The Jellyfish ClipArt gallery includes 82 line drawings of the phylum cnidaria, Jellyfish are free-swimming creatures that are also called medusa.
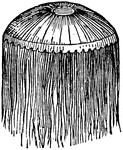
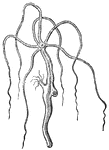
Acaleph
"One of the Acalephae; a name given to a large number of marine animals; and redpresenyted chiefly by…

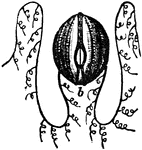
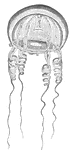
Acalephae
"The under surface, showing the mouth in the center, surrounded by the tentacula, and overial chambers…
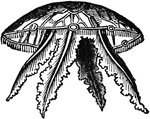
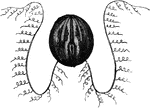
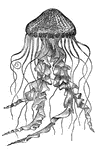
Acalephae
"Side-view, showing the tentacula hanging down in their natural position." — Chambers' Encyclopedia,…
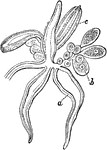
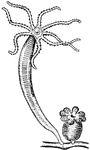
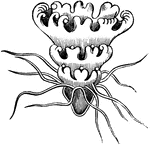
Athorybia Gonoblastidium
"Gonoblastidium of Athorybia rosacea, bearing three hydroclysts, a, a gynophore, b, and two androphores,…
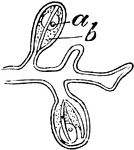
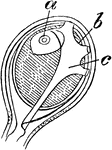
Athorybia Gonophores
"A, female gonophores of Athorybia rosacea on their common stem or gynophore: a, ovum; b, radial canals."…
Athorybia Gonophores
"C, female gonophores: a, genital vesicle; b, vitellus; c, radial canals." -Whitney, 1911
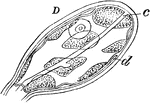
Athorybia Gonophores
"D, female gonophores, enlarged: c, radial canals; d, canal of manubrial cavity." -Whitney, 1911
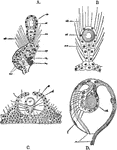
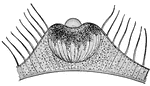
Auditory Organs of the Jellyfish
Auditory and equilibrative organs of jellyfishes. A, of Cunarcha. B, of Pectis. C, of Rhopalonema. D,…
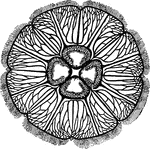
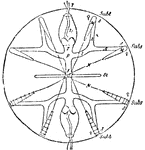
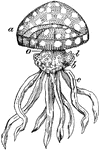
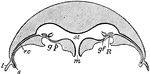
Aurelia
"Surface view of Aurelia. Showing four genital pockets in centre, much branched radial canals, eight…
Aurelia
"Vertical section of Aurelia. m., Mouth; st., stomach; r.c., radial canal; R., reproductive organs;…
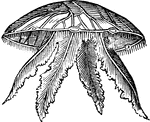
Medusa, aurita
"One of the commonest species, and must have been observed by those who frequent the sea-shore. In the…
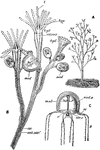
Bougainvillea Ramosa
"Bougainvillea ramosa. A, entire colony, natural size; B, portion of the same magnified; C, immature…
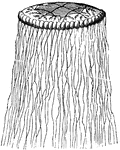
Cuvieria carisochroma
"Which is without a central peduncle, yet has numerous long appendages hanging from its border." —…

Carmarina
"Carmarina (Geryonia) hastata, one of the Trachomedusae. a, nerve-ring; a', radial nerve; b, tentaculocyst;…

Chrysaora
"In the sub-order Rhizostomae the edges of the oral opening use together at an early age and leave several…
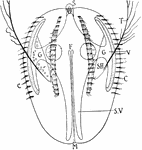
Ctenophore
"Diagram of a Ctenophore. M., Mouth; S., sensory organ; T., tentacle cut short; SH., pouch of tentacle;…
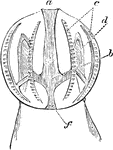
Ctenopore
The phylum Ctenophora , commonly known as comb jellies, is a phylum that includes the sea gooseberry…
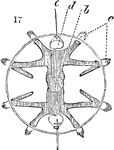
Transverse Section of Ctenopore
The phylum Ctenophora , commonly known as comb jellies, is a phylum that includes the sea gooseberry…

Rhizostoma cuvieri
"The Rhisostoma Cuvieri, a British species, measures two feet, or ever more, in diameter, while…
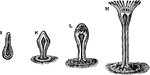
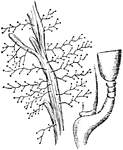
Eudendrium
"Stages in the development of two zoophytes; I-M, fixation of the planula and development of the hydrula."…
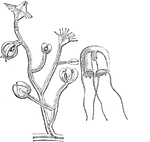
Eudendrium
An illustration of Eudendruim ramonsum. The Idrozoi are a class of the phylum of Cnidarians, and in…

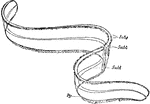
Venus' girdle
"The most singular of the Callianiridae is the Venus' Girdle, Celestum Veneris, which…
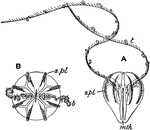
Hormiphora Plumosa
"Hormiphora (Cydippe) plumosa. A, from the side; B, from the aboral pole. mth, mouth; s. pl, swimming…

Hydra
Hydra are in the Jellyfish family, class Hydrozoa. Cross-section of the body showing the two layers…
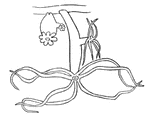
Hydra
If undisturbed, the body and tentacles may occasionally sway gently. If disturbed, a hydra usually shortens…
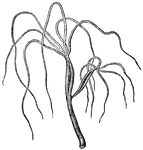
Hydra Viridis
"The Hydra Viridis is another freshwater polyp, common to ponds and still waters Sometimes…
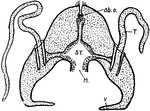
Hydroctena
"Hydroctena. A medusoid with suggestion of Ctenophore structure, but a true medusoid nonetheless. ab.o.…
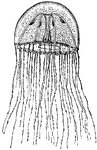
Medusa of a Hydroid
Colonial, plant-like animals closely related to jellyfish, with stinging cells, Any member of the invertebrate…
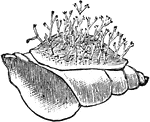
Hydrozoa Encrusting a Small Shell
Hydrozoa (hydrozoans) are a taxonomic class of very small, predatory animals which can be solitary or…
!["Hydrozoon is a name given to the great class of the sub-kingdom Cœlenterata, of which hydra is the type. They exhibit a definite histological structure, their tissues having a cellular organization. These tissues are two, an outer or ectoderm, and an inner or endoderm. In most the prey is seized by tentacles surrounding the mouth and furnished with offensive weapons called thread cells, The hydrozoa are all aquatic, and nearly all marine. Their distribution is world-wide. [Pictured] Hydra fusca, with a young bud at b, and a more advanced bud at c."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15400/15469/hydrozoon_15469_mth.gif)
Hydrozoon
"Hydrozoon is a name given to the great class of the sub-kingdom Cœlenterata, of which hydra is…
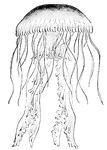
Jellyfish
Jellyfish are saucer-shaped and can be a foot or more in diameter. They are gelatinous and semitransparent.
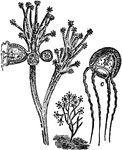
Jellyfish
An illustration of a small jellyfish. Jellyfish are free-swimming members of the phylum Cnidaria. ellyfish…
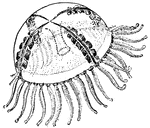
Gonionemus Jellyfish
Gonionemus is a type of hydrozoan related to jellyfish. It uses adhesive discs near the middle of each…
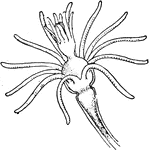
Gonionemus Jellyfish
Gonionemus is a type of hydrozoan related to jellyfish. It uses adhesive discs near the middle of each…
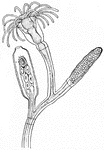
Gonionemus Jellyfish
Gonionemus is a type of hydrozoan related to jellyfish. It uses adhesive discs near the middle of each…

Gonionemus Jellyfish
Gonionemus is a type of hydrozoan related to jellyfish. It uses adhesive discs near the middle of each…
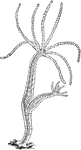
Hydra Jellyfish
Fresh water Hydra, a jellyfish, is a many celled animal. Shown enlarged 25 times, is the entire animal.
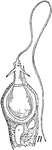
Hydra Jellyfish
Fresh water Hydra, a jellyfish, is a many celled animal. Shown is a Hydra nettle cells.

Hydra Jellyfish
Fresh water Hydra, a jellyfish, is a many celled animal. The organs of defence, nettle cells or lasso…
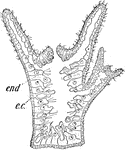
Hydra Jellyfish
Fresh water Hydra, a jellyfish, is a many celled animal. The organs of defence, nettle cells or lasso…
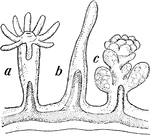
Hydroid Jellyfish
Hydroids, related to the jellyfish, have three basic life-cycle stages: a tiny free-swimming planula…

Lion's Mane Jellyfish
"Scyphistoma stage of Cyanaea capillata, showing two ordinary hydrae tubae, between which are two others,…