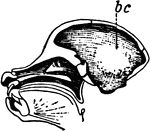
Dissected Fish
"Dissected fish. a, air bladder; b, urinary bladder; b, urinary bladder; br, brain; c, spinal cord;…

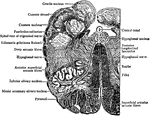
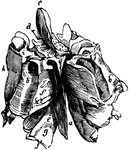
Dissected Frog
"Frog with the left side cut away and some of the organs pulled downward. a, aorta leading from the…
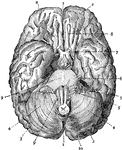
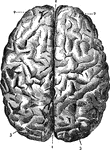
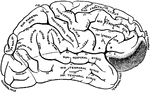
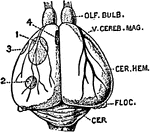
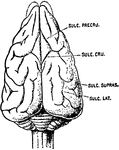
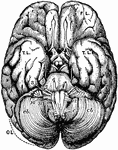
Brain
The brain seen from below. 1: Great fissure; 2: Anterior lobes of cerebrum; 3: Posterior lobes of cerebrum;…
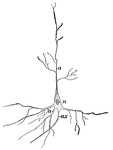
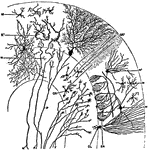
Nerve Cell
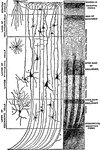
Nerve cell from the brain; a, processes by which it communicates with other cells near by;…
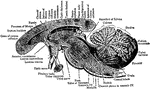
Brain
Mesial section through the Corpus Callosum, the Mesencephalon, the Pons, Medulla and Cerebellum. Showing…
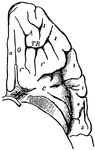
Brain
Transverse section through the human mesencephalon at the level of the superior quadrigeminal body
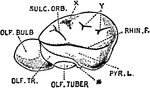
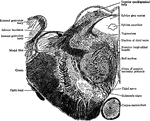
Brain
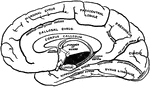
Orbital surface of the left frontal lobe and the island of Reil; the tip of the temporo-sphenoidal lobe…
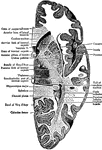
Brain
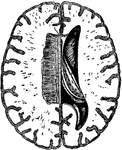
Horizontal section through the Right Cerebral Hemisphere at the Level of the Widest Part of the Lenticular…
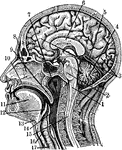
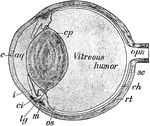
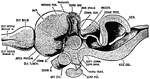
Sectional view of the Head
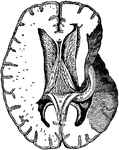
Section through the Head and Neck on the Median Line. 1. Medulla Oblongata 2. Pons 3. Right lobe of…
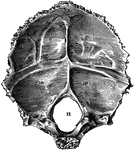
Occipital Bone of the Human Skull
Occipital bone of the human skull, inner surface. It is situated at the back and base of the skull.…

Parietal Bone of the Human Skull
Parietal bone of the human skull, inner surface. The parietal bones form the greater part of the sides…
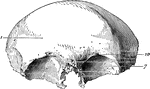
Frontal Bone of the Human Skull
Frontal bone of the human skull, outer surface. The frontal bone forms the forehead, roof of the orbital…
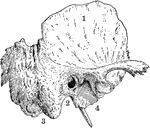
Temporal Bone of the Human Skull
Temporal bone of the human skull. The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull.…
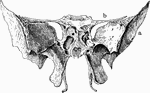
Sphenoid Bone of the Human Skull
Sphenoid bone, situated the anterior part of the base of the skull, articulating with all the other…
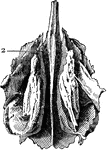
Ethmoid Bone of the Human Skull
Ethmoid bone, posterior surface. The ethmoid bone is an exceedingly light, spongy bone, placed between…

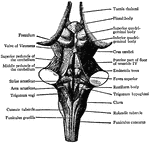
Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Base of Brain
Base of brain, spinal cord, and spinal nerves. Labels: V, 5th nerve; VI, 6th nerve; VII, a, facial nerve,…
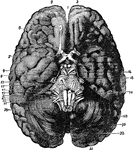
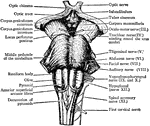
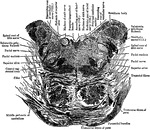
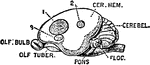
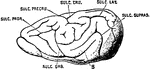
Base of Brain
The base of the brain. Labels: 1, longitudinal fissure; 2, 2, anterior lobes of cerebrum; 3, olfactory…
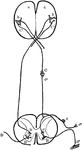
Nervous System Diagram
Diagram of nervous system. Labels: a, a, cortex of cerebral hemispheres; b, b, cell body and dendrites…
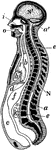
Longitudinal Section of Body
Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the body. Labels: a, the neural tube, with its upper enlargement…
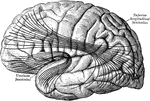
Cerebral Cortex
The most important association tracts of the brain. The fibers are projected upon the external surface…
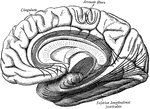
Cerebral Cortex
The most important association tracts of the brain. The fibers are projected upon the mesial (medial)…
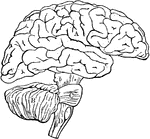
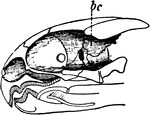
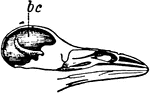
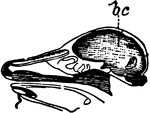
Brain
Diagram illustrating the general relationships of the parts of the brain. Labels: A, fore-brain; b,…
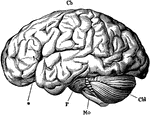
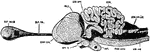
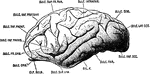
Brain
The brain from the left side. Labels: Cb, the cerebral hemispheres forming the main bulk of the fore-brain;…
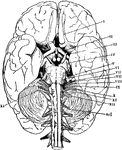
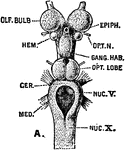
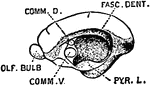
The Base of the Brain
The base of the brain. The cerebral hemispheres are seen overlapping all the rest. Labels: I, olfactory…
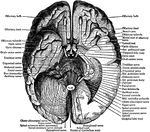
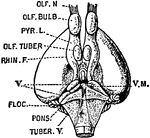
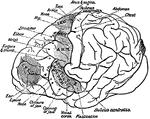
Under Surface of the Brain
View of the under surface of the brain, with the lower portion of the temporal and occipital lobes,…
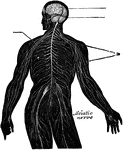
The Nervous System
View of the nervous system of man, showing the nerve centers (brain and spinal cord) giving off nerves…