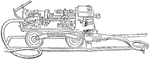
Coal-cutting Machine
"This machine consists essentially of a horizontal piston and cylinder engine fixed upon a platform…

Mimic Beetle
"The Mimic Beetles seldom exceed one-third of an inch in length, and are of very solid consistence,…

Pschent
A sovereign crown of Egypt, composed of the tall pointed miter, or white crown, of southern Egypt, combined…

Fredrick Muller's Dredge
"Muller gives a quaint description not very unlike that used by Hall and Forbes, only the mouth of the…
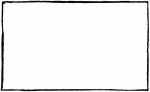
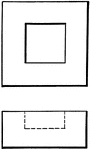
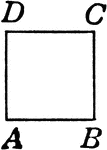
Rectangle
A quadrilateral plane figure having four right angles and its opposite sides equal in length. The adjacent…
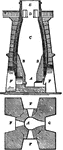
Furnace
"The section and ground plan of one of the older forms of open-mouthed furnaces used at Dowlais (Truran),…
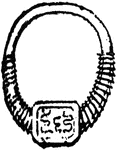
Signet Ring
"A signet ring has a square revolving bezel on which are four serpents interlaced." —The Encyclopedia…

Mountain Rupture
"Rupture of a Mountain.—There is no doubt, but in the operations of nature, great effects are…
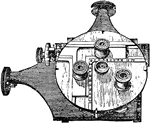
Micrometer
"A plate of glass about 2.5 inches square is ruled with twenty-one lines in one direction .1 inch apart,…
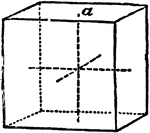
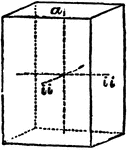
Primitive Crystal
"In this the four lateral planes are rectangular and equal; they may be either oblong or square; in…
Primitive Crystal
"If the base is a square and the prism stands erect—that is, if its sides or lateral planes, as…
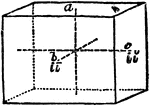
Primitive Crystal
"When the base is a rectangle instead of a square, the form is a right rectangular prism." —The…
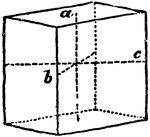
Primitive Crystal
"When the base is a rhombus, and the prism stands erect, the form is a right rhombic prism." —The…
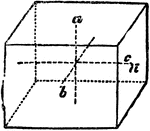
Primitive Crystal
"When the base is a rhomboid, and the prism stands erect, it is only the opposite laeral faces that…
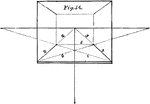
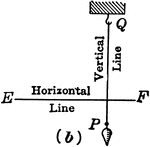
Parallel Perspective
The perspective shown in this plate is parallel perspective; and the subject here intended to be represented…

Barkantine
A three masted vessel, with the foremast square rigged, and the mainmast and mizzemast fore and aft…
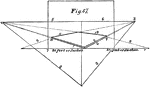
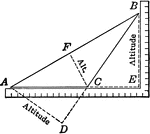
Angular Perspective
The perspective in this plate is "angular perspective," and the figure it represents is a flat square…
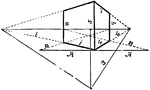
Angular Perspective
This object is a cube, having therefore all its faces of equal dimensions; and as both sides recede,…

Towers of London
The White Tower, the square building with turrets on each corner that gave it its name, is actually…

Desert of Sahara
The Sahara is the world's largest hot desert, 9,000,000 square kilometers, almost as large as the United…

Australian Scenery
Australia's 7,686,850 square kilometers landmass is on the Indo-Australian Plate. Surrounded by Indian,…

Scene of Mississippi
The Mississippi Valley lies between the predominant and secondary mountain-systems. It is over 300,000…

Bark
Or Barque, a three-masted vessel of which the foremast and mainmast are square-rigged, but the mizzenmast…
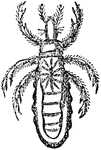
Crab Louse
Pediculus Pubis. The crab-louse is gray-black and is a much broader square form than the other two species…
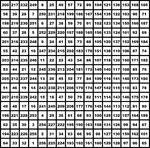
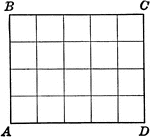
Magic Square
A square divided into equal squares, like a chessboard, in each of which is placed one of a series of…
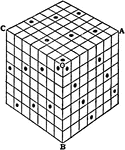
Nasik Cube
Squares that have many more summations than just rows, columns, and diagonals. Frost extended this idea…
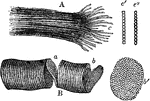
Fragments of Striped (Striated) Muscle Fibers
Fragments of striped (striated) muscle fibers, showing a cleavage in opposite directions, magnified…
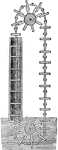
Chain Pump
"It consists of a number of square pieces of board, or of thin iron, connected together through their…
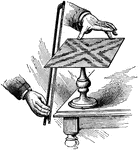
Vibrating Plates
"Support, as shown, a glass or brass plate, square or round, and strew it evenly with fine sand. Place…
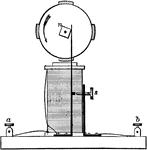
Electric Motor
"An electric motor that uses a square nut to engage the electromagnet which drive the motor." -Avery…
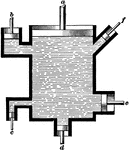
Water Pressure Demonstration
"Let the are of the piston a be 20 square inches; of b, 7 sq. in.; of c, 1 sq. in.; of d, 6 sq. in.;…

Pascal's Law and Water Pressure
"...let the area of the piston a be 1 square inch; of b, 40 square inches. According to Pascal's law,…
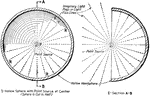
Light Intensity
"The radiation of light, or the intensity of light is inversely proportional to the square of the distance…
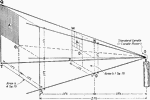
Light Intensity Versus Distance
"Another illustration of how luminous density varies inversely as the square of the distance." —Croft…
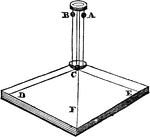
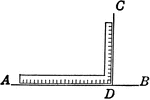
Resultant Motion with Ball
"The ball C is placed on a square frame between two upright wires, on each of which a ball slides so…
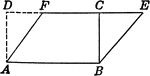
Parallelogram and Rectangle Relationship
Parallelogram with dimensions drawn to show relationship to the area of a rectangle.
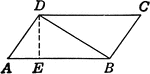
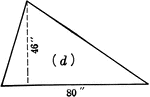
Area of Triangle
Parallelogram illustration to show where the area of a triangle formula comes from.

Rectangle With Dimensions
Rectangle with dimensions labeled. Rectangle can be used to calculate area.

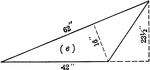
Parallelogram With Dimensions
Parallelogram with dimensions labeled. Parallelogram can be used to calculate area.

Parallelogram With Dimensions
Parallelogram with dimensions labeled. Parallelogram can be used to calculate area.