
Lambeth Palace, 1867
Lambeth Palace is the official London residence of the Archbishop of Canterbury. It is located in Lambeth,…

Morgan Dix
Morgan Dix (born November 1, 1827 in New York City; died April 29, 1908) was an American priest, "divine"…

Trinity Church
Trinity Church, at 79 Broadway in New York City, is a historic full service parish church in the Episcopal…

Trinity School
Trinity School is a private, preparatory, co-educational day school for grades K-12 located in New York…

Parthenon
The Parthenon is a temple of the Greek goddess Athena, built in the 5th century BC on the Athenian Acropolis.…

Henry, Patrick, Give me liberty or give me death!
A drawing of Virginia Convention in 1775, at St. John's Church in Richmond, Virginia, when Patrick Henry…

John Bell Hood
John Bell Hood (June 1 or June 29, 1831 - August 30, 1879) was a Confederate general during the American…

The Old Church at Sleepy Hollow
A drawing of the old church from "The Legend of Sleepy Hollow" by Washington Irving.

Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis de Richelieu, Cardinal-Duc de Richelieu (September 9, 1585 – December 4, 1642),…

Jester
A jester, joker, jokester, fool, wit-cracker, prankster, or buffoon is a member of a profession that…

St. John's Church
"St. John's Church, Richmond, VA. Where the famous orator Patrick Henry made is great speech." -Gordy,…

The Alamo
The Battle of the Alamo was fought in February and March 1836 in San Antonio, Texas. The conflict, a…

Thomas Truxtun's Grave
Thomas Truxtun (February 17, 1755 – May 5, 1822) was an American naval officer who rose to the rank…

Lutheran Church, Barren Hill, Lafayette's Headquarters
This is the Lutheran Church in Barren Hill where Lafayette took post and occupied his headquarters.

Stephen Van Rensselaer
Stephen Van Rensselaer III (November 1, 1765 – January 26, 1839) was Lieutenant Governor of New York…
Sir Roger de Trumpington
An illustration of a monumental brass erected in honor of Sir Roger de Trumpington located at St. Mary…
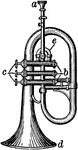
Saxhorn
The saxhorn is a brass instrument with: a, mouthpiece; b, valves; c, keys; d, bell; e, crook.

Earls Barton Church
The tower is the only remaining piece of the Earls Barton Church in Northamptonshire, England. It is…

Hvalsey Church, near Qaqortoq, Greenland
Hvalsey (Greenlandic Qaqortukukooq) is a location near Qaqortoq, Greenland and the site of a number…
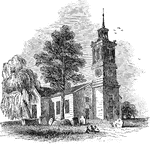
St. John's Church
St. John's Episcopal Church is the oldest church in Richmond, built in 1741 and giving its name to the…
Washington's Pew at St. Paul's, New York
In some churches, pews were installed at the expense of the congregants, and were their personal property;…

The Webb House
Joseph Webb House is a historic Georgian-style house in Wethersfield, Connecticut that was the site…

Mohawk Church
Her Majesty's Royal Chapel of the Mohawks, the oldest church in Ontario, is one of six Royal chapels…

Communion Plate Presented by Queen Anne
During the reign of Queen Anne a valuable communion set was presented by her Majesty to the Mohawk chapel…

Pohick Church
Pohick was the first permanent church in the colony to be established north of the Occoquan River, sometime…
![John Wesley (28 June [O.S. 17 June] 1703 – 2 March 1791) was an Anglican cleric and Christian theologian who was the founder of the (Evangelical) Arminian Methodist movement. "Methodism" was originally an unflattering nickname of the "Holy Club" at Oxford University founded by Charles Wesley but led by brother John. Methodism was well advanced in England through George Whitefield who had taken over the responsibility of the Holy Club while the Wesley brothers were in Savannah, Georgia British North America.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/57500/57587/57587_john_wesley_mth.gif)
John Wesley
John Wesley (28 June [O.S. 17 June] 1703 – 2 March 1791) was an Anglican cleric and Christian…

Westminster Abbey
The Collegiate Church of St Peter at Westminster, which is almost always referred to by its original…

Gloucester Cathedral
"Lady Chapel of Gloucester Cathedral, England, looking toward the nave." -Whitney, 1911

William White
The Most Reverend William White (April 4, 1748 N.S. – July 17, 1836) was the first and fourth…

George Whitefield
George Whitefield (December 16, 1714 – September 30, 1770), was a preacher in the Church of England…

John Winthrop
John Winthrop (12 January 1588 – 26 March 1649) led a group of English Puritans to the New World,…

Van Cortlandt's Sugar House
Van Cortlandt's Sugar House was a famous (or infamous) prison of the Revolution. It stood on the northwest…

Lutheran Church, Philadelphia
The Lutheran Church in Philadelphia that Congress met at to "return thanks to the Almighty God for crowning…

Brigham Young
Brigham Young (June 1, 1801 – August 29, 1877) was an American leader in the Latter Day Saint movement.…

Nicolaus Ludwig Zinzendorf
Nikolaus Ludwig von Zinzendorf und Pottendorf, Imperial Count of Zinzendorf and Pottendorf, (May 26,…

Sedilia
The sedilia in Southwell Minster, England. In church architecture, a sedile is a seat near the altar…
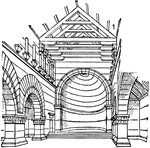
Church at Kalb Louzeh
Christian architecture is Syria diverged from Roman traditions. The abundance of hard stone, the total…
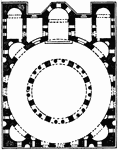
Cathedral at Bosra
Circular and polygonal plans appear in a number of Syrian examples of the early sixth century. Their…
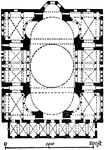
Plan of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia is a former patriarchal basilica, later a mosque, now a museum in Istanbul, Turkey. Famous…

Section of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia is a former patriarchal basilica, later a mosque, now a museum in Istanbul, Turkey. Famous…
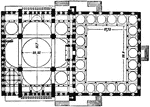
Fatih Mosque (Plan)
The Fatih Mosque (Mosque of Mehmet II, Mosque of Mehmet the Conqueror) was constructed by order of Fatih…
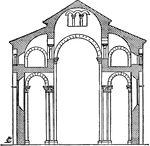
Section of Notre-Dame du Port
"It was in Central France, and mainly along the Loire, that the systematic development of vaulted church…
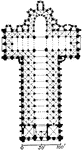
Plan of St. Sernin, Toulouse
"It was in Central France, and mainly along the Loire, that the systematic development of vaulted church…

Bay of Speyer Cathedral
A bay is a module in classical or Gothic architecture, the distance between two supports of a vault…
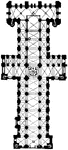
Plan of Durham Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of Christ, Blessed Mary the Virgin and St. Cuthbert of Durham, commonly referred…
One Bay of Transept, Winchester Cathedral
The transept is the area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building in Romanesque…

Front of Iffley Church
Very few examples remain of important Norman façades in their original form, nearly all of these…

Constructive System of a Gothic Church
Constructive system of a Gothic church illustrating the principles of isolated supports and buttressing.

Rose Window, Church of St. Ouen, Rouen
A Rose window (or Catherine window) is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but…

Early Gothic Carving
The facade of a large church or cathedral, often referred to as the West Front, is generally designed…
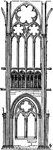
Bay of Abbey of St. Denis
A bay is a module in classical or Gothic architecture, the distance between two supports of a vault…

One Bay of Choir, Lichfield Cathedral
Lichfield Cathedral is situated in Lichfield, Staffordshire, England. It is the only medieval English…

Section of Elisabeth Church, Marburg, Germany
The Elisabeth Church in Marburg was built by the Order of the Teutonic Knights in honor of Elisabeth…

One Bay, Nave of Lucca Cathedral
The Cathedral of St Martin (Italian Duomo) is a church in Lucca, Italy. It was begun in 1063 by Bishop…

Section of the Dome of Duomo, Florence
The Basilica di Santa Maria del Fiore is the cathedral church (Duomo) of Florence, Italy, begun in 1296…




