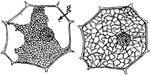
T. Zebrina Cell
In onion cells: "C, a cell from the epidermis of the mid-rib of Tradescantia zebrina, in its natural…
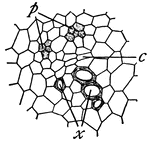
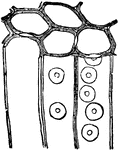
Vascular Bundle
Young vascular bundle: p, primary phloem; x, primary xylem; c, first divisions of cambium cells.
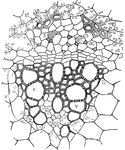
Vascular Bundle
This illustration shows a vascular bundle enlarged: x, xylem; v, vessels or ducts; p, phloem; s, sieve…
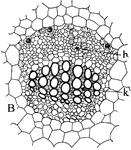
Collateral Vascular Bundle
Types of vascular bundles: "B, the collateral type, with phloem, h, standing in front of the xylem,…
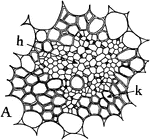
Concentric Vascular Bundle
Types of vascular bundles: "A, the concentric type, with xylem, k, surrounding the phloem, h." -Stevens,…
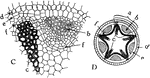
Radial Vascular Bundle
Types of vascular bundles: "C, a portion of the radial type, shown complete in D, where the part outlined…
Plant Vein
"Diagram indicating the succession of the conducting tissues of a vein from the base toward the apex.…

Crab's-Eye Vine
"Crab's-eye vine. Weather Plant. Fig. 64. - Height 10-12 ft.; frequently trailing over the ground S.:…
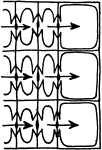
Water Flow in Pine
"Diagram to show the radial flow of water in pine wood, from the tracheids of the late growth of one…
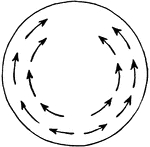
Water Flow in Plants
"Diagram to show the tangential flow of water from the side where there is less demand to the side where…
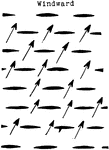
Water Flow in Plants
"Diagram showing by the arrows how the water can flow tangentially around a plant without traversing…
Leaf Water Flow
"Semi-diagrammatic cross section of a leaf showing by arrows how the water passes from the tracheal…

Leaf Water Flow
"Diagram to show the path of the water as it rises to, and escapes from, the leaves." -Stevens, 1916
White Lily
Magnified section of a leaf of White Lily, to exhibit the cellular structure, both of upper and lower…
White-Lily
Small portion of epidermis of the lower face of a White-Lily leaf, with stomata, in the closed state.

Grapevine Wood
"Tangential section through the wood of grapevine. m, cells of medullary ray, and n, of xylem parenchyma,…
L. Tulipifera Wood
"Tangential section of wood of Liriodendron tulipifera, showing frequency of contact of medullary rays…

Oak Wood
"Outline of tangential section of wood of oak, to show frequency of medullary rays. The section is 1…
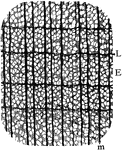
Yellow Poplar Wood
"Cross section of yellow poplar wood. E, early; L, late growth; m, medullary ray." -Stevens, 1916
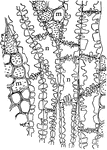
Yellow Poplar Wood
"Showing pitted connections between medullary rays and xylem parenchyma, and between contiguous xylem…
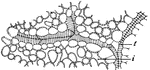
Xylem
Ending of a xylem strand among the cells of the mesophyll in a leaf of lilac; t, tracheid; i, intercellular…
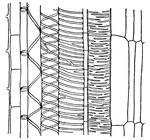
Xylem
Longitudinal section (diagrammatic) of a young xylem strand; c, cambium; y, young trachea,; p, pitted…
Xylem Development 1
"Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. A, progressive steps in the development of…
Xylem Development 2
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "B, stages in the formation of tracheids from…
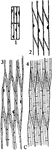
Xylem Development 3
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "C, steps in the development of wood fibers…
Xylem Development 4
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "D, steps in the formation of wood parenchyma…