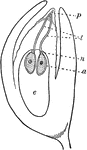
Spruce Ovule
"Longitudinal section through fertilized ovule of a spruce. p, pollen grains; t, pollen tubes; n neck…
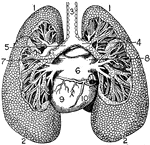
Lungs
"The Lungs. 1, Summit of lungs. 2, Base of lungs. 3, Trachea. 4, Right bronchus. 5, Left bronchus. 6,…
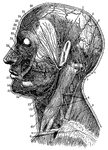
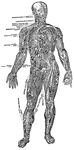
Arteries and Nerves
"Superficial arteries and nerves of the face and neck. 1, Temporal artery; 2, artery behind the ear;…
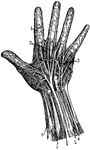
Hand Nerves
"Nerves of the had. 1, Nerves of the skin; 2, tendons; 3, arteries of the palm of the hand; 4, elbow…
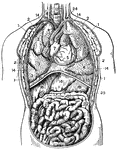
Thorax and Abdomen
"Thorax and abdomen. 1, 1, 1, 1. Muscles of the chest. 2, 2, 2, 2. Ribs. 3, 3, 3. Upper, middle and…

Honore de Balzac
(1799-1850) French novelist and playwright most famous for Eugenie Grandet and La Comedie Humaine.
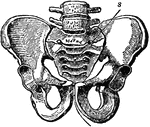
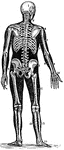
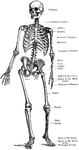
Pelvic Bone, Male
A bony structure located at the bottom of the spine. The human sacrum forms the back part of the pelvis,…
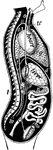
View of Organs from the Side
The chief organs of the body from the side. Labels: a, arch of the aorta or main artery of the trunk;…

Comparison of the Molar Teeth of a Human, Horse, and Dog
The molar teeth of a human, horse and dog. The first image to the left in a molar tooth of a horse.…
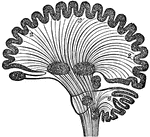
Diagram of Human Brain in Vertical Section
Diagram of human brain in vertical section, showing the situation of the different ganglia and the course…
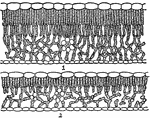
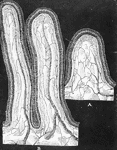
Oak Leaf Cross-Section
"Cross-sections of leaves of an oak (Quercus novimexicana), showing the effect of different light conditions…
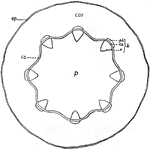
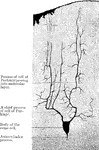
Castor-Oil Plant Stem
"Diagram showing tissue-systems in young stem of castor-oil plant (Ricinus communis), as seen in cross-section.…
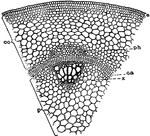
Castor-Oil Plant Stem
"The castor-oil plant (Ricinus communis). Portion of cross-section of young stem. co, Cortex; p, pith…
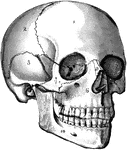
The Skull
The human skull. Labels: 1, frontal lobe; 2, parietal lobe; 3, temporal lobe; 4, the sphenoid bone;…
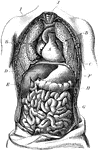
Torso
The human torso. Labels: A, the heart; B, the lungs drawn aside to show the internal organs; C, the…
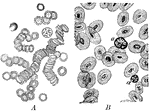
Corpuscles of Human and Animal Blood
A magnified view of corpuscles of human blood compared to animal blood. Labels: A, corpuscles of human…
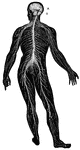
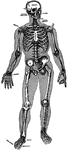
Nervous System
The human nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and the nerves. Labels: A, cerebrum; B, cerebellum.
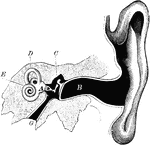
Ear
The human ear. Labels: A, vestibule or antechamber; B, auditory canal; C, the hammer, anvil, and the…
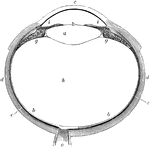
Eye
The human eye. Labels: a, crystalline lens; b, retina; c, cornea; d, sclerotic; e, choroid; g, ciliary…
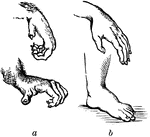
Comparison of the Hand and the Foot of a Monkey and Human
The power possessed by the hand of a human is chiefly depended upon the size and power of the thumb,…

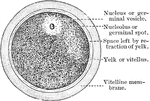
The Human Ovum Undergoing Segmentation
The diagram of a human ovum undergoing segmentation. Labels: a, human ovum; b, ovum divided into two;…
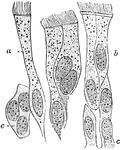
Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated epithelium from the human trachea. Large fully formed cell. Labels: b, shorter cell; c, developing…
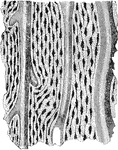
Microscopic Structure of Bone
The bone contains a multitude of small irregular spaces, approximately fusiform in shape, called lacunae,…
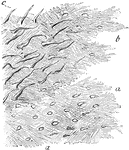
Lamellae
Lamellae torn off from a decalcified human parietal bone at some depth from the surface. Labels: a,…
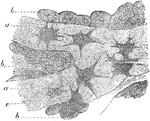
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts from the parietal bone of a human embryo, thirteen weeks old. Labels: a, bony septa with…
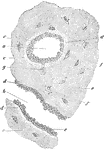
Formation of Compact Bone in a Human
Transverse section of femur of a human embryo about eleven weeks old. Labels: a, rudimentary Haversian…
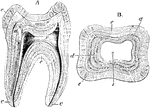
Structure of a Molar
Longitudinal section (A) and transverse section (B) of a human molar tooth. Labels: c, cement; d, dentine;…
Muscular Fibers of the Human Tongue
Transverse section through muscular fibers of human tongue. The muscle corpuscles are indicated by their…
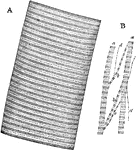
Muscular Fiber
A. Portion of a medium sized human muscular fiber. B. Separated bundles of fibrils equally magnified.…
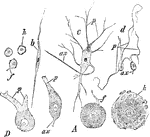
Different Forms of Ganglion Cells
Different forms of ganglion cells. A, a, round ball-shaped unipolar cell from the human Gasserian ganglion.…
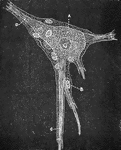
Ganglion Cell, Structure of
An isolated ganglion cell of a human, showing sheath with nucleated cell lining, B. A Ganglion cell,…

Pacinian Corpuscles in a Human
The Pacinian bodies or corpuscles are elongated oval bodies situated on some of the cerebrospinal and…

Pacinian Corpuscle of a Human
The Pacinian bodies or corpuscles are elongated oval bodies situated on some of the cerebrospinal and…

Touch Corpuscle of Meissner
Touch corpuscles are found in the papillae of the skin of the fingers and toes, or among its epithelium;…
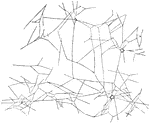
Reticulum of Fibrin
The clotting of the blood is due to the development in it of a substance called fibrin which appears…

Effect of Acetic Acid on Red Blood Cells
Acetic acid (dilute) causes the nucleus of the red blood cells in the frog to become more clearly defined;…
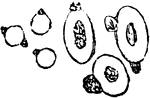
Effect of Tannin on Red Blood Cells
When a 2 percent fresh solution of tannic acid is applied to frog's blood it causes the appearance of…
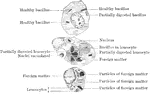
The Change of Colorless Blood Corpuscles
Human colorless blood corpuscle, showing its successive changes of outline within ten minutes when kept…
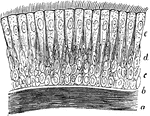
Ciliary Epithelium
Ciliary epithelium of the human trachea. Labels: a, layer of longitudinally arranged elastic fibers;…
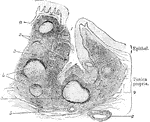
Crypt of Tonsil
A tonsil consists of an elevation of the mucous membrane presenting 12 to 15 orifices which lead into…
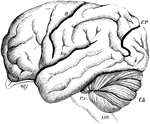
Brain of the Orangutan
Brain of the Orangoutang, showing arrangement of the convolutions. Sy, fissure of Sylvius; R, fissure…
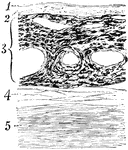
Section Through the Choroid Coat
Section through the choroid coat of the human eye. Labels: 1, elastic membrane, structureless or finely…

Layers of the Retina
Section through the macula lutea and fovea centralis of the human retina. Labels: a, fovea; b, descent…
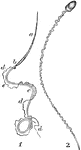
Spermatozoa of a Salamander and Human
Spermatozoa of the salamander (1) and human (2). Labels: a, long pointed head; b, elliptical structure…
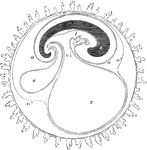
Membranes of the Ovum
Diagrammatic section showing the relation in a mammal between the primitive alimentary canal and the…
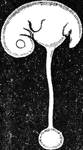
Embryo of Fifth Week
Human embryo of fifth week with umbilical vesicle. The human umbilical vesicle never exceeds the size…

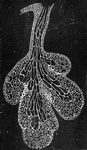
Chorion Villi
Very soon after the entrance of the ovum into the uterus, in the human subject, the outer surface of…