Reed Warbler
"Warbler is a popular name often applied to well-known singing birds of northern climes, whose notes…

Nest of Reed Warbler
"Warbler is a popular name often applied to well-known singing birds of northern climes, whose notes…
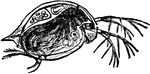
Daphnia Pulex Water Flea
"Water Flea is a popular name for minute aquatic Crustaceans such as daphnia, cypris, and cyclops. The…

Water Beetle
"Water Beetles are beetles which live on or in the water. The Dytiscus, common in stagnant water, is…

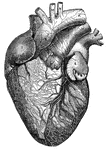
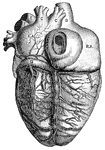
Whale
"Whale is a name that may be taken as equivalent to Cetacean, and applied to any member of that order…

Green Woodpecker
"Woodpecker is the popular name of the old Linnæan genus Picus, now greatly divided. Woodpeckers…

Wren
"Wren is a genus of birds, having a slender, slightly curved, and pointed bill; the wings very short…

Tree-coral
"These animals are generally called Tree-corals, on account of the forms of the polypidons…
Spinal column
"The spine or backbone, serves as a support for the whole body. It is made up of a number of…
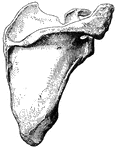
Scapula
"The shoulder-blade is a large, flat, three-sided bone, which is placed on the upper and back…

Muscles of the Back and Shoulder
"Some of the Larger Muscles on the Back of the Shoulder and the Arm." — Blaisedell, 1904
Thigh Muscles
"Some of the Larger Muscles on the back of the Thigh. Powerful tendons at the hip and on the back of…

Muscles of the neck and back
"One of the Deep Layers of Muscles of the Neck and the Back." — Blaisedell, 1904
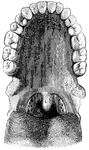
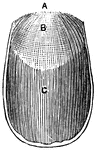
Back view of the adult mouth
"The head is represented as having been thrown back, and the tongue drawn forward. A, B…

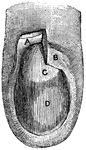
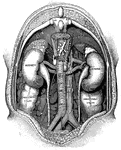
Lateral section of the chest
"A, a muscle which aids in pushing the food down the esophagus; B, esophagus; C,…
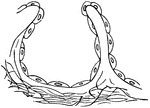
!["Hydrozoon is a name given to the great class of the sub-kingdom Cœlenterata, of which hydra is the type. They exhibit a definite histological structure, their tissues having a cellular organization. These tissues are two, an outer or ectoderm, and an inner or endoderm. In most the prey is seized by tentacles surrounding the mouth and furnished with offensive weapons called thread cells, The hydrozoa are all aquatic, and nearly all marine. Their distribution is world-wide. [Pictured] Hydra fusca, with a young bud at b, and a more advanced bud at c."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15400/15469/hydrozoon_15469_mth.gif)
Hydrozoon
"Hydrozoon is a name given to the great class of the sub-kingdom Cœlenterata, of which hydra is…

Iguana
"Iguana is a genus of saurian reptiles, natives of Brazil, Cayenne, the Bahamas, and neighboring localities…

Jay
"Jay is the popular name of a species of birds belonging to the crow family, of a vinous red color;…

Kinkajou
"Kinkajou is a genus of carnivorous mammals. They have prehensile tails, with which they hang on to…
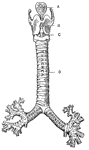
Diagrammatic view of an air sac
"A, epithelial lining wall; B, partition between two adjacent sacs, in which run capillaries;…

Lizard
"Lizard is the popular name of numerous reptiles having usually two pairs of limbs and an elongated…
Surface of a nail
"Concave or Adherent Surface of the Nail. A, border of the root; B, whitish portion…
Vertical Section of the Back
"The spinal column below the twelfth dorsal vertebra at A has been removed, as well as the…

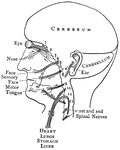
Nervous System
"Diagram illustrating the General Arrangement of the Nervous System. (posterior view.)" — Blaisedell,…
Distribution of the Cranial Nerves
"The cranial nerves are thus arranged in pairs: 1, olfactory nerves, special nerves of smell; 2, optic…
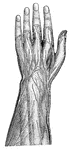
Superficial Nerves of the Forearm and Hand
"Superficial, or Cutaneous, Nerves on the Back of the Left Forearm and Hand." — Blaisedell, 1904
Nerve trunks
"The Main Nerve Trunks of the Right Forearm, showing the Accompanying Radial and Ulnar Arteries. (Anterior…
Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Posterior Tibial) on the Back of the Leg, with its Accompanying Artery of the Same Name."…
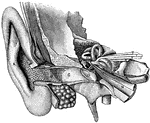
General view of organ of hearing
"A, pinna; B, cavity of the concha, showing the openings of a great number of sebaceous…

Egyptian Water Lily
"Lotus is a name given to various flowers, including several beautiful species of water lily, especially…

Lumpfish
"The Lump Fish, or Sucker, is named from the clumsiness of its form. The back is arched and sharp, the…

Mastodon
"Mastodon is an extinct genus of proboscideans, closely allied to the true elephants. The genus ranged…

Tomb of Midas
"Midas was, in Greek legend, a King of Phrygia. For his kindness to Silenus he was promised by Dionysus…
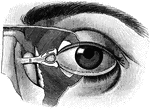
Eyeball
"The Relative Position of the Lachrymal Apparatus, the Eyeball, and the Eyelids. A, lachrymal canals,…
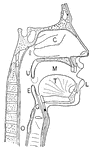
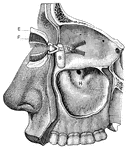
Nasal and throat passageways
"Diagram of a Sectional View of Nasal and Throat Passageways. C, nasal cavities; T,…
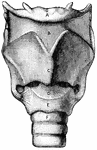
Front view of the larynx
"Cartilages and Ligaments of the Larynx. (Front view.) A, hyoid bone; B, membrane…
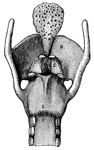
Posterior view of the larynx
"Cartilages and Ligaments of the Larynx. (Front view.) A, epiglottis; B, thyroid cartilage;…

City Hall of New York
"New York is a city in Southern New York; coextensive with New York, Kings, Queens, and Richmond counties,…
!["New York is a city in Southern New York; coextensive with New York, Kings, Queens, and Richmond counties, on New York Bay, the Hudson and East rivers, Long Island Sound and the Atlantic Ocean; the first city in the United States in population and commercial importance, and after London, the largest metropolitan center in the world. New York is noted for the number and height of its office buildings. In 1911 there were 50 such structures in occupancy, ranging from 14 to 50 stories in height, or from 179 to 700 feet above ground level, and 16 more were nearing completion. The tallest building was that of the Metropolitan Life Insurance Company, 700 and one quarter feet to top of lantern on its majestic tower. Other conspicuous ones [include the] Park Row, 382 [feet]."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15600/15666/nyparkrow_15666_mth.gif)
Park Row Building of New York
"New York is a city in Southern New York; coextensive with New York, Kings, Queens, and Richmond counties,…
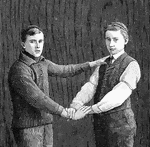
Hand seat
"Improvised Hand Seats: the Three-Handed Seat. THe usefull three-handed seat is made by one bearer grasping…

Osprey
"The Osprey, the fish hawk, bald buzzard, or fishing eagle. A bird of prey, of almost world wide distribution…
Pastoral Staff
"The Pastoral Staff is, in the Roman Catholic Church, the official staff of a bishop or abbot. The pastoral…

Demosthenes
"In the oratory of more thn two thousand years Demosthenes stands in the front rank, and will always…

Pheasant
"The Pheasant is one of the most highly prized game birds. The adult male pheasant is a beautiful bird,…

Pompeiian House
"House construction consists mainly of concrete or brick, and sometimes of stone blocks, especially…

Marcus Aurelius Antoninus
"Marcus Aurelius Antoninus stands almost alone in the history of the world as a philosopher and philanthopist…

Byzantine court
"Constantine, the first Christian emperor, removed the capital of the world-empire from Rome to Byzantium,…

Apotheosis
"The enrollment of a mortal among the gods. The mythology of Greece contains numerous instances of the…

Cantharus
"A king of drinking cup, furnished with handles. It was the cup scred to Bacchus, who is frequently…