This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 140 illustrations of the peripheral nervous system, which includes the nervous structures not included in the central nervous system such as peripheral nerves that extend from the spine through the torso and limbs.
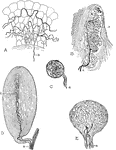
Peripheral Nerve Beginnings
Axons terminate peripherally in various ways and may be most conveniently studied in the efferent and…
Nerve Cells
"Nerve tissue is really made up of a great number of distinctive units called nerve cells.…
The Relation of Nerve Cells to Muscle
Diagram to show the relationship of nerve cell (NC) to Muscle (M) through its nerve fiber.
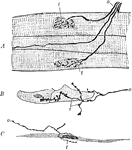
Motor Nerve Endings
Diagram of motor nerve endings in A. striated muscle. B, cardiac muscle. C, nonstriated muscle. Labels:…
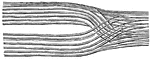
Portion of a medullated nerve fiber
"The axis cylinder is in the center. On either side is seen the medullary sheath, represented by dark…
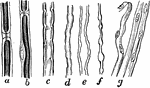
Nerve Fibers
Nerve fibers. Labels: a, nerve-fiber, showing complete interruption of the white substance; b, another…
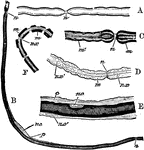
Nerve Fibers
To illustrate the structure of nerve fibers. Labels: A, nerve fiber examined fresh; n, node. B, nerve…
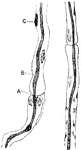
Nerve Fibers of the Sciatic Nerve
Two nerve fibers of the sciatic nerve. Labels: A. Node of Ranvier. B. Axis cylinder. C. Sheath of Schwann…

Primitive Nerve Fibers
Primitive nerve fibers. A, A perfectly fresh tubule with a single dark outline. B. A tubule or fiber…
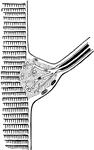
Termination of a Nerve in a Fiber of Cross-Striped Muscle
Motorial end-plate, the termination of a nerve in a fiber of cross-striped muscle.
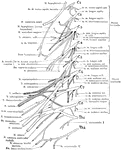
Cervical and Brachial Nerve Plexuses
The right cervical and brachial plexuses. The shaded portions are the derivatives of the superior rami.

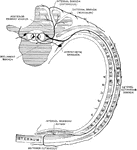
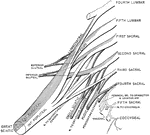
Lumbar and Sacral Nerve Plexuses
Right lumbar and sacral plexuses, schematic, viewed from in front The darkly shaded trunks are derivatives…
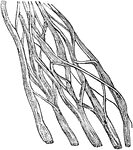
Nerve Portion
This cut represents a portion of nerve, showing the filaments of which it is composed, and one of them…
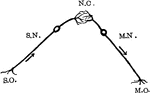
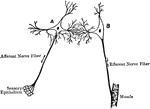
Nerve Reflex Arc
Reflex arc schematic. Labels: S.O., sensory organ; S.N., sensory neuron; N.C., nerve center; M.N., motor…
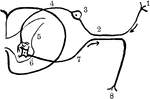
Nerve Reflex Arc
Reflex arc, as it is approximately in man. Labels: 1, nerve terminal, or sensory epithelium; 2, dendrite…
Nerve trunks
"The Main Nerve Trunks of the Right Forearm, showing the Accompanying Radial and Ulnar Arteries. (Anterior…
Nerve Tubules
A diagram of nerve tubules A nerve tube consists of a white portion which is fatty, and which protects…
Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Posterior Tibial) on the Back of the Leg, with its Accompanying Artery of the Same Name."…

Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Crural) and its branches on the Front of the Thigh. The femoral artery with its cut…
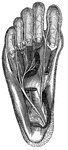
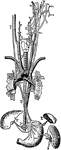
Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Plantar) and its Branches which supply the Bottom of the Feet. Note the cut tendons…
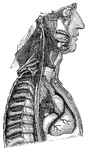
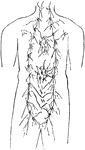
Sympathetic nerve
"The Cervical and Thoracic Portions of the Sympathetic Nerve and their Main Branches. In the center…
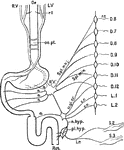
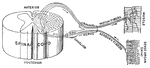
Nerves of the Alimentary Canal
Diagrammatic representation of the nerves of the alimentary canal. Oe to Rct, the various parts of the…
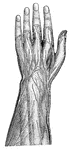
Superficial Nerves of the Forearm and Hand
"Superficial, or Cutaneous, Nerves on the Back of the Left Forearm and Hand." — Blaisedell, 1904
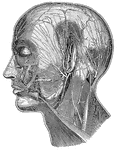
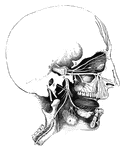
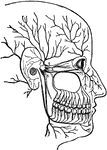
Superficial Nerves of the Head
"Showing some of the superficial nerves on the left side of the neck and the head. A few superficial…
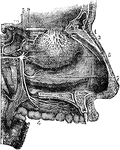
Nerves of the Nasal Fossae
Nerves of the outer walls of the nasal fossae. 1, network of the branches of the olfactory nerve, descending…
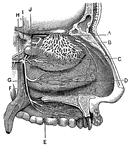
Nerves of the Nostril
"A, branches of the nerves of smell; B, nerves of touch to the nostrils; E, F,…
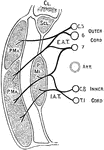
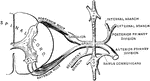
Nerves of the Pectoral Muscles
Diagram of the origin and distribution of the nerves to the pectoral muscles. E.A.T., external thoracic…
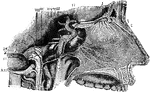
Nerves of the Septum Nasi
Nerves of the septum nasi, seen from the right side. I, the olfactory bulb; 1, the olfactory nerves…
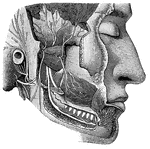
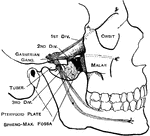
Cranial Nerves
"Dental Branch of One of the Divisions of the Fifth Pair of Cranial Nerves, supplying the Lower Teeth.…
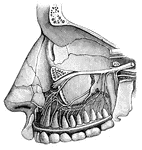
Cranial Nerves
"Dental Branches of One of the Divisions of the Fifth Pair of Cranial Nerves, supply the Upper Teeth."…
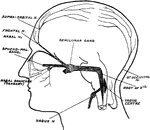
Facial Nerves
Diagram to show the proximity of the sensory nuclei of the fifth and tenth cranial and first and second…
Nervous Fibers
Nervous fibers, deprived of their neurilema and unraveled, showing the smaller threads, or filaments,…

Nervous Fibers
Ultimate fibers of nerve highly magnified; showing the strings of globules of which they consist.
Nervous System
Element of Nervous System. a: Sensory fiber; b: Motor fiber; c: Center; f: End of sensory fiber; m:…

Nervous System
"Diagram illustrating the General Arrangement of the Nervous System. (posterior view.)" — Blaisedell,…

Sympathetic Nervous System
"Part of the sympathetic nervous system seen from in front, n, one of the two chief cords, t, i, and…
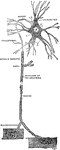
Scheme of the Central Motor Neuron
Scheme of the central motor neuron. The motor cell body, together with all its protoplasmic processes,…
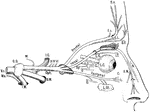
Ophthalmic Nerve
Scheme of the distribution of the ophthalmic nerve. Labels: Vs, trigeminal nerve, afferent root; Mo,…
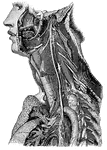
Trunk of the Pneumogastric Nerve
"Showing its distribution by its branches and ganglia to the larynx, pharynx, heart, lungs, and other…
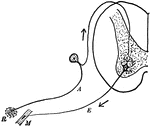
Reflex Arc
"Diagram of the simple reflex arc. R, receptor; A, afferent (sensory) neuron; E, efferent (motor) meuron;…
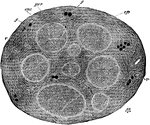
Section of the Internal Saphenous Nerve
Section of the internal saphenous nerve. Stained in osmic acid and subsequently hardened in alcohol.…
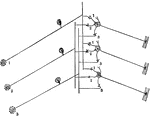
Sensory Neuron
"Diagram to illustrate how a single sensory neuron may communicate with several motor neurons, and a…
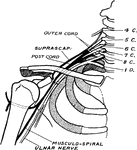
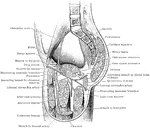
Nerves of the Shoulder
Showing the dorsal preaxial origin of the musculospiral (radial) nerve, and the ventral post-axial origin…
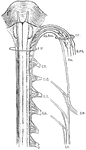
Spinal Accessory Nerve
Scheme of the origin, connection, and distribution of the spinal accessory nerve. Labels: Sp.Acc, spinal…