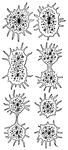General Hospital Interior
"United States General Hospital, Hilton Head, S. C., interior. The United States General Hospital at…

Battle of Chickamauga
"Battle of Chickamauga, Ga., September 19th-20th, 1863, between Generals Rosecrans and Bragg. Our sketch…

War in Tennessee
"The war in Tennessee. Federal pickets approached by Confederates in cedar bushes near Chattanooga.…

Fort Stevens
"The operations near Washington, scene of the fight in front of Fort Stevens, July 12th-13th, 1864.…

War in Tennessee
"The war in Tennessee. Capture of Mission Ridge, near Rossville, by General Thomas, November 25th, 1863.…

A Hole in a Tree
The decayed hole where a limb was removed. The wood-destroying fungi caused the tree to break.

Stub of a Limb of a Tree
A long stub left in pruning. The wound cannot heal. The tape shows how far the trunk is hollow. The…

Bealington
"Engagement at Bealington, Va., between Ohio and Indiana regiments and a detachment of Georgia troops.…

Wood Sparrow
Somewhat aloof from human habitiation, the wood-sparrow can often be seen mingline with other sparrow…

Fort Anne
Site of Fort Anne. This view is from the bridge which crosses Wood Creek, looking south. The distant…

Battleground near Fort Anne
Battleground near Fort Anne. This sketch was taken from the rail-road, looking north. The forest upon…

Capercaille
Also known as the wood-grouse, the capercaille averages about three feet in length and feeds on berries…

Wood-terrapin
Sometimes referred to as the fresh-water terrapin, the wood-terrapin ranges from Canada to Pennsylvania.

Old South
"The Old South. This venerable and venerated edifice, that stood through all the storms of the Revolution,…

Goshen Monument
"Monument at Goshen. During the battle, Major Wood, of Goshen, made a masonic sign, by accident, which…

Society of the Cincinnati
"Society of the Cincinnati, member's certificate. This engraving is a fac simile of a certificate, about…

Smith's House
"Smith's House. This view is from the slope in front of the house. The main building is of stone; the…

Beverly Dock
"View at Beverly Dock. This view is taken from the Hudson River rail-road, looking north. The dock,…

Annapolis State House
"The State House in Annapolis. This fine building is situated upon an elevation in the center of the…

Mount Vernon
"Mount Vernon. This view is from the lawn in front, looking down the Potomac. The mansion is built of…

Apollo Room
"The Apollo Room. The room used for public meetings is in the rear building of the old Raleigh tavern…

Acacia
"An Egyptian tree; the bark and pods are frequently used in tanning and the aqueous extract of the wood…

Cocktails
"The larvae are very similar to the perfect insects, both in appearance and habits. Many of them feed…

Deathwatch Beetles
"Other species, which also bore into timber in their larva state, are well known by the name of Death-watch…
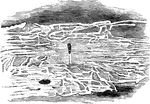
Typograhic Beetle
"The typographic beetle recieves it's name... from the circumstance that the burrows formed by it in…
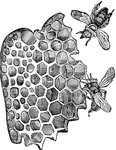
Cells of Honey Bees
"The hexagonal cells for the honey are build upon precisely that mathematical angle which affords the…
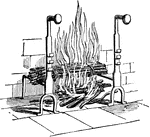
Andiron
"One of a pair of metallic stands used to support wood burned on an open hearth."-Whitney, 1902

Ichneumon
"The ichineumons, with long ovipositors, as the European species, Ichneumon manifestator, seek…

Sawfly
"On the continent of Europe the Sirex gigas often appears in immense numbers, and does great…

Troilus Butterfly
"The Troilus Butterfly, Papilio Troilus, is a superb insect, the wings denticulated, black,…

Battering Ram
"The Battering Ram is an ancient military contrivance used for battering down walls. It consisted of…

Wood-louse
"The family Oniscidae, including the well-known Wood-Louse, Oniscus murarius, and many similar…

Calymene
"The trilobite's general form is shown in the annexed figure of the Calymene Blumenbachii;…

Coffee Plant
"Coffee is the seed of an evergreen shrub, which is cultivated in hot climates, and is a native of Abyssinia…

Coffee Bean
"Coffee is the seed of an evergreen shrub, which is cultivated in hot climates, and is a native of Abyssinia…

Coffee Bean
"Coffee is the seed of an evergreen shrub, which is cultivated in hot climates, and is a native of Abyssinia…

Song Thrush
"Thrush, in ornithology, is the name for any of the Turdidæ. They are universally distributed,…

Reed Warbler
"Warbler is a popular name often applied to well-known singing birds of northern climes, whose notes…

Nest of Reed Warbler
"Warbler is a popular name often applied to well-known singing birds of northern climes, whose notes…

Green Woodpecker
"Woodpecker is the popular name of the old Linnæan genus Picus, now greatly divided. Woodpeckers…

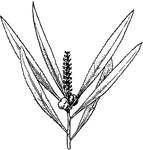
Wormwood
"Wormwood is the genus Artemisia. The stem is one to three feet high, grooved, and angled; the leaves…

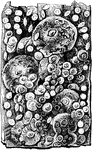
Protozoans
"Their bodies consist either of aa simple elementary cell, with its contents, or of an aggregation of…
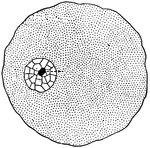
Cell
"In a general what we may describe a cell as a tiny mass of jelly in which floats another still smaller…
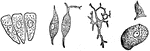
Various forms of cells
"A, columnar cells found lining various parts of the intestines (called columnar epthelium);…

Various kinds of epithelial cells
"A, columnar cells of intestine; B, polyhedral cells of the conjuctiva; C, ciliated conical cells of…
Spindle Cell of Involuntary Muscle
"The involuntary muscles consist of ribbon-shaped bands which surround hollow tubes or cavities…
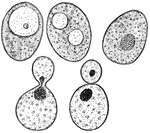
Yeast cake
"Showing a Bit of Common Yeast Cake when mixed with Water and examined under the Microscope. There are…
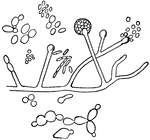
Fermentation of wine
"Organisms found upon the Skin o a Grape and concerned in the Fermentation of Wine." — Blaisedell,…
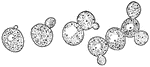
Growing yeast cells
Growing Yeast Cells, showing Method of budding and forming Groups of Cells. Each bud appears as a little…
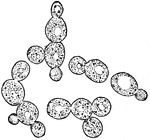
Yeast cells
"Yeast Cells, found in the Juice of Apples, which cause the fermentation of Cider." — Blaisedell,…
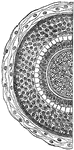
Cross-section of a human hair
"Cross-section of One Half of a Human Hair. A hair is made up of horny cells of the outer layer of the…

Sweat gland
"The convoluted gland is seen surrounded by fat cells and may be traced through the true skin to its…