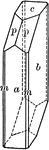This science ClipArt gallery offers 324 illustrations of crystals of numerous minerals. These crystalline minerals are created through natural processes, and so often times there are numerous crystal shapes for any given mineral (polycrystalline materials).
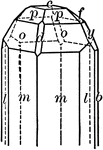
Quartz
"Terminated usually by a combination of a positive and negative rhombohedron, which often are so equally…
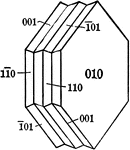
Quartz
"Terminated usually by a combination of a positive and negative rhombohedron, which often are so equally…
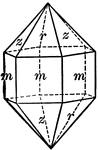
Quartz
"Terminated usually by a combination of a positive and negative rhombohedron, which often are so equally…
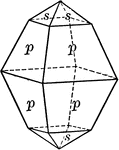
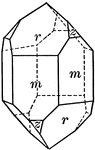
Quartz
This illustration shows Quartz or Silica. Quarts is the most abundant mineral in the Earth's continental…
Left-handed quartz
"The quartz crystals are said to be right or left handed, depending upon whether these faces are to…
Right-handed quartz
"The quartz crystals are said to be right or left handed, depending upon whether these faces are to…
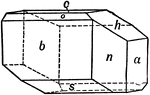
Rhodonite
This figure shows a crystal of Rhodonite (manganese meta-silicate), whose forms are: (c), (b), (a),…
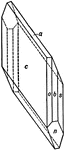
Rhodonite
An alternate combination of manganese meta-silicate (Rhodonite), showing forms: (c), (b), (a), (n),…
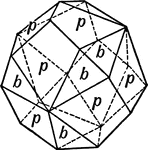
Rhombic Dodecahedron Combined With the Trigonal Tristetrahedron
This form shows a rhombic dodecahedron (d) combined with the trigonal tristetrahedron (q). It sometimes…
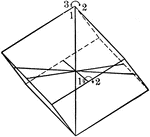
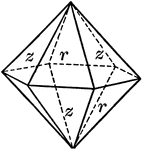
Symmetry of Rhombohedral Class
"The vertical crystallographic axis is one of trigonal symmetry, and the three horizontal crystallographic…
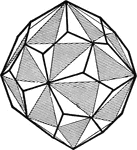
Right-Handed Pentagonal Icositetrahedron
Crystal; If the alternate planes of the hexoctahedron extend until the intersect, a new for will result.…
Rutile Growing Upon Titanic Iron
The tetragonal rutile grows upon the rhombohedral titanic iron, so that its prism of the second order,…
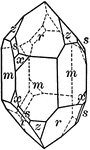
Scapolite
"A crystal of scapolite, upon which the faces of the third-order pyramid are shown." — Ford, 1912
Scapolite
This figure shows a combination of forms sometimes observed on the silicate Scapolite, with the unit…
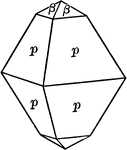
Scheelite
"Tetragonal; tri-pyramidal. Crystals usually simple pyramids of first order. Closely resemble isometric…
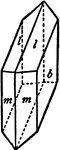
Simple Crystal of Gypsum
"...to be cut in half by this plane (the twinned plane, reference Twinned Crystal of Gypsum) and one…
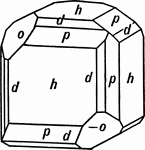
Sodium Chlorate
This is a crystal of Sodium Chlorate, exhibiting the tetrahedron (-o) and the pentagonal dodecahedron…
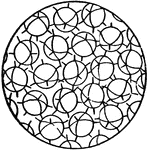
Solid State Showing No Regularity of Molecular Orientation
This figure represents a solid state where there is no regularity of molecular orientation, as in the…

Dogtooth Spar
"...a variety of calcite, crystallizing in scalenohedral forms; so named from a fancied resemblance…
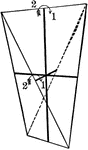
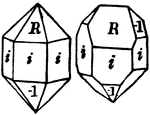
Symmetry of Sphenoidal class
"The Sphenoidal Class corresponds in the Tetragonal system to the Tetrahedral class in the Isometric…
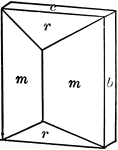
Sphenoidal Crystallization
An example of sphenoidal crystallization is Iron-Copper-Sulfide (FeS_2_Cu), also known as chalcopyrite.
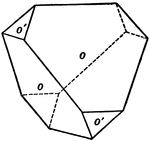
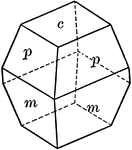
Spinel Contact Twin
This figure shows a contact twin of Spinel, one of the three simplest isometric holohedrons according…
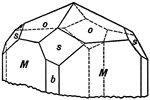
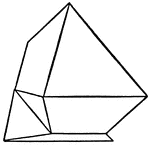
Staurolite
"Orthohombic. Habit prismatic, showing usually a combination of prism with large angle, brachypinacoid,…
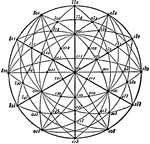
Stereographic Projection of a Holosymmetric Rhombohedral Crystal
"...in this figure the thicker lines are the projections of the three planes of symmetry, and on these…
Stilbite
"Monoclinic. Uniform in cruciform twins. Commonly tabular parallel to clinopinacoid. Crystals usually…
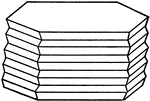
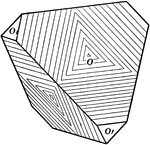
Striation of Crystal Planes
Striation of crystal planes may be produced by repeated polysynthetic twinning. This is well illustrated…
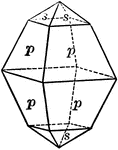
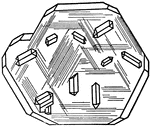
Sulphur
"Resinous luster. Color sulphur-yellow, varying with impurities to yellow shades of green, gray, and…
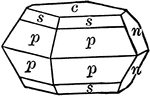
Sulphur
"Resinous luster. Color sulphur-yellow, varying with impurities to yellow shades of green, gray, and…
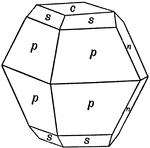
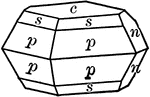
Sulphur
This figure shows an orthorhombic crystal of sulphur, showing the forms: (p), (s), (c), and (n).
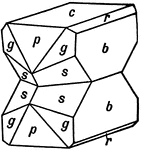
Supplementary Twin
This figure shows a case of a supplementary twin, formed from two hemimorphic crystals, placed symmetrically…
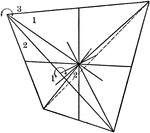
Symmetry of tetrahedral class
"The symmetry of this class is as follows: The three crystallographic axes are axes of binary symmetry;…
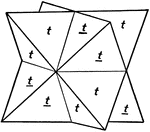
Tetrahedrite
This figure shows two tetrahedrons with parallel axes, and symmetrically placed with reference to the…
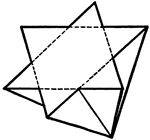
Tetrahedrite Penetration Twin
This figure shows a penetration twin of two tetrahedrons, symmetrical to the octohedral face (tetrahedrite).
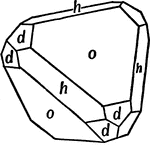
Tetrahedron, Cube, and Dodecahedron in Combination
This form shows a tetrahedron (o), cube (h), and dodecahedron (d) in combination.
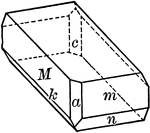
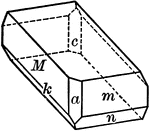
Titanite
"Monoclinic. Crystals varied in habit. Often with prominent basal plane which is steeply inclined and…
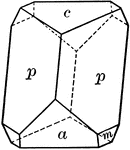
Titanite
"Monoclinic. Crystals varied in habit. Often with prominent basal plane which is steeply inclined and…
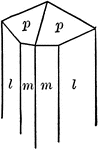
Topaz
"Orthohombic. In prismatic crystals terminated by pyramids, domes, and basal plane." — Ford, 1912
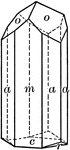
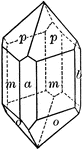
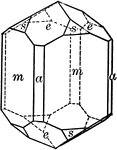
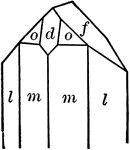
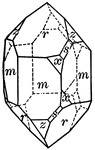
Tourmaline
"Tourmaline crystals show the forms of the Rhombohedral Class but with hemispherical development. They…
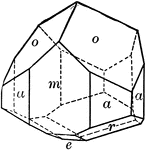
Tourmaline
"Tourmaline crystals show the forms of the Rhombohedral Class but with hemispherical development. They…
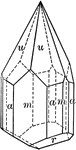
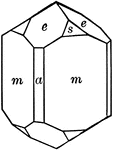
Tourmaline
"Tourmaline crystals show the forms of the Rhombohedral Class but with hemispherical development. They…
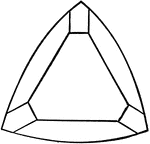
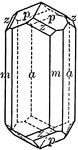
Tourmaline
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral; hemimorphic. Crystals usually prismatic, vertically striated. A triangular…
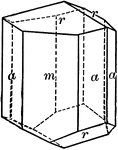
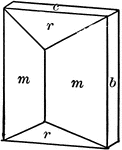
Tourmaline
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral; hemimorphic. Crystals usually prismatic, vertically striated. A triangular…
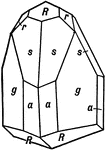
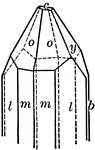
Tourmaline
This crystal of Tourmaline exhibits hemimorphism in the direction of the vertical axis. Its forms are…
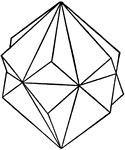
Twin Rhombohedrons
This figure shows two twin rhombohedrons, symmetrical with reference to a prism of the first order,…
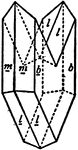
Twinned Crystal of Gypsum
"...the two portions are symmetrical with respect to a plane parallel to the ortho-pinacoid." -The Encyclopedia…