
The Hartford
USS Hartford, a sloop-of-war, was the first ship of the United States Navy named for Hartford,…

Interior of the Monitor's Turret
USS Monitor was the first ironclad warship commissioned by the United States Navy. Monitor…

John Berrien Montgomery
John Berrien Montgomery (1794 – 25 March 1872) was an officer in the United States Navy who served…

Charles Morris
Commodore Charles Morris, USN (1784 – 1856) was a U.S. naval administrator and officer whose service…

Charles Morris's Monument
Commodore Charles Morris, USN (1784 – 1856) was a U.S. naval administrator and officer whose service…

United States Naval Academy, Annapolis, MD - Officer's Row
The United States Naval Academy is an undergraduate college in Annapolis, Maryland, United States, that…

United States Protected Cruiser USS Olympia
USS Olympia was a protected cruiser in the United States Navy during the Spanish-American War.

United States Frigate of 1812
The original six frigates of the United States Navy were authorized by the Congress with the Naval Act…

The School-Ship USS Sabine
The first USS Sabine was a sailing frigate built by the United States Navy in 1855.

Johnston Blakeley's Medal (Front
Johnston Blakeley (October 1781 - October 1814) was an officer in the United States Navy during the…

Johnston Blakeley's Medal (Back)
Johnston Blakeley (October 1781 - October 1814) was an officer in the United States Navy during the…

Gideon Welles
Gideon Welles (July 1, 1802 – February 11, 1878) was the United States Secretary of the Navy from…
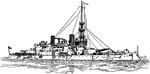
USS Oregon
USS Oregon (BB-3) was a pre-Dreadnought Indiana-class battleship of the United States Navy.

Hiram Paulding
Hiram Paulding (December 11, 1797 – October 20, 1878) was a Rear Admiral in the United States…

Warrington Medal (front)
Lewis Warrington (3 November 1782 – 12 October 1851) was an officer in the United States Navy…

Warrington Medal (back)
Lewis Warrington (3 November 1782 – 12 October 1851) was an officer in the United States Navy…

Oliver Hazard Perry
Commodore Oliver Hazard Perry (August 20, 1785 – August 23, 1819) was an officer in the United…

Political Cartoon about Oliver Hazard Perry
A political cartoon discussing Commodore Oliver Hazard Perry, an officer in the United States Navy.

John Ancrum Winslow
Rear Admiral John Ancrum Winslow (1811 – 29 September 1873) was an officer in the United States…

John Lorimer Worden
John Lorimer Worden (12 March 1818 – 19 October 1897) was a U.S. Admiral who served in the American…

David Porter
David Porter (February 1, 1780 – March 3, 1843) was an officer in the United States Navy in a…

Medal Presented to Edward Preble (Front)
The Congressional Gold Medal presented to Edward Preble, and officer in the U.S. Navy.

Medal Presented to Edward Preble
The Congressional Gold Medal presented to Edward Preble, and officer in the U.S. Navy.

Gunboats Ascending the Yazoo River
The Yazoo River was of major importance during the American Civil War. The first electrically detonated…

Sir James Lucas Yeo
Sir James Lucas Yeo KCB (7 October 1782 – 21 August 1818) was a British Naval commander who served…

Samuel Chester Reid
Samuel Chester Reid (24 August 1783 – 28 January 1861) was an officer in the United States Navy…

Commodore John Rodgers
John Rodgers was an American naval officer who served in the United States Navy from its organization…

Rear Admiral John Rodgers
John Rodgers (8 August 1812 – 5 May 1882) was an admiral in the United States Navy.

Stephen Clegg Rowan
Stephen Clegg Rowan (1808 – 31 March 1890) was an admiral in the United States Navy who served…

William Thomas Sampson
William Thomas Sampson (9 February 1840 – 6 May 1902) was a United States Navy admiral known for…

Winfield Scott Schley
Winfield Scott Schley (9 October 1839 - 2 October 1911) was an admiral of the United States Navy.

Raphael Semmes
Raphael Semmes (September 27, 1809 – August 30, 1877) was an officer in the United States Navy…

Signal Book
A signal book used in the United States Navy which includes a key to interpret messages.

Charles Dwight Sigsbee
Charles Dwight Sigsbee (January 16, 1845 - July 13, 1923) was an admiral in the United States Navy.

Charles Stewart
Charles Stewart (28 July 1778 - 6 November 1869) was an officer in the United States Navy. He is pictured…

Silas Horton Stringham
Silas Horton Stringham (7 November 1798 - 7 February 1876) was an admiral in the United States Navy.

Impressment of American Sailors
The English Royal Navy would impress American sailors, kidnapping them to force them to serve in the…

Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys, FRS (23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English naval administrator and Member…

David Glasgow Farragut
David Glasgow Farragut (July 5, 1801 – August 14, 1870) was a flag officer of the United States…

Norfolk Navy Yard Burning
The Norfolk Naval Yard, also known as the Norfolk Naval Shipyard became an integral shipyard during…

Admiral Andrew Hull Foote
Andrew Hull Foote (1806 - 1863) was an admiral in the United States Navy who served during the Civil…

USS Carondelet
The USS Carondelet was a City class ironclad gunboat constructed for the Union Navy by James…

Gunboats at the Battle of Baton Rouge
Gunboats at the Battle of Baton Rouge, also known as Magnolia Cemetery, was a ground and naval battle…

Destruction of the Arkansas
Destruction of the Arkansas during the Battle of Baton Rouge naval battle.

Retrenchment of U.S. Armed Forces
Uncle Sam criticizes Congress proposal to reduce the Army and Navy.

Monroe's Barge
"In June of 1817 President Monroe took a very extensive journey through the States, visiting all the…
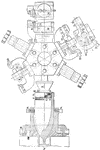
Navy Ordnance Shells
A diagram illustrating the by using a fixed revolver head while spinning the lathe to create the cone…
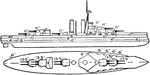
Iron Duke Class British Battleship
A 1912 British navy battleship Iron Duke class. Battleships in this class is operated by steam and have…
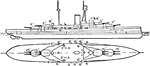
British Navy Queen Elizabeth Class Battleship
The Queen Elizabeth class of 1912 powered by steam. The battle ship have two chimney stacks to burn…
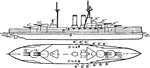
British Navy Royal Sovereign Class Battleship
The British Navy's Royal Sovereign class battleship powered by coal. The Royal Sovereign class was designed…
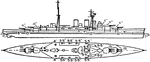
British Navy Renown Battle Cruiser
The British Royal Navy's Renown battle cruiser design launched in 1916. The cruiser is a modified design…
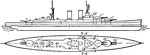
British Navy Hood Battle Cruiser
The Royal Navy's Hood class battle cruiser launched on 1918. The cruiser was used as an anti—torpedo…
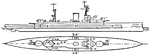
British Navy H.M.S. Courageous Large Light Cruiser
A British Royal Navy light large cruiser, H.M.S. Courage, built in early 1915. The cruiser had light…
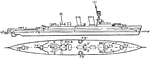
British Royal Navy Raleigh Class Heavy Cruiser
The British Royal Navy's Raleigh Class heavy cruiser. The cruiser went at a speed of 31 knots (36 mph),…
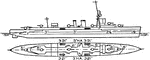
British Royal Navy D Class Torpedo Boat Destroyer
British Royal Navy's D class Torpedo Boat Destroyers (TBDs) launched in 1918. The ship had 12 guns,…
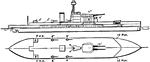
British Royal Navy H.M.S. Erebus Battleship
British Royal Navy battleship, H.M.S. Erebus. The ship was completed in 1870, at Napier shipyard as…
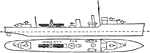
British Royal Navy Destroyers and Flotilla Leaders Battleship
"These vessels (destroyers and Flotilla leaders) gradually increased in size and power, and war requirements…
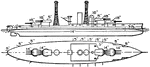
United States Navy Arizona Battleship
An illustration showing USS Arizona. USS Arizona was a Pennsylvania class battleship, built by U.S.…
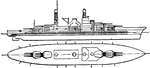
Massachusetts Battleship United States Navy
USS Massachusetts commissioned by United States Navy in 1942. The ship was used during the World War…
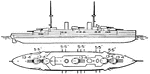
Bretagne Class Battleship French Navy
The Bretagne class battleship built by the French navy during 1913. The ship has a top speed 20 knots…