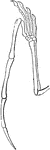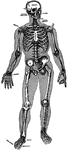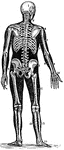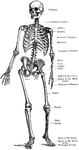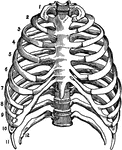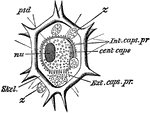
L. Annularis
"Liteocircus annularis. cent. caps, central capsule; ext. caps. pr, extra-capsular protoplasm; int.…
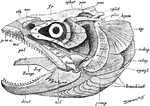
Fish Skull
"Salmo fario, the entire skull, from the left side. art, articular; branchiost, branchiostegal rays;…
Crocodile Skeleton
"Skeleton of crocodile. C, causal region; D, thoracic region of spinal column; F, fibula; Fe, femur;…
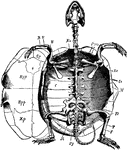
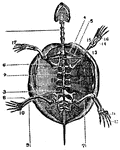
Marsh Turtle Skeleton
"Cistudo lutaria. Skeleton seen from below; the plastron has been removed and is represented on one…
Green Turtle Skeleton
"Chelone midas. Transverse section of skeleton. C, costal plate; C', centrum; M, marginal plate; P,…
Freshwater Hydra
A freshwater hydra, magnified. Example of an animal with no skeleton. There are animals without a skeleton…

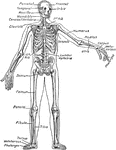
Diagram of the Body Plan
Plan of the body in cross-section. The systems in the body are arranged in a certain way which is the…
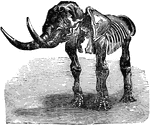
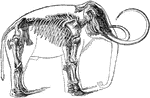
Skeleton of a Cow
A skeleton of a cow shown to illustrate the internal skeleton which all vertebrates share. Labels: 1,…
Skeleton of a Tortoise
A skeleton of a tortoise The ribs of which are expanded, forming the dorsal part of its shell. Labels:…

Skeleton of a Haddock
The skeleton of a haddock. In some species such as the haddock, there is a modified form of the coracoid…
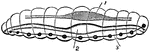
Diagram of an Annulosa
A diagram of an annulosa showing its external skeleton made up of segments or rings arranged along a…
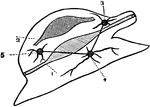
Diagram of a Mollusca
A diagram of a mollusca. Mollusca are soft-bodied animals that are usually protected by an external…
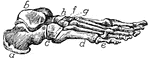
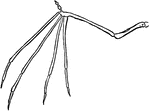
Foot Bones
"The foot. a, calcaneum; b, astragalus; c, cuboid; d, metatarsal, of which there are five; e, phalanges,…
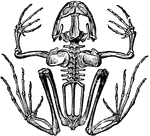
Skeleton of a Frog
"The skull in reptiles is flat, and the cerebral cavity is not filled with brains. There are no ribs."
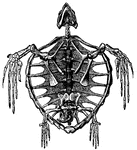
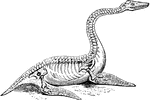
Skeleton of a Turtle
"The Tortoise will continue to live on for six months after it is deprived of its brain."

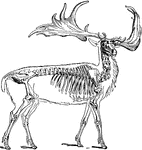
Skeleton of the Swan
"The external air penetrates into every part of their body by the respiratory tubes, which ramify the…

The Knight and the Lady
"The Knight and the Lady. By Albrecht Dürer. From the engraving on copper." -Heath, 1901

Dance of Death, The Astrologer
The Astrologer, from Hans Holbein's series of engravings, Dance of Death.

Porpita Pacifica
"The Porpitae consist of colonies of floating animals furnished with a cartilaginous, horizontal…
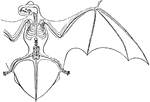
Skeleton and Wing Membranes of the Noctule Bat
The bat genus Nyctalus (Noctule bats) are Evening bats. They are distributed in the temperate and subtropical…
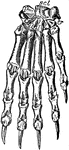
Bear Foot
"Palmar aspect of left fore foot of a black bear (Ursus americanus). scl, scapholunar; c, cuneiform;…
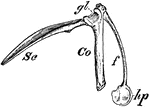
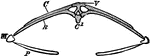
Bird Scapula
"Right shoulder-girdle or scapular arch of fowl, showing hp, the hypoclidium; f, furculum; Co, coracoid;…
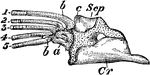
Pike Scapulocoracoid
"Pectoral arch and fore limb of the pike (Esox lucius), an osseous fish, showing scapulocoracoid, composed…

Precious Coral
An illustration of part of a stock of precious coral (red coral). Precious coral or red coral is the…
Gill Arch and Plates
Section through the gill arch and plates of a bony fish. Labels: b, gill plates with capillaries; c,…
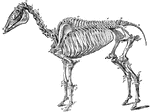
Skeleton of a Horse
The skeleton of a horse. Axial Skeleton. The Skull. Cranial Bones: a, occipital, 1; b, wormian, 1; c,…
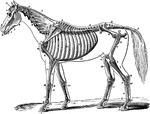
Skeleton of a Horse
The skeleton of a horse. Showing its relation to the contour of the animal, viewed laterally. Labels:…
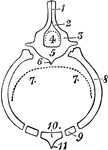
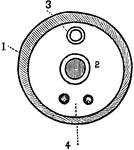
Diagram of Mammilian Thorax
Diagrammatic transverse section from the skeleton of a mammalian thorax, showing the chief features…
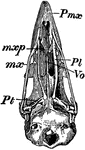
Bird Skull
"Schizognathous skull of common fowl. pmx, premaxilla; mxp, maxillopalatine; mx, maxilla; pl, palatine;…
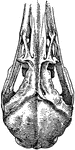
Curlew Skull
"Schizorhinal skull of curlew (top view), showing the long cleft, a, between upper and lower forks of…
Horse Leg
External view of bones of right carpus, metacarpus, and digit of a horse. 1, distal end of radius; 2,…
Horse Leg
External view of bones of left tarsus, metatarsus, and digit of a horse. Labels: 1, distal end of tibia;…
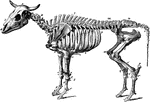
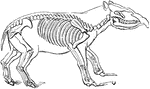
Ox Skeleton
The skeleton of an ox. Axial Skeleton. The skull. Cranial Bones- occipital, 1: b, parietal, 2; a, frontal,…
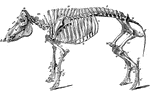
Skeleton of a Hog
Skeleton of the hog. Axial skeleton. The skull. Cranial bones- a, occipital, 1; b, parietal, 2; d, frontal,…
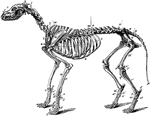
Skeleton of a Dog
The skeleton of the dog. Axial skeleton. The skull. Cranial bones- a, occipital, 1; b, parietal, 2;…