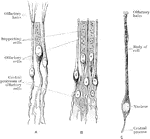
Olfactory and Supporting Cells
Olfactory and supporting cells in a frog and a human. A. Frog. B. Human. C. Human.

Cones and Rods of Retina
A. A cone and two rods from the human retina (modified from Max Schultze); B. Outer part of rod separated…
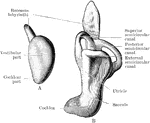
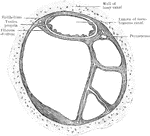
Development of Labyrinth
A, Left labyrinth of a human embryo of about four weeks; B, left labyrinth of a human embryo of about…

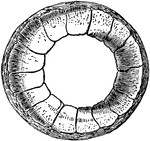
Tongue of Human and Rabbit
A, Section through papilla vallata of a human tongue. B, Section through part of the papilla foliata…
Ailmentary Canal of Bluebird
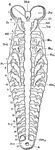
An illustration of the "ailmentary canal of Bluebird, reduced; after Audobon. a,b, gullet or oesophagus;…
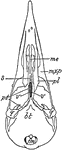
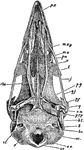
Woodpecker Skull
"Saurognathous skull of woodpecker (Colaptes auratus). v, v, the posterior parts of the abortive vomer;…
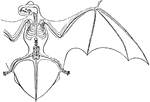
Skeleton and Wing Membranes of the Noctule Bat
The bat genus Nyctalus (Noctule bats) are Evening bats. They are distributed in the temperate and subtropical…

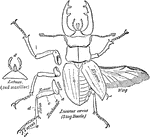
Cockroach
An illustration of a male (right) and female (left) cockroach. Cockroaches (or simply "roaches") are…
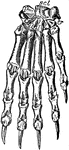
Bear Foot
"Palmar aspect of left fore foot of a black bear (Ursus americanus). scl, scapholunar; c, cuneiform;…
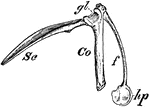
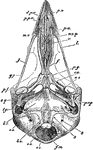
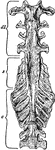
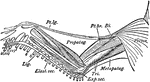
Bird Scapula
"Right shoulder-girdle or scapular arch of fowl, showing hp, the hypoclidium; f, furculum; Co, coracoid;…
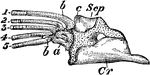
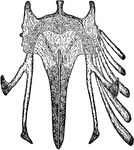
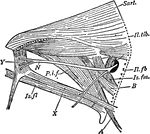
Pike Scapulocoracoid
"Pectoral arch and fore limb of the pike (Esox lucius), an osseous fish, showing scapulocoracoid, composed…

Watercress
Watercresses are fast-growing, aquatic or semi-aquatic, perennial plants native from Europe to central…

American Harpy Eagle
The American Harpy Eagle (Harpia harpyja) is a neotropical eagle, often simply called the Harpy Eagle.…

Sphinx
A Sphinx is a zoomorphic mythological figure which is depicted as a recumbent lion with a human head.
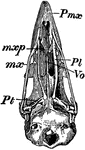
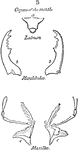
Bird Skull
"Schizognathous skull of common fowl. pmx, premaxilla; mxp, maxillopalatine; mx, maxilla; pl, palatine;…
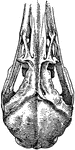
Curlew Skull
"Schizorhinal skull of curlew (top view), showing the long cleft, a, between upper and lower forks of…
Magpie Foot
"Diagram of plantar aspect of schizopelmous foot of a magpie (Pica caudata), showing the deep plantar…

Black Rock Scorpion
The Black Rock Scorpion (Scorpio (Buthus) Afer), "seen from above. At, the chelicerae, or chelate antennae;…
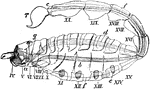
Scorpion Diagram
"Diagram of structure of Scopionidae (most of the appendages removed). IV. to XX., fourth to twentieth…
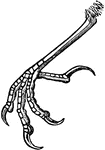
Bluebird Foot
"Scutellate. Foot of bluebird, with laminiplantar and mostly booted tarsus and of the toes." -Whitney,…
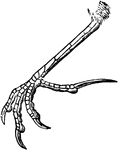
Lark Foot
"Scutelliplantar foot of horned lark: the tarsus scutellate before and behind, and the toes all scutellate…

Chirotherium Tracks
An illustration of a fossil containing Chirotherium tracks. Chirotherium (also known as Cheirotherium)…
Securifera
The securifera or saws of the sawfly (Lophyrus suffusus), an insect related to the wasps and bees.

Sedan
The sedan or litter is a wheelless, human-powered vehicle used to carry one person sitting inside.
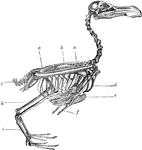
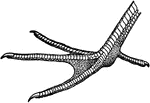
Skeleton of a Bird
The skeleton of a bird. Labels: a, radius and ulna; b, dorsal vertebrae; c, sacrum and pelvis; g, ploughshare…
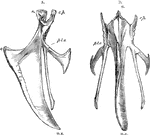
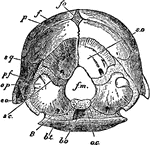
Sternum of a Bird
The sternum of a bird. Label: a, lateral aspect; b, inferior aspect; r, rostrum; c.p, costal process;…
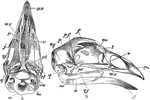
Skull of a Bird
The skull of a bird. Labels: a, inferior aspect, the mandible being removed; b, lateral aspect; px,…
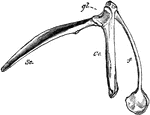
Pectoral Arch of a Bird
The pectoral arch of a bird. Labels: sc, scapula; co, coracoid bone; f, clavicle, terminating below…
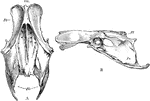
Pelvis of a Bird
The pelvis of a bird. Labels: a, superior; b, lateral aspect; sm, sacrum; Il, ilium; Is, ischium; Am,…

Pixy and a Man
A pixy named Thomas alarmed that a human has just invaded his lawn by jumping over Thomas' wall.
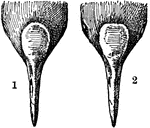
Moorhen Frontal Shields
"Frontal Shield of (1) European Gallinule (Gallinula chloropus), (2) American Gallinule (Gallinula galeata)."…
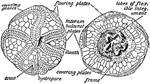
Sea Urchin
An diagram of the anatomy of a sea urchin. Sea urchins are small, globular, spiny sea creatures, composing…
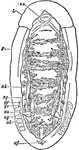
Dissection of the Renal Organs of a Chiton
An illustrative view of the dissection of he renal organs of a chiton. "F, foot; L, Edge of the mantle…

Foxglove
An illustration of: 1, Coralla cut open showing the four stamens; 2, Unripe fruit (lengthwise); 3, ripe…

Masked Crab
Corystes cassivelaunus, the masked crab, helmet crab or sand crab, is a burrowing crab of the North…

Entrance to the Great Temple at Abu Simbel
In 1959 an international donations campaign to save the monuments of Nubia began: the southernmost relics…

Winged Bull from Nimrud
The Sumerian word lama, which is rendered in Akkadian as lamassu, refers to a beneficient protective…
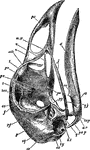
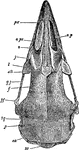
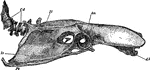
Fowl Skull
The skull of an adult fowl. Here the temporal fossa is bridged over by the junction of the post-frontal…
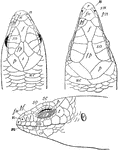
Skink Head
"Head-shields of Scinid Lizards. cs, chin-shields; d, disk on lower eylid; e, ear-opening; f, frontal;…