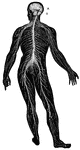
Nervous System
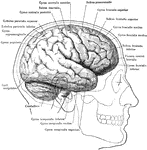
The human nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and the nerves. Labels: A, cerebrum; B, cerebellum.
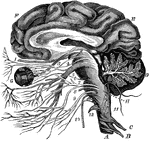
The Brain and the Cranial Nerves
The brain and the origin of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves. Labels: F, E, the cerebrum; D, the cerebellum,…
The Structure of the Retina
Next to the choroid and comprising about 1/4 the entire thickness of the retina is a multitude of transparent,…
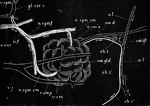
Submaxillary Gland of Dog with Nerves and Blood Vessels
Diagrammatic representation of the submaxillary gland of the dog with its nerves and blood vessels.…
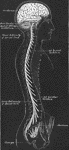
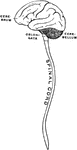
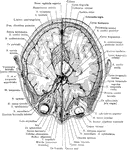
Central Nervous System
View of the cerebrospinal axis of the nervous system. The right half of the cranium and trunk of the…
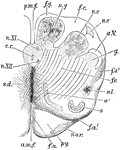
Medulla Oblongata
Anterior or dorsal section of the medulla oblongata in the region of the superior pyramidal decussation.…
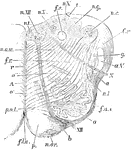
Medulla Oblongata
Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olivary body. f.l.a., anterior median fissure;…
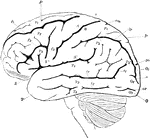
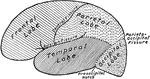
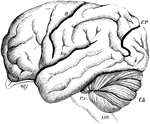
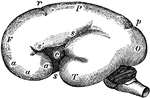
Lateral View of the Brain
Lateral view of the brain. F, Frontal lobe; P, Parietal lobe; O, Occipital lobe; T, Temporal lobe; S,…
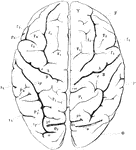
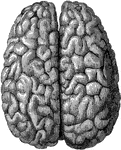
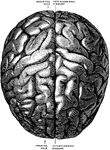
View of Brain from Above
View of brain from above. F, Frontal lobe; P, Parietal lobe; O, Occipital lobe; T, Temporal lobe; S,…
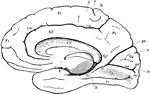
Right Hemisphere of the Brain
View of the right hemisphere in the median aspect. CC, corpus callosum longitudinally divided; Gf, gyrus…
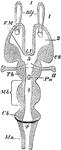
Horizontal Section of a Vertebrate Brain
Diagrammatic horizontal section of a vertebrate brain. Mb, midbrain: what lies in front of this is the…
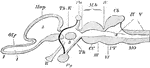
Vertical Section of a Vertebrate Brain
Longitudinal and vertical diagrammatic section of a vertebrate brain. Mb, midbrain: what lies in front…
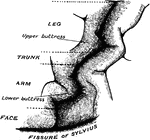
Brain of the Orangutan
Brain of the Orangoutang, showing arrangement of the convolutions. Sy, fissure of Sylvius; R, fissure…
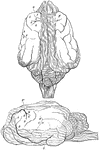
Brain of a Dog
Brain of dog, viewed from above and in profile. F, frontal fissure sometimes termed crucial sulcus,…
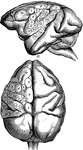
Brain of a Monkey to Show effects of Electric Stimulation
Diagrams of monkey's brain to show the effects of electric stimulation of certain spots. Labels: 1.…
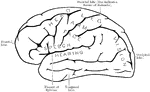
Motor Centers of the Brain
Diagram to indicate position of centers on the external surface of the brain.
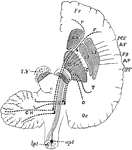
Brain Showing Connection of Frontal Occipital Lobe with Cerebellum
Diagram to show the connecting of the Frontal Occipital Lobes with the Cerebellum. The dotted lines…
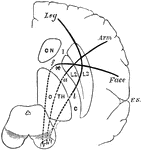
Motor Tracts of the Brain
Diagram to show the relative position of several motor tracts in their course from the cortex to the…
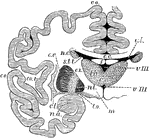
The Cerebrum and Basic Ganglia of the Brain
Vertical section through the cerebrum and basic ganglia to show the relation of the latter. Labels:…
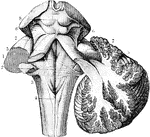
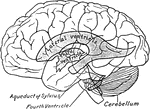
The Cerebrum and Fourth Ventricle of the Brain
The cerebellum in section and fourth ventricle, with the neighboring parts. Labels: 1, median groove…
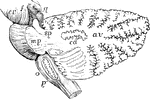
The Cerebellum of the Brain
Outline sketch of a section of the cerebellum, showing the corpus dentatum. The section has been carried…

Cerebellum of Dog's Brain
Vertical section of dog's cerebellum. Labels: p m, pia mater; p, corpuscles of Purkinje, which are branched…
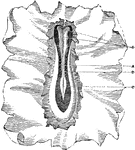
Germinal Membrane of a Dog
Portion of the germinal membrane, with rudiments of the embryo, from the ovum of a dog. The primitive…
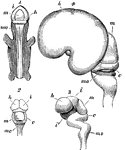
Development of the Brain
Early stages in development of human brain. 1, 2, 3, are from an embryo about seven weeks old; 4, about…
Fetal Brain at Six Months
Side view of fetal brain at six months, showing commencement of formation of the principal fissures…
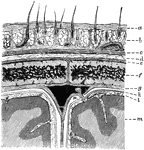
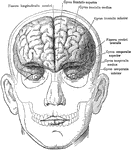
Layers of the Scalp and Membrane of the Brain
Diagram showing the layers of the scalp and membranes of the brain in section. Labels: a, skin; b, subcutaneous…
Principle Fissures of the Brain
Showing the lines which indicate the position of the principal fissures of the brain.
Precentral Gyrus in the Brain
The convolutionary projections of the precentral gyrus, and their relationship to motor areas.
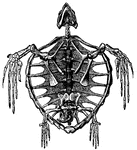
Skeleton of a Turtle
"The Tortoise will continue to live on for six months after it is deprived of its brain."
Relations of the Ventricles to the Surface of the Brain
Scheme showing relations of the ventricles to the surface of the brain.
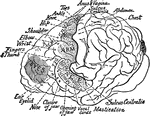
Motor Area of the Brain of a Chimpanzee
Location of the motor areas in the brain of a chimpanzee. The extent of the motor area is indicated…
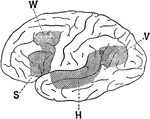
Association Area of the Brain
Lateral view of a brain hemisphere; cortical area V, damage to which produces "mind blindness" (word…
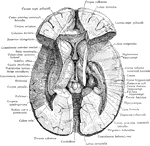
Dissection of the Brain
Dissection of the brain showing basal ganglia, third ventricle and adjacent structures viewed from above.
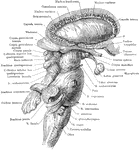
Brain Stem and Adjacent Structures
The right lateral aspect of the brain stem after the cerebral hemisphere (except the Corpus striatum)…
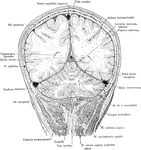
Frontal Section of the Head
Frontal section of the head passing through the parietal and occipital cerebral lobes and he cerebellar…
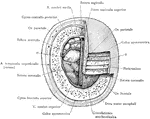
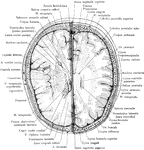
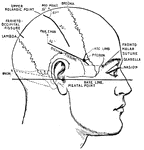
Cross Section of Head
Section two inches above supraorbital border. Upper surface. The (*) on right indicates subaponeurotic…
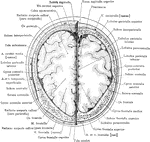
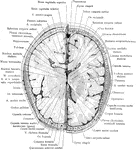
Cross Section of Head 4 cm above Supraorbital Border
Section of head 4 cm above supraorbital border.
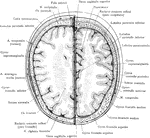
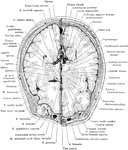
Cross Section of Head 3 cm above Supraorbital Border
Section of head 3 cm above supraorbital border.
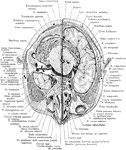
Cross Section of Head Through Lower Portion of Orbit
Section of the head through lower portion of orbit.
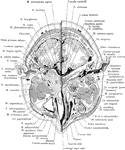
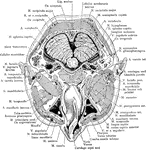
Cross Section of Head Exposing Maxillary Sinus
Section of the head immediately below the orbits, at the level of Reid's base line exposing the maxillary…
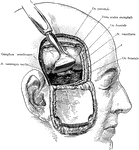
Incision of the Head Showing Gasserian Ganglion
Exposure of the Gasserian ganglion and middle meningeal artery though a flap incision of the scalp and…
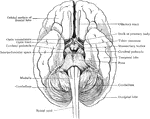
Relation of Brain Stem to Spinal Cord
Simplified drawing of brain as seen from below, showing relations of brain stem to spinal cord and cerebrum.
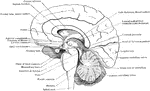
Brain in Mesial Section
Simplified drawing of brain as seen in mesial section, showing relation of brain stem, cerebrum and…
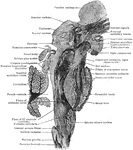
Sagittal Section of Brain Stem
Sagittal section of brain stem; plane of section is somewhat lateral to midline.
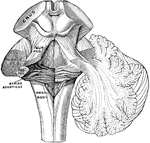
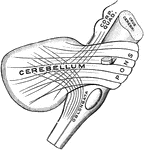
Peduncles of the Cerebellum
The peduncles of the cerebellum. On the left the three peduncles have been cut at their entrance into…
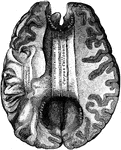
Brain Showing Corpus Callosum
Shown is the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum is a thick stratum of transversely directed nerve…
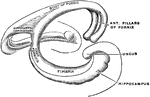
Fornix
The fornix is a paired structure consisting of bilaterally symmetrical halves composed of longitudinally…