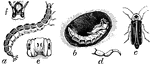
Common Eastern Firefly
"Common Firefly (Photinus pyralis). a, larva; b, pupa in its earthen cell; c, beetle. d, e, f, leg,…
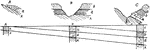
Progressive Overlap of Shore
Natural and columnar sections at each end and at the center of a line 100 miles long and at right angles…
Clastic Deposits in the Sea
Natural and columnar sections at each end and in the center of a line 100 miles long and extending at…

Inclined Strata Dip and Strike
Diagram illustrating the relationships of dip and strike of the inclined strata of an outcropping series…

Bones of Human Foot
"Bones of Human Foot, or Pes, the third principal segment of the hind limb, consisting of tarsus, metatarsus,…
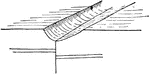
Fault Line Valley
A fault line valley. A fault line, is a planar fracture in rock in which the rock on one side of the…
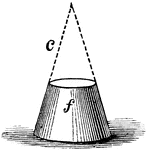
Frustum of a Cone
"The part of any solid between two planes, which may be either parallel or inclined to each other: as,…

Black Forest Village
View of a village in the Schwartzwald, or Black Forest. The Black Forest stands in the elbow formed…

Shelduck
Tadorna cornuta, the Sheld-Drake or Bargander, ...shews a white collar on the lower neck followed by…

Weston Coat of Arms
"The male figure is that of Sir John de Weston, of Weston-Lizars, in Staffordshire, and Isabel his wife,…
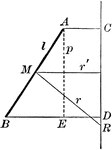
Area of Surface Generated by a Straight Line
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "The area of the surface generated by a straight line revolving about…
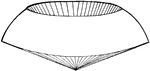
Spherical Cone
"If a sector revolves about its bounding radius as an axis, it generates what may be called a spherical…
Volume of Spherical Segment
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "The volume of a spherical segment is equal to the sum of two cylinders…
Line Engrailed
A line engrailed for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by…
Line Invected
A line invected for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by lines…
Line Wavy
A line wavy or undé for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided…
Line Embattled
A line embattled or crenelle for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are…
Line Nebule
A line nebule for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by lines…
Line Indented
A line indented for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by lines…
Line Dancette
A line dancette for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by lines…
Line Angled
A line angled for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by lines…
Line Bevilled
A line bevilled for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by lines…
Line Escartelle
A line escartelle for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by…
Line Nowy
A line nowy or franché for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are…
Line Dove-Tailed
A line dove-tailed for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by…
Line Embattled Grady
A line embattled grady or battled embattled for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one…
Line Potent
A line potent for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by lines…
Line Double Arched
A line double arched for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided…
Line Arched
A line arched or enarched for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided…
Line Urdée
A line urdée for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided…
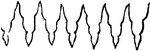
Line Radient
A line radient for dividing a field. "Escutcheons that have more than one tincture are divided by lines…
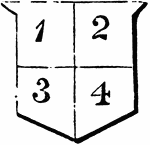
Quartered Per Cross
"QUARTERED PER CROSS—The shield is divided into four parts, called quarters, by an horizontal…

Chief Ordinary
"Argent, on a chief, gules, two mullets, sable. The chief is an ordinary terminated by an horizontal…

Chief Indented
"Argent, a chief, azure, indented. The chief is an ordinary terminated by an horizontal line, which,…
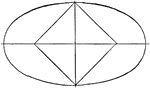
Parts of Ellipse
Diagram of an ellipse that can used to illustrate the different parts. Segment MN is the major axis,…
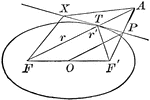
Tangent to an Ellipse
Diagram an ellipse with a tangent line that illustrates "A line through a point on the ellipse and bisecting…
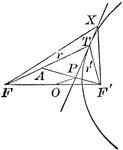
Tangent to a Hyperbola
Diagram part of a hyperbola with a tangent line that illustrates "A line through a point on the hyperbola…
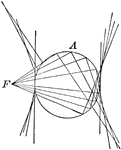
Construction of a Conic
Diagram showing how to construct a conic when given the focus and the auxiliary circle. If the focus…
Positioning Pen for Constructions
Illustration showing the correct and incorrect position of a right line pen against a T-square, triangle,…

Non-Vocal Primary Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
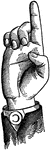
Non-Vocal Primary Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
Non-Vocal Mixed Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Divided Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
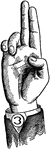
Non-Vocal Divided Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed-Divided Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed-Divided Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Shut Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Shut Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Nasal Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
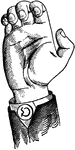
Non-Vocal Nasal Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Primary Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Primary Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Primary Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
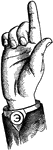
Vocalized Primary Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
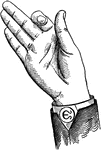
Vocalized Mixed Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
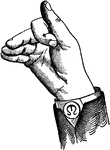
Vocalized Mixed Top Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Mixed Point Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Mixed Lip Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
