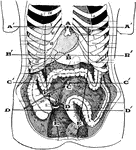
Abdominal Region
Showing the average position of the abdominal viscera with their surface markings. Labels: A, sterno-ensiform…

Patella Granatina (Linnaeus)
"Ruby-eyed Limpet, from the Antilles. If the common Limpet is alarmed, no human force, pulling in a…
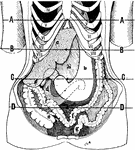
Position of the Viscera in the Condition of Visceroptosis
Showing the position of the viscera in the condition of visceroptosis (Glenard's disease). Labels: A,…
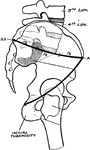
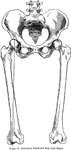
Displacement of the Femur
Diagram showing the line used by Nelaton to test upward displacement of the femur, and another which…
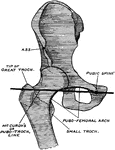
Pubic Spine
Diagram showing that the pubic spine (tubercle) and the tip of the great trochanter are on the same…
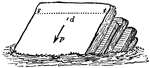
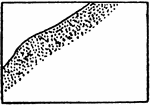
Dip
"Dip, in geology, the name given to the angle of slope of inclined rock strata, as dip in the diagram...The…
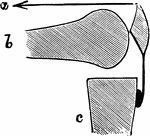
Mechanism of Fracture of the Patella by Muscular Action
Diagram to show mechanism of fracture of the patella by muscular action. a, Line of action of quadriceps…
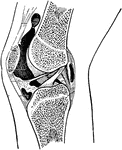
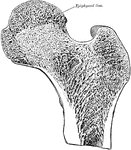
Epiphyseal lines in the Knee Joint
Epiphyseal lines in the neighborhood of the knee joint and their relationship to the synovial membrane.
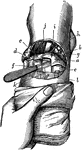
Lisfranc's Amputation at the Tarsometatarsal Joint
Lifrac's operation consists in amputation through the tarsometatarsal line of joints. Labels: a, b,…

Landscape Perspective
"Perspective- Place roofs and tree tops above the horizon line, and the tree trunks and main part of…

Single Stroke Vertical Capitals
In this chart of single stroke letters, the capitals are arranged in "family order," first the straight…
Single Stroke Vertical Lower Case Letters
Words lettered in lower case or "small" letters are easier to read than when made in capital letters.…
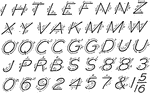
Single Stroke Inclined Capitals
In this chart of single stroke letters, the capitals are arranged in "family order," first the straight…
Single Stroke Inclined Lower Case Letters
Words lettered in lower case or "small" letters are easier to read than when made in capital letters.…
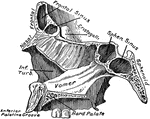
Section of Face Showing Vomer
Sagittal section of face, a little to the left of the middle line, showing the vomer and its relations.
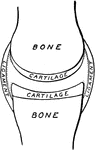
Synovial Membrane
Diagram of articular synovial membranes. The cartilages are represented as drawn apart for the sake…
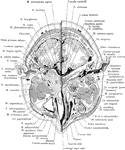
Cross Section of Head Exposing Maxillary Sinus
Section of the head immediately below the orbits, at the level of Reid's base line exposing the maxillary…
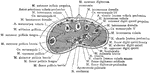
Cross Section on a Line with the Palmar Arch of the Hand
Section on a line with the deep palmar arch of the right hand.
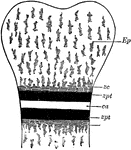
Bone Ossification
Schematic diagram, showing epiphysis and diaphysis and line of ossification. Labels: Ep, epiphysis of…

Gyrinus Distinctus
"A distinct species, which exists in a little lake of mineral waters in France, where visitors amuse…
Microscopic view of a fermented apple
"Portions of the rotting pulp were placed on a microscopic slide, divided into hundredths and thousandths…

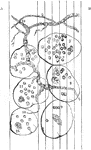
Textularia Variabilis
One group will take the spherical form and produce a shell in the shape of the nautilus. In this case,…
![While not exceptionally high, the Niagara Falls are very wide. More than six million cubic feet (168,000 m³) of water falls over the crest line every minute in high flow,[1] and almost 4 million cubic feet (110,000 m³) on average.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/53700/53784/53784_niagara_fall_mth.gif)
Niagara Falls (American Side), from Goat Island
While not exceptionally high, the Niagara Falls are very wide. More than six million cubic feet (168,000…
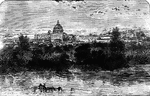
St. Peter's and the Vatican, from the Tiber Banks
It occupies a "unique position" as one of the holiest sites and as "the greatest of all churches of…
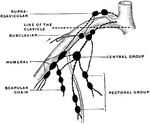
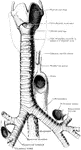
Lymph Node of Upper Extremity
An axillary node is a lymph node of the upper extremity. Shown is the scheme of the axillary nodes.…
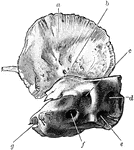
Temporal Bone at Birth
Inner surface of right temporal bone at birth. am squamozygomatic; b, petrosquamosal suture and foramen…
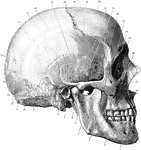
Side of the Skull
Shown is norma lateralis, which refers to the side of the skull. Labels: 1, mental foramen; 2, body…
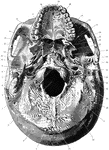
Base of the Skull
Shown is norma basalis, which refers to the base of the cranium. Labels: 1, external occipital crest;…
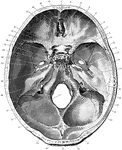
Base of the Skull Seen From Above
Shown is the base of the skull seen from above. Labels: 1, frontal bone; 2, slit for nasal nerve; 3,…

Hanging Clothes
An illustration of clothes hanging on a clothes line with shoe sand gloves resting beneath.

Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ca. 14 February 1400) was King of England from 1377 until he was…

Richard II of England
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ca. 14 February 1400) was King of England from 1377 until he was…

Henry V of England
Henry V (16 September 1386 – 31 August 1422) was one of the most significant English warrior kings…
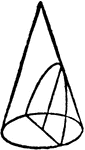
Parabola
Illustration showing a parabola as a curve formed by the intersection of the surface of a cone with…
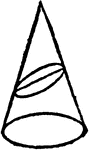
Ellipse
Illustration showing an ellipse formed by the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane neither…
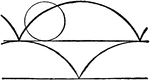
Cycloid
Illustration showing a cycloid curve. "The curve generated by a point in the plane of a circle when…

Cycloids
Illustration showing cycloid curves. "The curve generated by a point in the plane of a circle when the…
Cycloid
Illustration showing a cycloid curve. "The curve generated by a point in the plane of a circle when…

Derrick
An illustration of an iron derrick, a lifting device composed of one mast or pole which is hinged freely…

Puritan Costumes
A Puritan of 16th and 17th century England was an associate of any number of religious groups advocating…

Mordecai Gist
Mordecai Gist (1743-1792) was a general who commanded the Maryland Line in the Continental Army during…
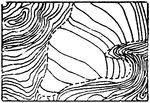
Glacier Contours
In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height)…

Glacier Form Lines
In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height)…
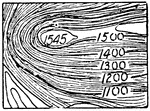
Contour System
In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height)…

Tidal Flats of any Kind
The typical representation of shore lines and low-water lines with tidal flats of any kind on a topographical…

Street Car
An illustration of a horse-drawn street car. The first passenger services in the world were started…
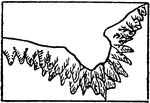
Rocky Ledges
The typical representation of shores and low-water lines with rocky ledges on a topographical map.

Gravel and Rocks
The typical representation of shores and low-water lines with gravel and rocks on a topographical map.

City Transportation
"Transportation in a large city, showing elevated road, surface line, and subway." -Gordy, 1916

Lather's Hatchet
It has a large flat blade with a straight edge. At the back is a peen or hammer head, and in the middle…