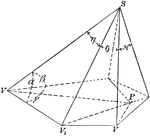
Face Angles of Convex Polyhedral Angle
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "The sum of the face angles of any convex polyhedral angle is less…
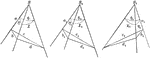
Symmetrical or Equal Trihedral Angles
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "Two trihedral angles, which have three face angles of the one equal…
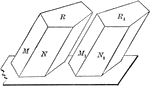
Two Equal Prisms
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "Two prisms are equal when the three faces about a trihedral of one…
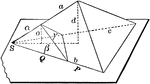
Two Proportional Tetrahedrons
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "Two tetrahedrons having a trihedral angle in each equal, are to…
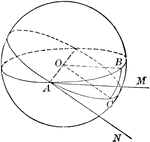
Measure of a Spherical Angle
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "A spherical angle is measured by the arc of a great circle described…
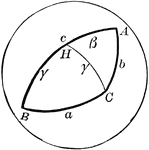
Side Comparison of Spherical Triangle
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "In a spherical triangle, the greater side is opposite the greater…
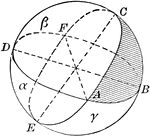
Area of Spherical Triangle
Diagram used to prove the theorem: "The area of a spherical triangle, expressed in spherical degrees,…
Label Difference
"The Heir, or first son, the LABEL. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in…
Crescent Difference
"Second Son, the CRESCENT. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in number.…
Mullet Difference
"Third Son, the MULLET. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in number. They…

Martlet Difference
"Fourth Son, the MARTLET. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in number.…
Annulet Difference
"Fifth Son, the ANNULET. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in number. They…

Fleur-De-Lis Difference
"Sixth Son, the FLEUR-DE-LIS. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in number.…
Rose Difference
"Seventh Son, the ROSE. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in number. They…

Cross Moline
"Eighth Son, the CROSS MOLINE. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in number.…
Double Quatrefoil
"Ninth Son, the DOUBLE QUATREFOIL. The differences used by armorists at the present time are nine in…
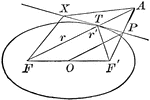
Tangent to an Ellipse
Diagram an ellipse with a tangent line that illustrates "A line through a point on the ellipse and bisecting…
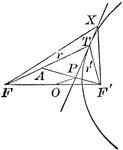
Tangent to a Hyperbola
Diagram part of a hyperbola with a tangent line that illustrates "A line through a point on the hyperbola…

Non-Vocal Primary Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Divided Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Mixed-Divided Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Shut Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Non-Vocal Nasal Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Primary Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
Vocalized Mixed Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
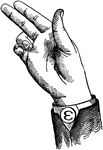
Vocalized Divided Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Mixed-Divided Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
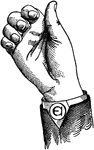
Vocalized Shut Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…

Vocalized Nasal Back Consonant
Consonants have a closed or narrowly expanded adjustment of the vocal organs, so that in their production…
![Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics of certain central-aperture consonants with the wide or expanded quality of vowels, but differing from vowels in not having a fixed configuration. ...in representing glides the peculiarities of consonants and vowels are blended: the accented fingers, by being straightened, contribute a consonant characteristic; while the second phalanx of the thumb, by being held at an angle to the plane of the palm, imparts to the glide positions the wide, without giving them the firm, quality of vowel positions. <p> Breath-Glide - A transitional aspiration, of organic quality corresponding to that of the adjoining elements [a soft effect of the Consonants, back primary; top primary; Point primary; Lip primary; etc.]. Although this glide has no fixed abiding place, and is of a somewhat variable organic formation, in its effect it is very closely allied to the Throat consonant aspirate, and is therefore represented with a posterior position of the palm and a separation of the index and center fingers, which are characteristic features of Throat positions. This is the only Non-Vocal glide, and hence is the only one in the representation of which the voice phalanx is unaccented.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/65900/65914/65914_glide_breath_mth.gif)
Breath-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
![Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics of certain central-aperature consonants with the wide or expanded quality of vowels, but differing from vowels in not having a fixed configuration. ...in representing glides the peculiarities of consonants and vowels are blended: the accented fingers, by being straightened, contribute a consonant characteristic; while the second phalanx of the thumb, by being held at an angle to the plane of the palm, imparts to the glide positions the wide, without giving them the firm, quality of vowel positions. Voice-Glide – Vowel murmur [a non-syllabic effect of the mid Mixed primary round vowel]. It is a Throat formation, and is shown to be so by the position which represents it.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/65900/65915/65915_glide_voice_mth.gif)
Voice-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
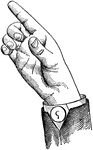
Back-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
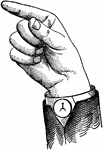
Top-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…

Point-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
![Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics of certain central-aperature consonants with the wide or expanded quality of vowels, but differing from vowels in not having a fixed configuration. ...in representing glides the peculiarities of consonants and vowels are blended: the accented fingers, by being straightened, contribute a consonant characteristic; while the second phalanx of the thumb, by being held at an angle to the plane of the palm, imparts to the glide positions the wide, without giving them the firm, quality of vowel positions. <p> Round-Glide – Rounded murmur [a non-syllabic effect of the mid Mixed primary round vowel]. This also is a Throat formation, and is represented by a position which suggests an unrepresented Vocalized Throat Mixed consonant.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/65900/65920/65920_glide_round_mth.gif)
Round-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
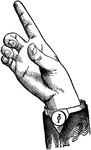
Throat-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
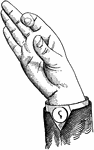
Back Mixed-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
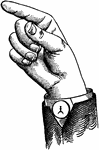
Top Mixed-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…

Point Mixed-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
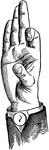
Lip Mixed-Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
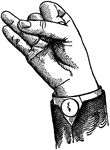
Indicated High Primary Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
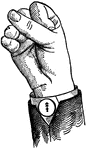
Indicated High Primary Top Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
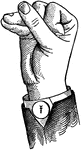
Indicated High Primary Point Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
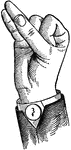
Indicated High Primary Lip Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
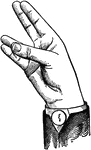
Indicated High Wide Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
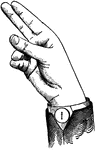
Indicated High Wide Top Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
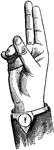
Indicated High Wide Point Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…

Indicated High Wide Lip Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
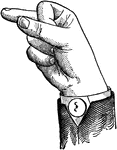
Indicated Mid Primary Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
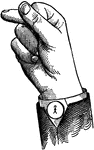
Indicated Mid Primary Top Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…

Indicated Mid Primary Point Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
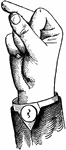
Indicated Mid Primary Lip Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
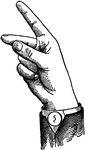
Indicated Mid Wide Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
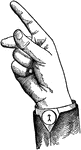
Indicated Mid Wide Top Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…

Indicated Mid Wide Point Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
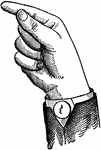
Indicated Low Primary Back Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
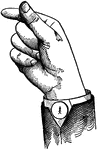
Indicated Low Primary Top Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…
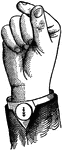
Indicated Low Primary Point Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…

Indicated Low Primary Lip Glide
Glides are only transitional sounds. They are intermediate to Consonants and Vowels, combining the characteristics…