Morven
"Morven, Stockton's estate. This sketch is from the lawn in front, which is shaded by venerable pines…

State House
"Walnut Street front of the State House in 1776. This gives the appearance of the shorter steeple, which…

Red Bank Monument
"Monument at Red Bank. This view includes the monument, a portion of the Delaware, and the mouth of…

Penn's House
"Penn's House. This view is from Second Street. The building is of imported brick, except the modern…

Washington's head-quarters
"Washington's head-quarters. This view is from the Reading rail-road, looking east, and includes a portion…

Observatory
"The observatory. This view is from the field, looking north. On the left is seen the winding Schuylkill,…

Monmouth
"The field of Monmouth. In the picture here given, the chief is seen most prominently on his white charger,…

Monmouth Battle-Ground
"Battle-ground at Monmouth. This view is from the orchard, upon the site of Wayne's position when Monckton…

Jefferis' Ford
"View at Jefferis' Ford. This view is from the easterly bank of the Brandywine. The ford was at the…

Birmingham Meeting-House
"Birmingham Meeting-house. This is a view of the southerly front of the meeting-house. The building…

Chad's Ford
"View at Chad's Ford. This view is from the east bank of the Brandywine, looking southwest. The ford…

Washington Monument
"Washington Monument. The following are the inscriptions on the monument: East front: 'To George Washington,…

Congress House
"The Congress House. This view is from Baltimore Street, looking southeast. The ront on the left is…

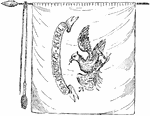
Pulaski's Banner Front
"Pulaski's Banner. On one side of the banner are the letters U. S., and in a circle around them the…
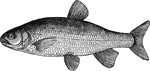
Chub
"Frequents deep places in the quiet parts of steams, sheltering itself usually under a bush or tree…

Strasburg Lookout
"View of the town of Strasburg, valley of the Shenandoah, occupied by the Federal forces under General…

Bridge at Strasburg
"View of the town of Strasburg, valley of the Shenandoah, occupied by the Federal forces under General…
!["Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine, July 30th, 1864. Immediately after the explosion of the mine a hundred cannons opened along the Federal front, and at half-past five the Ninth Corps charged, carrying the fort with a part of the line on each side. The Second Division, which was in the centre, advanced and carried the second line a short distance beyond the fort, and rested, holding ground with the utmost determination. It was at the time the [African American] Division, under General White, was pushed forward and ordered to charge and carry the crest of the hill, which would have decided the contest. The troops advanced in good order as far as the first line, where they received a galling fire, which checked them, and although quite a number kept on advancing, the greater number seemed to become utterly demoralized, part taking refuge in the fort, and the remainder running to the rear as fast as possible. They were rallied and again pushed forward, but without success, the greater part of the officers being killed or wounded."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/13900/13915/petersburg_1_13915_mth.gif)
Siege of Petersburg
"Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine,…
!["Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine, July 30th, 1864. Immediately after the explosion of the mine a hundred cannons opened along the Federal front, and at half-past five the Ninth Corps charged, carrying the fort with a part of the line on each side. The Second Division, which was in the centre, advanced and carried the second line a short distance beyond the fort, and rested, holding ground with the utmost determination. It was at the time the [African American] Division, under General White, was pushed forward and ordered to charge and carry the crest of the hill, which would have decided the contest. The troops advanced in good order as far as the first line, where they received a galling fire, which checked them, and although quite a number kept on advancing, the greater number seemed to become utterly demoralized, part taking refuge in the fort, and the remainder running to the rear as fast as possible. They were rallied and again pushed forward, but without success, the greater part of the officers being killed or wounded."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/13900/13917/petersburg_2_13917_mth.gif)
Siege of Petersburg
"Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine,…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Hand with Gun
"Picture of a hand with a gun at the Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the…

Grafton Occupied by Federal Troops
"View of Grafton, West Virginia, occupied by the Federal Troops, under the command of General McClellan,…

Railroad at Grafton
"View of Grafton, West Virginia, occupied by the Federal Troops, under the command of General McClellan,…

Federal Troops at Grafton, West Virginia
"View of Grafton, West Virginia, occupied by the Federal Troops, under the command of General McClellan,…

Battle of Antietam
"Battle of Antietam, Burnside's Division, left wing- brilliant and decisive bayonet charge of Hawkins's…

Battle of Antietam
"Battle of Antietam, Burnside's Division, left wing- brilliant and decisive bayonet charge of Hawkins's…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Mount Vernon
"Mount Vernon. This view is from the lawn in front, looking down the Potomac. The mansion is built of…

James River
"Scene on the James River, at Richmond. This view is from a long shaded island extending up the river…

Jamestown Island
"Distant view of Jamestown Island. This view is from the north side of what was once a marsh, but now…

Jamestown Ruins
"Ruins at Jamestown. This view is from the old church-yard, looking toward James River, a glimpse of…

Old Magazine
"The Old Magazine. This view is from the square, looking southeast. South of it is a neat frame building,…

Apollo Room
"The Apollo Room. The room used for public meetings is in the rear building of the old Raleigh tavern…

Raleigh Tavern
"Raleigh Tavern. When I visited Williamsburg in December, 1848, the front part of the old Raleigh tavern…
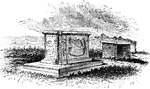
Nelson Tombs
"The Nelson Tombs. This view is from the burial-ground looking down the York River toward Chesapeake…

Redoubt
"View from the site of the Redoubt. This view is from the mounds looking northwest, up the York River.…

Nelson Mansion
"The Nelson Mansion. This view is from the street looking northwest. A long wooden building, with steep…

Moore's House
"This is a view from the lawn, looking south. It is a frame building with a brick foundation. At the…

Monticello
"Monticello, Governor Jefferson's place of retirement. This venerated mansion is yet standing, though…

Tryon Palace
"Front view of Tryon's Palace. The view here given was the north front, toward the town. The center…

Regulator Battle-ground
"The Regulator battle-ground. This view is from the south side of the Salisbury Road, which is marked…

Trading Ford
"Trading Ford. This view of the Trading Ford, where greene, with Morgan and his light troops, crossed…

Guilford Battle-ground
"View of the battle-ground. This view is from the eminence southwest of the site of old Guilford Court…

Tuckesege Ford
"View at Tuckesege Ford. This view is from the western bank of the Catawba, looking down the stream."—Lossing,…

King's Mountain Battle-Ground
"View at King's Mountain battle-ground. This view is from the foot of the hill, whereon the hottest…

Morgan Medal Front
"Gold medal awarded to Morgan. The following are the devices and inscriptions upon the front of the…

Morgan Medal Back
"Gold medal awarded to Morgan. The following are the devices and inscriptions upon the back of the medal:…

Howard Medal Front
"Silver medal awarded to Colonel Howard. The following are the device and inscriptions upon the front:…

Washington Medal Front
"Silver medal awarded to Washington. The following are the device and inscriptions on the front: An…

Cherokee Ford
"View at the Cherokee Ford. This view is from the east bank of the river. Toward the extreme right is…

Catawba
"View of the Great Falls of the Catawba. This view is from the west side of the Catawba, looking northeast,…