Clipart tagged: ‘oblique’
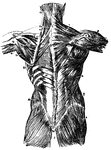
Back Muscles
Muscles of the back. 1, trapezius; 2, its origin; 3, spine of scapula; 4, latissimus dorsi; 5, delltoid;…
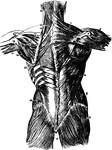
Muscles of the Back
Second layer of muscles of the back. Labels: 1, trapezius; 2, a portion of the ten dinous ellipse formed…
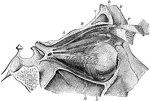
Muscles of the Eye
The muscles of the right eye. Labels: A, superior straight; B, superior oblique passing through a pulley,…
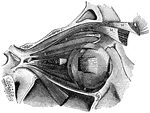
Muscles of the eyeball
"A, attachment of tendon connected with the four recti muscles; B, external rectus,…
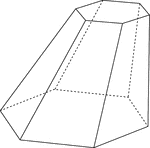
Frustum Of A Skewed Hexagonal Pyramid
Illustration of a skewed hexagonal pyramid that has been cut by a plane parallel to the base. The top…
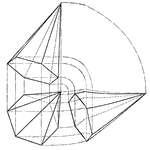
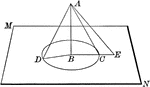
Projection Of Hexagonal Pyramid
Illustration of the projection of a hexagonal pyramid that is obliquely inclined.

Inclined Plane
"An inclined plane is a smooth, hard, inflexible surface, inclined so as to make an oblique angle with…
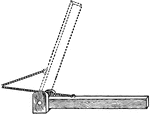
Oblique Pull
"It is worthy of note that, owing to the oblique direction in which the muscles are commonly inserted…
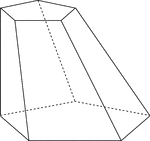
Frustum Of A Skewed Pentagonal Pyramid
Illustration of a skewed pentagonal pyramid that has been cut by a plane parallel to the base. The top…
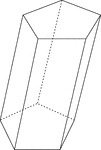
Skewed Pentagonal Prism
Illustration of a skewed pentagonal prism. The prism is non-right. The hidden edges are shown.
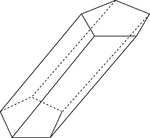
Skewed Pentagonal Prism
Illustration of a skewed pentagonal prism. The prism is non-right. The hidden edges are shown.
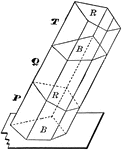
Oblique Prism Truncated Into 3 Sections
Illustration of an oblique prism constructed by the combination of three truncated prisms.
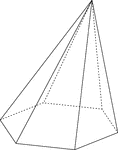
Skewed Hexagonal Pyramid
Illustration of a non-right, or skewed, hexagonal pyramid with hidden edges shown. The base is a hexagon…

Skewed Rectangular Pyramid
Illustration of a non-right, or skewed, rectangular pyramid with hidden edges shown. The base is a rectangle…
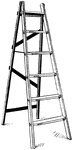
Open Stepladder
Illustration of a stepladder that is opened to form an isosceles triangle with the ground.

Open Stepladder
Illustration of a stepladder that is opened to form an isosceles triangle with the ground.
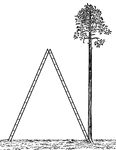
Skyscraper Giant Stepladder
Illustration of a giant stepladder, sometimes called a skyscraper stepladder, that is opened next to…
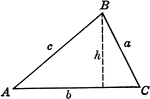
Triangle ABC With Height h
Triangle ABC with sides a,b,c labeled and angles A,B,C labeled and h labeled as height.
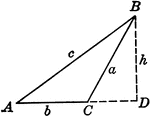
Obtuse Triangle ABC With Height h
Triangle ABC with sides a,b,c labeled and angles A,B,C labeled and h labeled as height.
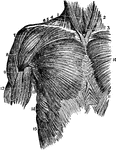
Muscles of the Upper Trunk
Superior muscles of the upper front of the trunk. Labels: 1, sterno-hyoid; 2, sterno-cleido-mastoid;…