Other Mollusks
The Other Mollusks ClipArt gallery includes 50 illustrations of miscellaneous mollusks. Mollusks are animals that usually have shells, although some no longer have the shell, which is mostly seen in the ones with marine movement.

Ancient Mollusks
Two ancient mollusks from the Carboniferous Age, the Productus Nebrascensis and the Athyris subtilita.
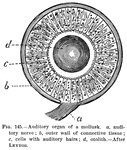
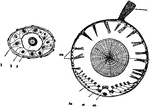
Auditory Organ
auditory organ of a mollusk. a, auditory nerve; b, outer wall of connective tissue; c, cells with auditory…
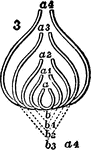
Successively Formed Chambers
Diagram to show the mode in which successively formed chambers may completely embrace their predecessors,…
Chiton chilensis
"The Chiton Chilensis has a smooth border; it is found in crevices of rocks under stones, near…

Chiton
Chiton is a peculiar marine mollusk. It is low and flat, creeping like the limpets. But the shell consists…
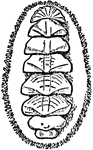
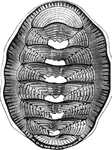
Chiton (Dorsal)
A dorsal view of a chiton, showing the eight shell plates. Chitons are small to large, primitive marine…
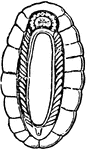
Chiton (Ventral)
A ventral view of a chiton, showing p, foot; o, mouth; kr, oval fringe; and br, the numerous ctenidia.…
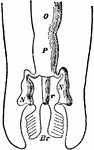
Chiton Excretory and Reproductive Organs
An illustration of a chiton's excretory and reproductive organs. O, Ovary; P, Pericardium; N, Nephridium;…
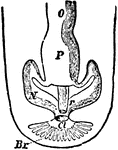
Chiton Excretory and Reproductive Organs
An illustration of a chiton's excretory and reproductive organs. O, Ovary; P, Pericardium; N, Nephridium;…
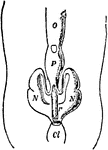
Chiton Excretory and Reproductive Organs
An illustration of a chiton's excretory and reproductive organs. O, Ovary; P, Pericardium; N, Nephridium;…
Chiton Excretory and Reproductive Organs
An illustration of a chiton's excretory and reproductive organs. O, Ovary; P, Pericardium; N, Nephridium;…
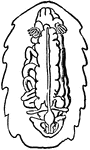
Chiton with Shell Removed
An illustration of the dorsal view of a chiton with the shell removed. Showing b, buccal mass; ov, ovary;…

Chitonidæ
They differ from all other mollusks in having a bilaterally symmetrical covered with a number of seperate…
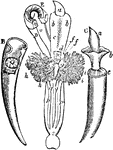
Dentalium
"Dentalium: B, the shell of Dentalium Entalis, broken longitudinally, showing the animal in a contracted…

Fu'sus
Fu'sus is a genus of gastropods, which are allied to the British whelk and American conch, and which…

Sea Hare
The name of a genus of gasteropodous mollusca. These animals are slug-like in appearance, and derive…
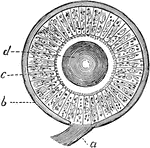
Sense of Hearing
Hearing is the perception of certain vibrations of bodies. These vibrations give rise to sound waves.…
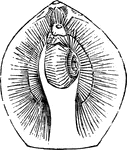
Lamp-shell
"The Lamp-Shell, Terebratula maxillata, has a smooth convex shell, the animal attached by a peduncle."…

Right Valve of a Mactra Stultorum
Mactra stultorum, previously sometimes known as Mactra corallina is a species of edible saltwater clam,…
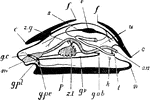
Mollusc Parts
"Ideal mollusc. m., Mouth; g.c., cerebral ganglia; c., edges of mantle skirt; z.g., duct of right lobe…
!["[From left to right:] Cockles, Imperial Volute, Clown Volute, Pholas, Helmet Shell" — Goodrich, 1859](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/13900/13981/mollusca_13981_mth.gif)
Mollusca
"[From left to right:] Cockles, Imperial Volute, Clown Volute, Pholas, Helmet Shell" — Goodrich,…
!["[From left to right:] Snail-shell and Egg, Ostrea and Spondylus, Carinaria, Vitreous Carinaria." — Goodrich, 1859](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/13900/13989/mollusca_13989_mth.gif)
Mollusca
"[From left to right:] Snail-shell and Egg, Ostrea and Spondylus, Carinaria, Vitreous Carinaria." —…
!["[From left to right:] Fusus Longissimus, Pearl Oyster and Coral, Volute, Thorny Woodcock." — Goodrich, 1859](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/13900/13992/mollusca_13992_mth.gif)
Mollusca
"[From left to right:] Fusus Longissimus, Pearl Oyster and Coral, Volute, Thorny Woodcock." —…
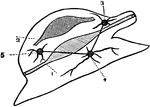
Diagram of a Mollusca
A diagram of a mollusca. Mollusca are soft-bodied animals that are usually protected by an external…
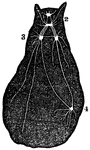
Diagram of a Type of Mollusca
In the Mollusca are found the ganglions and connective arrangement, with both sensitive and motor nerves,…

Goniatites Mollusk
An ancient mollusk from the Paleozoic time, Goniatites Marcellensis from the Hamilton group.
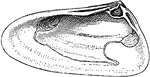
Right Valve of Mollusk
Bivalves are molluscs belonging to the class Bivalvia. They have two-part shells, and typically both…
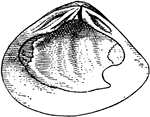
Right Valve of Mollusks
An illustration of the right valve of a mollusk. Bivalves are molluscs belonging to the class Bivalvia.…
!["[From left to right:] Shell from Malabar, Large Mussel, Thorned Murex, Large Helmet Shell." — Goodrich, 1859](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/14000/14018/murcidai_14018_mth.gif)
Murcidae
"[From left to right:] Shell from Malabar, Large Mussel, Thorned Murex, Large Helmet Shell." —…
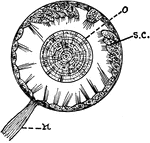
Otocyst
"Otocyst in a mollusk. n, nerve; ;o, otolith; s.c., sensory cells in wall of otocyst." — Galloway
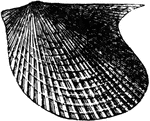
Pterinea Mollusk
A mollusk radiate from the Paleozoic time, Pterinea emacerata from the Niagara group.
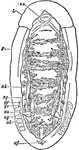
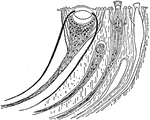
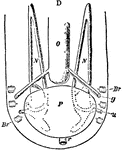
Dissection of the Renal Organs of a Chiton
An illustrative view of the dissection of he renal organs of a chiton. "F, foot; L, Edge of the mantle…

Rhynchotreta Mollusk
A mollusk radiate from the Paleozoic time, Rhynchotreta cuneata from the United States and Great Britain.

Chiton spinosus
"The Chiton spinosus is bordered by long, black, aculeted spines; found in the South Seas;…
Elephant's tooth
"It has an aperture at each end; the animal inhabiting it is of a cylindrical form, and inclosed in…