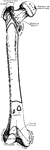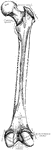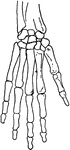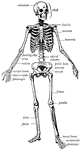
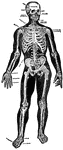
Human skeleton
"The human body, like a great building, has a framework which gives the body its shape and provides…
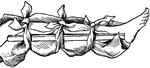
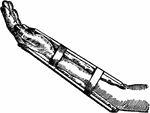
Splint
"When an arm or a leg is broken, it should be kept stretched out straight so that the sharp, broken…
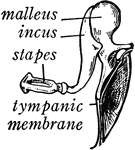
Bones of the Ear
"Across the middle ear a chain of three small bones stretches from the tympanic membrane to the inner…
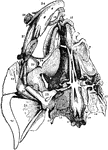
Spine
"The spine, sawn in two lengthwise, showing the spinal canal and the holes between the vertebrae, where…
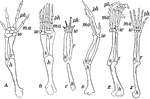
Forearms of vertebrates
"Fore limbs of vertebrates showing similarity of structure. A, salamander; B, turtle;…

Splint
"No one but a good surgeon is able to set a broken bone successfully. However, if a person with a fracture…
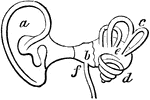
Ear
Interior of the ear. There is external to the head a wide-mouthed tube, or ear-trumpet (a), for catching…
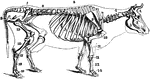
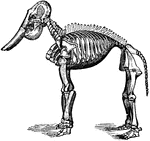
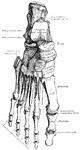
Cow Skeleton
Skeleton of the cow. 1: Frontal bone of the head. 2: Upper jaw, superior maxillary. 3: Lower jaw, inferior…
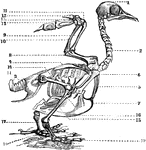
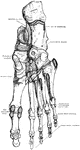
Bird Skeleton
Skeleton of a bird. 1: The head. 2: Cervical Vertebrae. 3: Dorsal and lumbar vertebrae. 4: Scapula.…
Wine-Glass Border
A border which resembles a wine glass and is especially common in the Caucasian textiles, particularly…
Wine-Glass Border
A border which resembles a wine glass and is especially common in the Caucasian textiles, particularly…
Wine-Glass Border
A border which resembles a wine glass and is especially common in the Caucasian textiles, particularly…
Wine-Glass Border
A border which resembles a wine glass and is especially common in the Caucasian textiles, particularly…
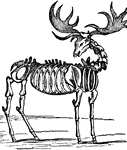
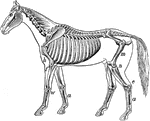
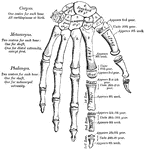
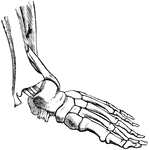
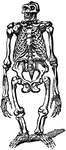
Skeleton
The framework of animals, which in vertebrates is composed of bone and cartilage. It serves to support…
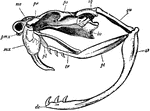
Rattlesnake Skull
This illustration shows the skull of a rattlesnake. ar, articular portion of lower jaw; de, dentary…
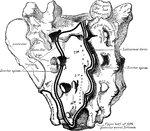
Sacrum
A large, triangular bone at the base of the vertebral column at the upper and back part of the pelvic…
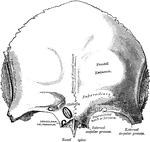
Frontal Bone
A bone in the human skull that consists of two portions, a vertical portion and a horizontal portion.…
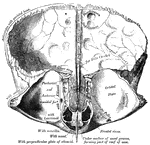
Frontal Bone
A bone in the human skull that consists of two portions, a vertical portion and a horizontal portion.…
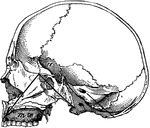
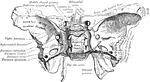
Temporal Bone
Bones situated at the sides and base of the skull. Each consists of five parts: the squama, the petrous,…
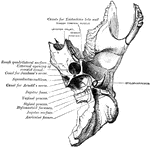
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
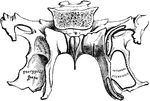
Sphenoid Bone
A bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporals and basilar part of the occipital.
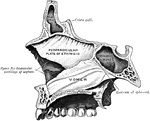
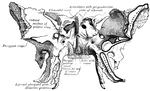
Vomer
The vomer is a single bone, situated vertically at the back part of the nasal fossae, forming part of…
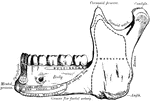
Mandible
The mandible is the largest and strongest bone of the face. It serves for the reception of the lower…
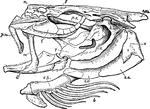
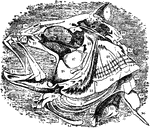
Cod Skull
"The skull of a cod. b, branchiostegal rays born on c.h., the ceratohyal bone; d, dentary portion of…

Compact Bone
"Compact bone consists of a series of concentric layers of bone disposed around a canal called the Haversian…
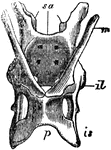
Echidna Pelvis
"The pelvis of the Echidna; sa, sacrum; il, illum; is, ischium; p, pubis; m, marsupial bone." —…
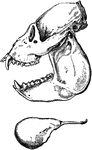
Howling Monkey Skull
"Side views of skull and hyoid bone of Howling Money." — Encyclopedia Britanica, 1893
Gangetic Dolphin
A dolphin with about 120 teeth, 50 vertebrae, extremely narrow jaw, no pelvic bone, rudimentary eyes,…
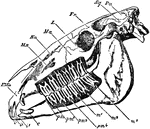
Horse Skull
"Side view of skull of horse, with the bone removed so as to expose the whole of the teeth. PMx, premaxilla;…
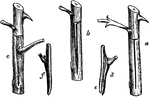
Shield-Budding
"The simplest and most generally practised form of budding is that called Shield budding or T-budding.…
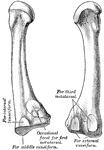
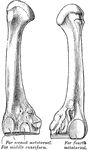
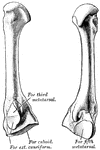
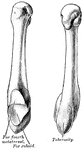
Humerus
"The humerus, which moves freely by a globular head upon the scapula, forming the shoulder-joint." —…