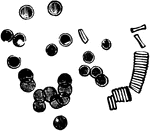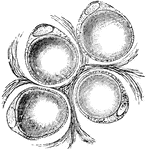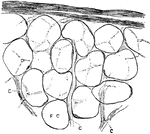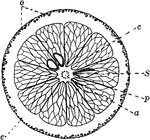
Orange
"Cross-section of an orange. a, axis of fruit with dots showing cut-off ends of fibro-vascular bundles;…

Frog Blood Corpuscles
Blood corpuscles of a frog. Highly magnified. The appearance of blood cells in different animals varies…
The Relation of Nerve Cells to Muscle
Diagram to show the relationship of nerve cell (NC) to Muscle (M) through its nerve fiber.
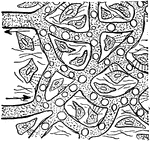
Serous and Mucous Membranes
A diagram exhibiting the relative position of the elements of Serous and Mucous membranes. Labels: 1,…

The Development of Muscular Fibers from Cells
The development of muscular fibers from cells. Labels: a, simple cell. b, a pair of cells fused together.…
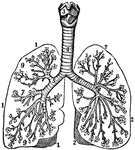
The Bronchia
The bronchia. Labels; 1, Outline of the right lung. 2, Outline of the left lung. 3, Larynx. 4, Trachea.…
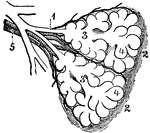
Diagram of the Two Primary Lobules of the Lung
Diagram of the two primary lobules of the lungs, magnified. Labels: 1, Bronchial tube. 2, A pair of…
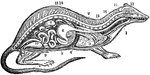
The Respiratory System of a Small Mammal
The respiratory apparatus of other mammals is similar to humans in both structure and function. The…
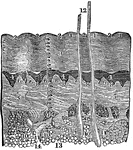
A Diagram of the Skin
A diagram of the skin. Labels: 1, The lines or ridges of the cuticle, cut perpendicularly. 2, The furrow…
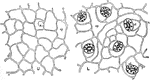
Leaf Epidermis
"Lizard's tail (Saururus cernuus). Portions of leaf-epidermis; U, upper epidermis; L, lower epidermis;…
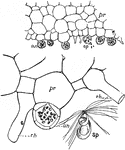
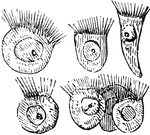
Fern Prothallus
"Fern prothallus; cross-sections showing antheridia (an), sperms (sp), and rhizoids (rh). Below at the…
Microscopic View of a Muscle
A microscopic view of a muscle showing, at one end, the fibrillae; and at the other, the disk, or cells…

Magnified View of the Cuticle
Magnified views of the cuticle. Labels: A, represents a vertical section of the cuticle. B, the lateral…
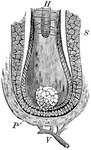
Hair Papilla
A hair. Labels: s, the sac (follicle); P, the papilla, showing the cells and the blood vessels (V).
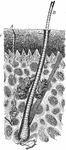
A Hair
A hair. Labels: A perspiratory tube with its gland; B, a hair with a muscle and two oil-glands; C, cuticle;…
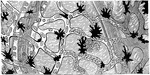
Circulation of Blood in a Frog's Foot
The circulation of the blood in the web of a frog's foot. A, an artery; B, capillaries crowded with…
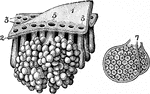
A Magnified Section of the Duodenum
A vertical section of the duodenum, highly magnified. Labels: 1, a fold-like villus; 2, epithelium,…
The Structure of the Retina
Next to the choroid and comprising about 1/4 the entire thickness of the retina is a multitude of transparent,…
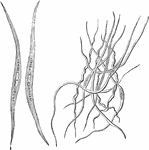
Smooth Muscle Fibers
The smooth muscle fibers consist of long spindle-shaped cells, the end of which are frequently spirally…

Branched Gastric Gland
Gastric glands are often branched at the bottom end. Labels: a, the peptic cells; b, the inert cells.
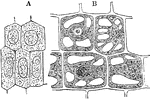
Vegetable Cell
A, A young vegetable cell, showing cell cavity entirely filled with granular protoplasm enclosing a…
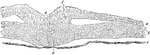
Cells of an Embryo Chick
A transverse section through an embryo chick (26 hours). Labels: a, epiblast; b, mesoblast; c, hypoblast;…
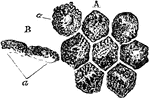
Pigment Cells from the Retina
Squamous epithelium is found arranged as a single layer of flattened cells as the pigmentary layer of…
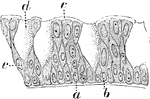
Columnar Epithelial Cells from a Cat
Columnar epithelium consists of cells which are cylindrical or prismatic is form containing a large…
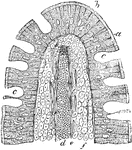
Intestinal Villus of a Cat
A vertical section of an intestinal villus of a cat. Labels: a, the striated basilar border of the epithelium;…
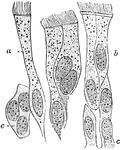
Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated epithelium from the human trachea. Large fully formed cell. Labels: b, shorter cell; c, developing…
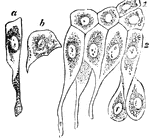
Epithelium of the Bladder
Epithelium of the bladder. Labels: a, one of the cells of the first row; b, a cell of the second row;…

Epithelium of the Rabbit's Cornea
The vertical section of the stratified epithelium of the cornea of a rabbit. Labels: a, Anterior epithelium…

Pavement Epithelium
The jagged cells from the middle layers of pavement epithelium, from a vertical section of the gum of…
Pigment Cells
Ramified pigment cells, from the tissue of the choroid coat of the eye. Labels: a, cell with pigment;…

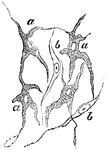
Connective Tissue Cells from a Frog
Flat, pigmented, branched connective tissue cells from the sheath of a large blood vessel of a frog's…

Fibrous tissue of Cornea
Fibrous tissue of cornea, showing bundles of fibers with a few scattered fusiform cells (A) lying in…

White Fibrous Tissue of the Tendon
Mature white fibrous tissue of tendon, consisting mainly of fibers with a few scattered fusiform cells.
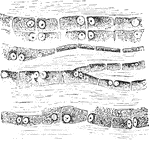
Structure of Tendon Cells
The cells in the tendons are arranged in long chains in the ground substance separating the bundle of…
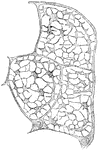
Branched Tendon Cells
The branched character of the cells is seen. Shown is a transverse section from a cross section of the…
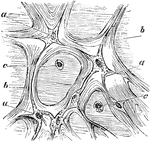
The Tissue of Whartonian Jelly
Tissue of the jelly of Wharton from a umbilical cord. Labels: a, connective tissue corpuscles; b, fasciculi…
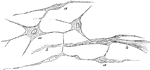
Tissue Growth of the Uterus
In the embryo the place of fibrous tissues is at first occupied by a mass of roundish cells, derived…
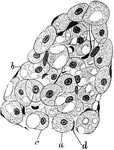
Developing Adipose Tissue in Fetus
A lobule of developing adipose tissue from an eight month fetus. Labels: a, Spherical or, from pressure,…
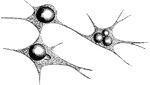
Branched Connective Tissue Corpuscles
Branched connective tissue corpuscles, developing into fat cells.
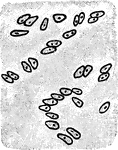
Hyaline Cartilage Cells
The cells of hyaline cartilage are irregular in shape and are generally grouped together. Shown is the…
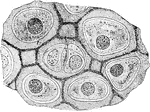
Hyaline Cartilage Cells
The matrix of hyaline cartilage has a dimly granular appearance like that of ground glass, and in man…
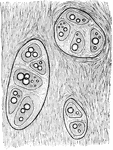
Costal Cartilage
The costal cartilages also frequently become calcified in old age. Fat globules may also be seen in…
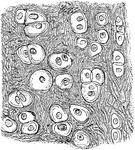
Yellow Elastic Cartilage
The cells in yellow elastic cartilage are rounded or oval, with well marked nuclei and nucleoli.
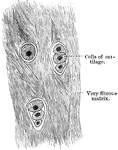
White Fibrocartilage
White fibrocartilage is composed of both cells and a matrix, but is almost exclusively composed of fibers…
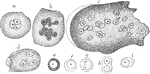
Cells of the Red Marrow
Red marrow occupies the spaces in the cancellous tissue; it is highly vascular, and this maintains the…
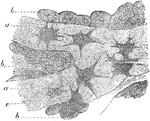
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts from the parietal bone of a human embryo, thirteen weeks old. Labels: a, bony septa with…
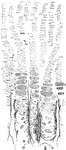
Ossifying Cartilage Showing Calcification
Longitudinal section of ossifying cartilage from the humerus of a fetal sheep. Calcified trabeculae…
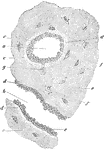
Formation of Compact Bone in a Human
Transverse section of femur of a human embryo about eleven weeks old. Labels: a, rudimentary Haversian…
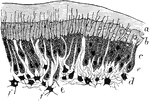
Deposition of Dentine
Part of section of developing tooth of a young rat, showing the mode of deposition of the dentine. Labels:…

Unstriped Muscle of a Newt
Unstriped muscle, or plain muscle, forms the proper muscular coats. Shown is unstriped muscle cells…

Unstriped Muscle of a Guinea Pig
Unstriped muscle, or plain muscle, forms the proper muscular coats. Shown is a plexus of bundles of…
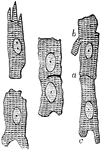
Muscular Fiber Cells from the Heart
Muscular fiber cells from the heart. The fibers which lie side by side are united at frequent intervals…
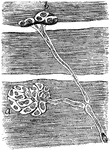
Muscular Fiber Cells of a Snake
From preparation of the nerve termination in the muscular fibers of a snake. A, End plate seen only…
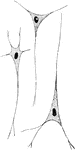
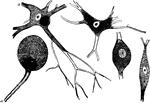
Ganglion Nerve Corpuscles
Nerve cells, also known as nerve corpuscles, comprise the second principle element of the nervous tissue.…