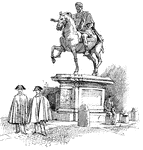
Gate at Herculaneum
The gate at Herculaneum. Herculaneum was an ancient Roman town famous for being preserved along with…
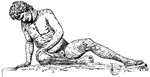
The Dying Gaul
A Roman copy of an ancient Greek sculpture. The copy is made of marble, while the lost original sculpture…

Gladiators
This illustration shows various types of gladiators, each type with with his specific weapons attributed…

Pompey the Great
Also known as Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. He was a military and political leader of the late Roman Republic.
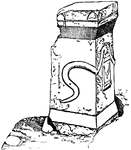
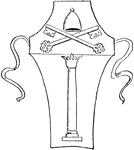
Greek Altar
"Round, triangular, or square in plan, often elaborately adorned with sculpture, and bearing inscriptions."-Whitney,…

Roman Griffin
The Roman Griffin has the body of a Lion and the head and wings of an Eagle. The Griffin is usually…
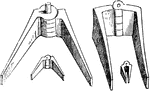
Roman hinges
"The Greeks and Romans used hinges exactly like those now in common use. The following cut exhibits…

Hollow Square
Military formation of the Romans, also agmen quadratum. Square formation with no troops in the middle.
!["[Caesar] mustered the soldiers in the Campius Martius, and requested a statement of their grievances. Their demands appeared to have a reference to a payment of their dues, the bestowal of promised presents, and a release from further duty. Caesar well knew that the best way to humiliate an insurrection is to grant what it clamors for. He accordingly made an address to his old legion, being careful to begin with "Citizens," instead of "Soldiers." This was gall and wormwood. To be addressed as citizens by their beloved commander! "I discharge you." said he. "You have had enough of fatigue and wounds. I release you from your oath. As to your presents, you shall be paid to the last sesterce." The old veterans could stand no more. They burst into tears, and began to beg for forgiveness. With a certain prudent hesitation, Caesar received them back to favor; but he took care that the leaders who had fomented the mutiny should be executed."—Ridpath, 1885](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/78900/78945/78945_citizens_01_mth.gif)
Citizens! I Discharge You.
"[Caesar] mustered the soldiers in the Campius Martius, and requested a statement of their grievances.…
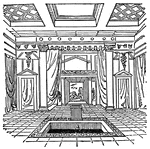
Impluvium
Part of ancient Roman architecture, a basin in the atrium or entrance hall of a building, to receive…

Ivory Carving
"Leaf of a diptych, Roman, probably about 4th century, South Kensington Museum collection." —…

Flavius Josephus
"Flavius Josephus was a strange amalgamation of Jew, Greek, and Roman, admittedly not what he should…

Julian
"Thus the prince, both when present and when coming, was alike victorius: and these things he achieved…

Death of Julian the Apostate
A depiction of Julian the Apostate, a noted philosopher and Roman Emperor, and his death.

Bust of Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman military and political leader. He played a critical role in the transformation…

Temple of Jupiter
"The door in front of a temple, as it reeached nearly to the ceiling allowed the worshippers to view…

Cloister of the Lateran
"The Benedictine system enjoined three virtues as essential; solitude, humility, and obedience." —…

Cabbage Lettuce
Cabbage Lettuce is distinguished by its broad leaves and low spreading habit. It is an annual plant,…

A Roman Litter
"The litter consists of an ordinary couch with four posts and a pair of posts. Curtains fastened to…

Man and Woman in Roman Clothing
An illustration of a man and woman standing in typical Roman clothing. Clothing in ancient Rome generally…

Marcus Aurelius and German Captives
"Marcus Aurelius receiving the submission of German captives. (From a Bas-relief in the Capitoline Museum,…

Bust of Marius
Gaius Marius was a Roman general and politician elected consul an unprecedented seven times during his…

Bust of Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius, known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and General. He was an important…

Minerva
"The name of a Roman goddess, identified by the later Graecising Romans with the Greek Athene, whom…

A Monk with a Pointed Hood and Crosses on His Habit
Illustration of a monk, displaying an open book. His hood is pointed and appears to be unattached from…

Roman Egg-and-Dart Moulding
The Roman egg-and-dart moulding is an egg pattern with darts in between.

Nerva
"Nerva, the successor of Domitian, and one of the most virtuous of the Roman emperors. He was born in…