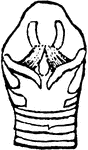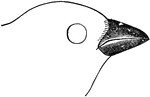
The Bill of a Purple Finch
"Carpodacus. Purple Bullfinch. Bill smaller and less turgid than in Pinicol or Pyrrhula, more regularly…
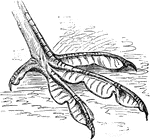
Coot Foot
"Fig. 53 shows the lobate foot of a coot. In the lobate foot, a paddle results not from connecting webs,…
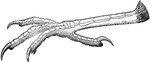
Grackle Foot
"Quiscalus. Grackle. The feet are large and strong, and the birds spend much of their time on the ground,…
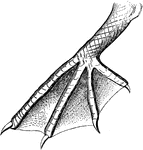
Pelican Foot
"Fig. 52 shows the totipalmate foot of a pelican. The totipalmate is a special case of palmation, in…

Phalarope Foot
"Fig. 53 bis - shows the lobate foot of a phalarope. In the lobate foot, a paddle results not from connecting…

Fin-Footed Coot Foot
"In ornithology, pinnatiped; having pinnate feet, the toes being separately furnished with flaps, as…
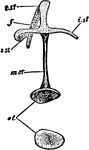
The Ear Bone of Fowl
"Mature stapes of fowl, about x4; after Parker. st, its foot, fitting fenestra ovalis; mst, main shaft,…
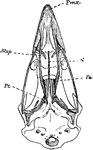
Common Fowl Skull
"Schizognathous skull of common fowl, nat. size, from nature, by Dr. R.W. Shufeldt, U.S.A. Letters as…
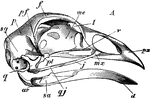
Skull of Common Fowl
"Typical Skull of Common Fowl (Galliformes). A, side view: sa, surangular bone of mandible; ar, articular…
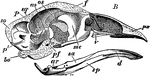
Skull of Common Fowl
"Typical Skull of Common Fowl (Galliformes). B, vertical longitudinal section: sa, surangular bone of…
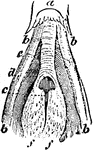
The Glottis of a Rook
"Glottis, or opening of trachea in the mouth; a, base of tongue; b, b, horns of hyoid bone; c, rima…
Goose Hyoid
"Fig 72 - Hyoid bones of a goose, nat. size; Dr. R.W. Shufeldt, U.S.A. a, cartilaginous end-piece of…
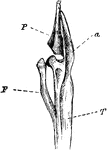
Leg Bones of a Grebe
"F. Fibula; T, tibia, with a, its cnemial process, and P, large patella, of a grebe." Elliot Coues,…

Blue Grosbeak Bill
"Guiraca. Blue Grosbeak. Bill Commissure strongly angulated far beyond base, with deep under mandible…

Song Grosbeak Bill
"Zamelodia. Song Grosbeak. Bill extremely heavy, with the lower mandible as deep as the upper or deeper,…
The Pelvis of a Young Grouse
"Pelvis of a young grouse, showing three distinct bones. Il,P, ilium, ischium, pubis. In front of former…
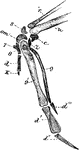
The Wing Bones of a Young Grouse
"Fig. 29., from a young grouse (Centrocercus urophasianus, six months old), is designed to show the…
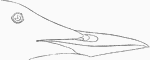
Californian Guillemot Bill
"Bill averaging somewhat longer, about 1.90; culmen, commissure, and gonys nearly straight; upper mandible…
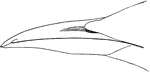
Common Guillemot Bill
"Bill black; bill along culmen 1.75; gape 2.50; gonys 1.15; depth at base .55; width .30." Elliot Coues,…
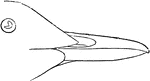
Pigeon Guillemot Bill
"Uria columba. Pigeon Guillemot. Bill stouter than that of grylle, and more obtuse." Elliot Coues, 1884
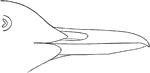
Sooty Guillemot Bill
"Bill larger than Pigeon Guillemot, 1.5-1.70 along culmen, along gape 2.20, from feathers on side of…
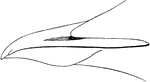
Thick-billed Guillemot Bill
"Lomvia arra. Thick-billed Guillemot. Arrie. Bill short, stout, wide, deep; culmen curved throughout;…
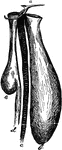
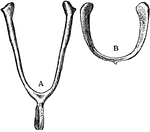
Bustard Gular Pouch
"Gular pouch of bustard; a, tongue; b, the pouch, opening under a, hanging in front of c, the trachea,…
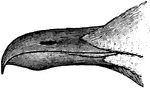
Gull Bill
The bill of the gull (Laridae) is epignathous: "hook-billed; having the end of the upper mandible decurved…
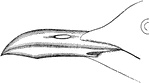
Laughing Gull Bill
"Chroicocephalus atricilla. Laughing Gull. Black-headed Gull. Bill longer than middle toe and claw,…

Harrier Ear Parts
"Circinae. Harriers. Face surrounded with an incomplete ruff (as in most owls); orifice of ear about…
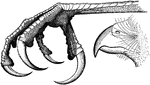
The Raptorial Foot of a Hawk
"Fig. 46. - Raptorial foot of a hawk, Accipiter cooperi. The raptorial is another modification of the…
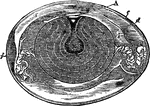
Hen's Egg
" Fig 110 - Hens egg, nat. size, in section; from Owen, after A. Thompson. A, cicatricle or "tread,"…
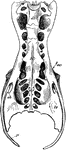
The Pelvis of a Heron
"Pelvis of a heron (ardea herodias), nat. size, viewed from below; from nature by Dr. R.W. Shufeldt,…

Restoration of Hesperornis regalis
"Hesperornis regalis, (a fossilized restoration) which stood about three feet high, had blunt teeth…
The Restoration of the Hesperornis Regalis
"Hesperornis regalis, (a fossilized restoration) which stood about three feet high, had blunt teeth…
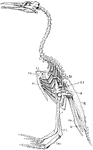
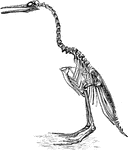
Hesperornis Skeleton
"Hesperornis. ST., Sternum; CO., coracoid; CL., clavicle; H., rudimentary humerus; SC., scapula; P.,…
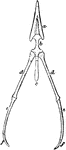
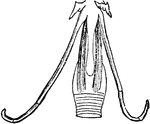
The Hyoid-bone of a Rook
"Hyoid bone; a, glosso-hyal, tipped with cartilage, its posterior horn being certo-hyals proper; b,…
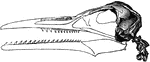
Skeleton Head of a Ichthyornis
"Ichthyornis victor and I. dispar, ...were small forms of about the size of a Partridge, with the habits…

Restoration of Ichthyornis
"Ichthyornis, though the wings are well developed, with fused metacarpals, and the sternum is keeled,…
A Feather from the Tail of a Kingbird
"Fig. 23 - A feather from the tail of a kingbird, Tyrannus carolinensis, almost entirely pennaceous;…
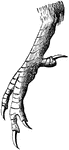
The foot of a Kingfisher
"Fig. 44- Syndactyle foot of a kingfisher. Thus a kingfisher shows what is called a syndactyle or syngnesious…
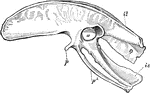
Diagram of the Pelvis of a Kiwi
"Pelvis of Apteryx austrlis. Lateral view. a, Acetabulum; il, ilium; is, ischium; p, pectineal process…
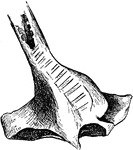
The Bony Labyrinth of a Sea Duck
"Bony labyrinth at the bottom of the trachea of the male Clangula islandica, seen from behind." Elliot…
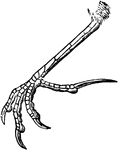
Lark Foot
"Scutelliplantar foot of horned lark: the tarsus scutellate before and behind, and the toes all scutellate…
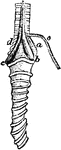
The Laryngeal Muscles of a Rook
"a, b, c, d, inferior laryngeal or syringeal muscles, not well made out in this figure; But typical…
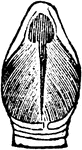
The Larynx Muscles of a Rook
"Muscles of the larynx. thyro-arytenoids, or openers of the glottis" Elliot Coues, 1884
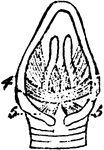
The Larynx Muscles of a Rook
"Muscles of the larynx. Thyro-cricoids, posterior thyro-cricoids." Elliot Coues, 1884

The Larynx of a Rook
"Larynx viewed from before (below); a, thyroid bone or cartilage." Elliot Coues, 1884
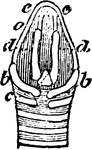
The Larynx of a Rook
"Larynx viewed from behind (above); a, thyroid bone; b, b, its appendages; c, cricoid; d, d, arytenoids;…
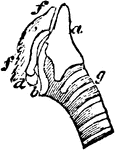
The Larynx of a Rook
"Larynx viewed from the right side; a, thyroid; b, appendage; c, cricoid; d, arytenoid; f, f, cartilage…
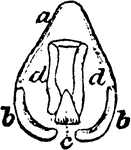
The Larynx of a Rook
"Larynx viewed from behind; a, thyroid; b, b, its appendages; c, cricoid; d, d, arytenoid." Elliot Coues,…
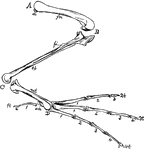
Bones of a Bird's Hind Limb
"Fig 34 - Bones of a bird's hind limb: from a duck, Clangula islandica. A, hip: B, knee: C, heel or…

Archaeopteryx Lithographica
"Archaeornithes is at present represented by but one member, the first undoubted fossil Bird, made known…

Archaeopteryx Lithographica
"Oldest known ornithological treatise, illustrating also the art of lithography in the Jurassic period,…
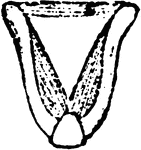
Magpie Foot
"Diagram of plantar aspect of schizopelmous foot of a magpie (Pica caudata), showing the deep plantar…
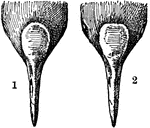
Moorhen Frontal Shields
"Frontal Shield of (1) European Gallinule (Gallinula chloropus), (2) American Gallinule (Gallinula galeata)."…
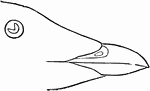
Black-throated Murrelet
"Synthliborhamphus antiquus. Nipper-nosed Murrelet. Bill somewhat as in Brachyrhamphus, but stouter…
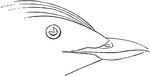
Japanese Murrelet Bill
"Synthliborhamphus umizusume. Japanese Murrelet. Temminck's Auk. Bill more elongate and acute than in…