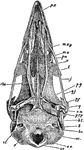
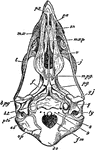
Parotid and Molar Glands of a Horse
Parotid and molar glands of the left side. Labels: a, parotid gland; b, Steno's duct; c, superior molar…

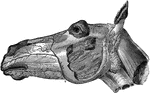
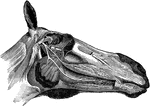
Horse Head
Right infero-lateral view of the head; the maxillary ramus, cheek, parotid gland, and upper lip being…
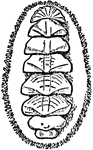
Chiton (Dorsal)
A dorsal view of a chiton, showing the eight shell plates. Chitons are small to large, primitive marine…
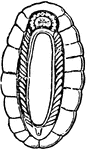
Chiton (Ventral)
A ventral view of a chiton, showing p, foot; o, mouth; kr, oval fringe; and br, the numerous ctenidia.…
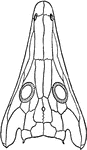
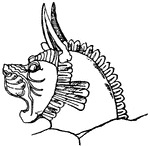
Archegosaurus Head
Archegosaurus is a genus of amphibian which lived during the Asselian to Wuchiapingian ages of the Permian,…
Head of Ichthyophis Glutinosus
Ichthyophis glutinosus or Ceylon Caecilian is a species of amphibian in the Ichthyophiidae family. Pictured…
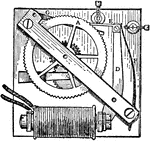
Dial Driving Device
An illustration of Hope Jone's dial-driving device. "Each time that a current is sent by the master…

Ladybug
Coccinellidae is a family of beetles, known variously as ladybirds (British English, Australian English,…
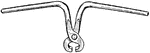
Rail Tongs
"Track-layers' tongs for lifting rails. They have short jaws designed to clasp the rail head and two…
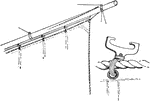
Railway
"Railway, with single traveler in detail. Nautical, iron jackstays bolted on the under side of standing…
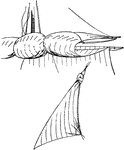
Spanish Reef Jib
"Spanish reef, a derisive term for a jib having a knot tied in its head, or for one of the square-sails…
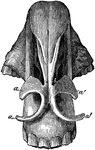
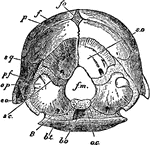
Nostriils of a Horse
Cartilaginous framework of the nostril-seen from above. Labels: a, right alar cartilage; a', left alar…

Head of a Horse
Longitudinal section of the head, showing the pharynx and nasal chamber-the septum nasi being removed.…

Head of a Horse Showing Arteries
Arteries of the head- the left maxillary ramus being remove. Labels: 1, occipital; 2, internal carotid;…
Head of a Horse Showing Arteries
Facial arteries of the left side. Labels: a, maxillo-muscular; a', posterior masseter; b, c, posterior…

Head and Neck of a Horse Showing Veins
Veins of the face and neck. Labels: 1, glosso-facial; A, its facial portion; 2, jugular; 3, occipial;…
Head of a Horse Showing Nerves
Nerves of the right side of the head- the maxillary ramus and cheek being removed. Labels: a, superior…

Head of a Horse Showing Nerves
Left side of the face- showing the distribution of the facial portions of the fifth and the seventh…

Head of a Horse Showing Nerves
Ninth, tenth, eleventh, and twelfth cranial, first cervical, and part of the sympathetic nerves- the…
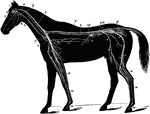
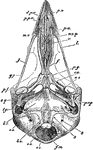
Nervous System of the Horse
The nervous system of the horse. Labels: 1, brain; 2, optic nerve; 3, superior maxillary nerve (5th);…

French Contrabassoon
An illustration of the front (right) and back (left) of the French contrabassoon.
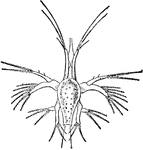
Nauplius of a Prawn
A nauplius (plural nauplii) is the first larva of animals classified as crustaceans (subphylum of Arthropoda).…

Hobby Horse
A hobby horse (or hobby-horse) is a child's toy horse, particularly popular during the days before cars.…
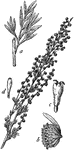
Sagebrush
"Pasture Sage-brush (Artemisia frigida). a, leaf; b, flower-head; c, fertile flower; d, marginal flower."…

Back View of the Temple of Philæ
The serious, solemn, and awe-inspiring efect which the general arrangement of the temple produces is…

Sarinda
"Sarinda. A Hindu viol, which has a body made of a single wooden block, elliptical in general contour,…

Capital in the Temple at Denderah
In some temples the pillars have, in lieu of capital, the face of a goddess, probably of Isis, with…
Profile of the Colossal Statue on a Pier at the Luxor Temple
Instead of columns, square piers are not infrequently introduced in the tombs. In structural buildings…
Front View of the Colossal Statue on a Pier at the Luxor Temple
Instead of columns, square piers are not infrequently introduced in the tombs. In structural buildings…

Entrance of the Great Temple at Abu Simbel
Four colossal 20 meter statues of the pharaoh with the double crown of Upper and Lower Egypt decorate…
Guilloche Ornament Painted on Burnt Clay, from the Ruins of Nineveh
Guilloche, usually spelled without the acute accent on the final e, describes a repetitive architectural…

Winged Bull from Nimrud
The Sumerian word lama, which is rendered in Akkadian as lamassu, refers to a beneficient protective…
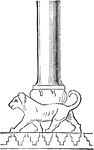
Pillar on a Lion's Back
In the fragment of a relief from Kuyunjik columns occur which rest on a cushion-shaped base on a lion's…

Capital and Entablature from the Rock Tomb of Darius
The columns in the ruins of Persepolis are circular and slender, and have capitals and bases. The capital…
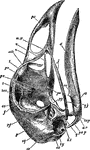
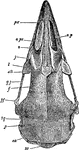
Fowl Skull
The skull of an adult fowl. Here the temporal fossa is bridged over by the junction of the post-frontal…
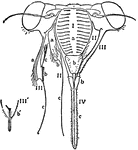
Head of Cicada
A cicada is an insect of the order Hemiptera, suborder Auchenorrhyncha, in the superfamily Cicadoidea,…
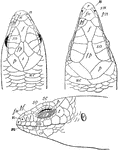
Skink Head
"Head-shields of Scinid Lizards. cs, chin-shields; d, disk on lower eylid; e, ear-opening; f, frontal;…

Greek Griffin
The Greek Griffin is associated with Antiquity and fire, usually appears on Candelabras and friezes.…

Roman Griffin
The Roman Griffin has the body of a Lion and the head and wings of an Eagle. The Griffin is usually…

Griffin Renaissance
The Renaissance Griffin is associated with Antiquity and fire, it appears on Candelabras and friezes.…
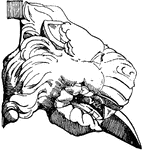
Gargoyle Lion Head
This Gargoyle Lion Head is made out of terracotta and is found in Athens, Greece.

Antique Lion Head
This Antique Lion Head shows the front view of the antique head. This Lion's Head is found at the Vatican.

Antique Lion Head
This Antique Lion Head shows the side view of the antique head. This Lion's Head is found at the Vatican.