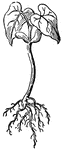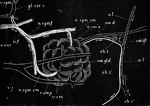
Submaxillary Gland of Dog with Nerves and Blood Vessels
Diagrammatic representation of the submaxillary gland of the dog with its nerves and blood vessels.…
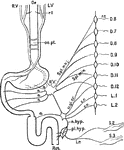
Nerves of the Alimentary Canal
Diagrammatic representation of the nerves of the alimentary canal. Oe to Rct, the various parts of the…
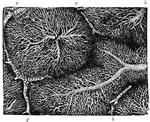
Capillary Network in the Lobules of a Rabbit's Liver
The liver is made up of small roundish or oval portions called lobules, each of which is composed of…
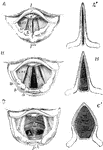
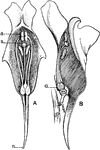
Movement of the Vocal Cords
Three laryngoscopic view of the superior aperture of the larynx and surrounding parts. Labels: A, the…
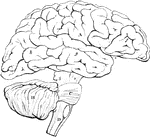
Outline of the Encephalon
Plan in outline of the encephalon, as seen from the right side. The parts are represented as separated…

Toilet-Stand Clock-Case
This Toilet-stand clock-case was made during the German Renaissance in 1597. A slender tall cabinet,…

Toilet-Stand Clock-Case
This Toilet-stand clock-case was made during the German Renaissance. Made of various colored wood, it…
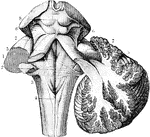
The Cerebrum and Fourth Ventricle of the Brain
The cerebellum in section and fourth ventricle, with the neighboring parts. Labels: 1, median groove…

Hair-Cap Moss
"Hair-cap moss (Polytrichum commune). A, male plant; B, same, proliferating; C, female plant, bearing…
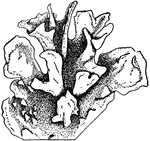
Anthoceros fusiformis
"Anthoceros fusiformis. Portion of lamellate, cristate thallus, which easily retains water." -Gager,…

Leafy Liverwort
"A leafy liverwort (Porella navicularis). Male plant, about natural size." -Gager, 1916
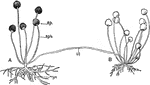
Bread Mold
"Bread mold (Rhizopus nigricans). A, older plant; myc, mycelia; sph, sporangiophore; sp, sporangium;…
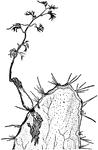
Parasitic Plant
"Cissus laciniata, parasitic on the cactus (Opuntia Blakeana). The parasitism was artificially induced…

Dog's-Tooth Violet Stages
"Dog's-tooth violet (Erythronium americanum). Stages of development from the seed. 1-5 show the stage…
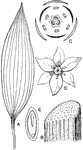
Monocotyledonous Morphology
"Morphology of typical monocotyledonous plant. A, leaf, parallel-veined; B, portion of stem, showing…
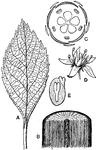
Dicotyledonous Morphology
"Morphology of a typical dicotyledonous plant. A, leaf, pinnately-netted veined; B, portion of stem,…
Common Toadflax
"Sections of flowers of the toad-flax (Linaria vulgaris). A, front view; a, anthers; s, stigma; n, nectar-gland.…
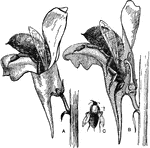
Common Toadflax with Insect
"Toad-flax (Linaria vulgaris). Flowers being visited by an insect for nectar. B, longitudinal section,…

Lesser Burdock
"Inflorescence and flowers of the burdock (Arctium minus). a, Inflorescences; b, longitudinal section…

Common Chicory
"Chicory (Cichorium Intybus). A, portion of flowering branch; B, basal leaf (runcinate-pinnatifid);…
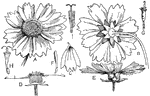
Tickseed
"A composite (Coreopsis sp.). A, B, E, views of the inflorescence or head; C, a ray-flower; D, section…
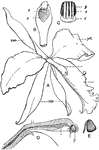
Orchid Organs
"Floral organs of an orchid (Cattleya sp.). A, the entire flower; sep, sepal; pet, petal; B, column,…
Wild Cliff-Cabbage
"Wild cliff-cabbage, hypothetical ancestor of the numerous modern horticultural forms." -Gager, 1916
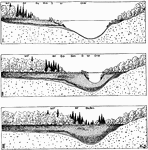
Lake and Vegetation
"Diagram illustrating the gradual filling up of lakes by the encroachment of vegetation, and also the…
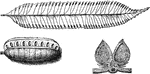
Marratia Fern
"Top, lateral pinna from a leaf of Marattia jraxinea. Below at left, synangium of same. At right, corss-section…

Cycadeoid
"Cycadeoidea dacotensis. Semi-diagrammatic sketch of a flower (bisporangiate cone), cut longitudinally;…
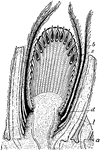
Cycadeoid
"Cycadeoidea Wielandi. Longitudinal section through the axis of a female inflorescence, or cone. l,…
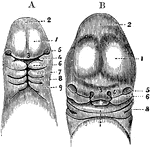
Head of an Embryo
A, Magnified view of the head and neck of a human embryo of three weeks. Labels: 1, anterior cerebral…
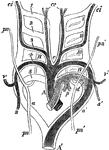
Aortic Arches in a Mammal
Diagram of the aortic arches in a mammal, showing transformations which give rise to the permanent arterial…
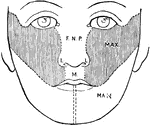
Development of the Face
Showing the development of the face. F.N.P., Part formed from the frontonasal process; L, from its lateral…
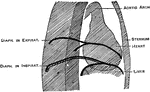
Orthodiagram of the Thorax
Orthodiagram of the thorax. The position of parts is shown in extreme inspiration; the position of the…
Snare Drum
"The snare drum, having two heads, the upper one only being played upon by two sticks of wood; strings…
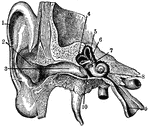
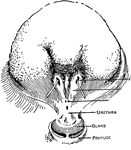
Ear
"Section through right ear. 1, helix; 2, concha; 3, outer passage; 4, 5, 6, semi-circular canals; 7,…

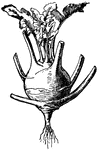
Castor-oil Plant
A plant native of the Indies, the plant is used to make castor-oil, which is used as a laxative and…

Cotton plant
The cotton plant is a shrub that produces a downy fiber, called cotton. This material is then woven…
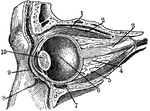
Eye Section
"Section through the left eye, closed. 1, lifting muscle; 2, upper straight muscle; 3, optic nerve;…
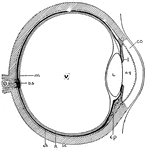
Eye Cross-Section
"Cross-section of the eye. Parts: co, cornea; I, iris; aq, anterior chamber of aqueous humor; L, lens;…

Small-Mouthed Black Bass
"1. Spiny portion of dorsal fin. 2. Soft portion of dorsal fin. 3. Caudal fin. 4. Anal fin. 5. Pectoral…
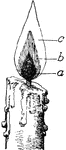
Flame Parts
"Flame. a, area of no combustion. b, area of partial combustion. c, area of complete combustion." -Foster,…
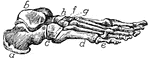
Foot Bones
"The foot. a, calcaneum; b, astragalus; c, cuboid; d, metatarsal, of which there are five; e, phalanges,…
Foxtail Grass
"Foxtail grass, the common name given to certain grasses, because of the shape of the large clusters…

Wild Turkey
"The turkey is indigenous to America; and it may still be found in some parts of our country in the…