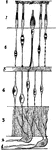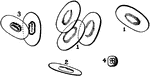
Blood Cells
Red corpuscles (blood cells) of the frog. The red blood cells of birds, reptiles, amphibians and fishes…

Blood Cells
White blood corpuscle (cell), sketched at successive intervals of a few seconds to illustrate the changes…
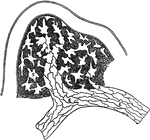
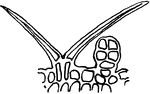
Lymphatics
Origin of lymphatics. Labels: S, lymph spaces communicating with lympathic vessel; A, origin of lymphatic…

Circulation in a Frog's Foot
Circulation in frog's foot under a microscope. Labels: A, walls of capillaries; B, tissue of web lying…

Epidermal Section
A section through the epidermis, somewhat diagrammatic, highly magnified. Below is seen a papilla of…
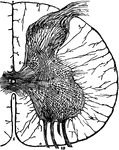
Spinal Cord Section
A thin transverse section of half the spinal cord magnified about 10 diameters. Labels: 1, anterior…

Sensation of the Skin
Section of skin showing two papillae of the dermis and some of the deeper cells of the epidermis, involved…

Olfactory Epithelium
Cells from the olfactory epithelium. Labels: 1, from the frog. 2, from the man; a, columnar cell, with…
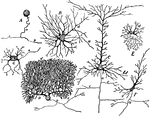
Nerve Cells
Forms of nerve cells. Labels: A, from spinal ganglion; B, from ventral horn of spinal cord; C, pyramidal…
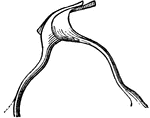
The Lamina Reticularsis
The lamina reticularis, which is a delicate perforated membrane which extends from the articulations…

Structure of the Teeth
Structure of the teeth. A tooth consists of 3 structures, the dentine (2), or ivory, the proper dental…
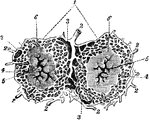
Lobules of the Liver
Lobules of the liver (1), which are small, granular-looking bodies, of polygonal shape, and about 1/20…

Structure of the Lungs
Structure of the lung. The lung has a serous coat; a sub-serous, elastic areolar tissue, investing the…
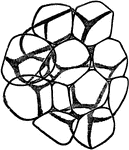
Adipose Tissue
Fat vesicles in adipose (fatty) tissue. Adipose tissue is a subtype of connective tissue consisting…

Cartilage Tissue
Fibrous cartilage connective tissue from the symphysis pubis, magnified. Cartilage is a structure without…
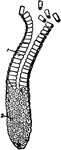
Columnar Epithelial Tissue
Columnar epithelium lining a gland. It consists of conical cells laid side by side, their ends forming…

Nerve Cells
Forms of nerve cells. They each have a nucleus and nucleolus and are connected to each other by means…
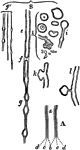
Nerve Tubules
A diagram of nerve tubules A nerve tube consists of a white portion which is fatty, and which protects…
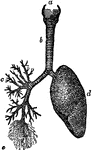
Structure of the Lungs
Diagram showing the structure of the lungs. At d is the left lung, and at c are represented…
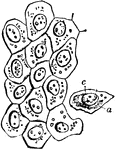
Flat Epithelium Cells
Flat epithelium cells from the surface of the peritoneum. Labels: a, cell body; c, nucleus.
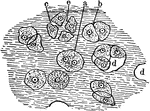
Cartilage Tissue Cells
A thin slice of cartilage, magnified, to how the cells embedded in the homogenous matrix. Labels: a,…
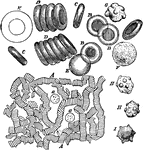
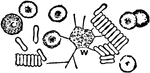
Blood Corpuscles
Blood corpuscles (cells). Labels: A, magnified about 400 diameters. The red corpuscles have arranged…

White Blood Corpuscle
A white blood corpuscle sketched at successive intervals of a few seconds to illustrate the change of…
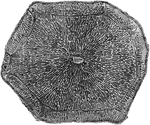
Liver Lobule of a Pig
A lobule of a pig liver, magnified, showing the hepatic cells radially arranged around the central intralobular…
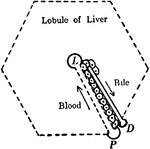
Liver Structure
Diagram to illustrate the relationship of blood capillaries, bile capillaries, and liver cells. Labels:…
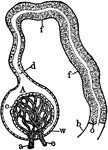
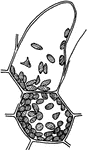
Kidney Glomerulus and Uriniferous Tubule
Diagram showing a kidney glomerulus and the commencement of an uriniferous tubule. Labels: a, afferent…
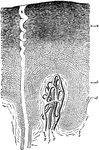
Epidermis and Sweat Gland
A section through the epidermis, highly magnified. Labels: Below is seen a papilla of the dermis, with…
Thigh Bone Section
The above cut represents a section of the thigh bone. The extremities (a, w) having a shell or thin…
Pluto and Cerberus
In Roman mythology, Pluto was the god of the dead. Cerberus was his dog who guard the underworld.
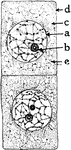
Onion Cells
"A, embryonic cells from onion root tip; d, plasmatic membrane; c, cytoplasm; a, nuclear membrane enclosing…
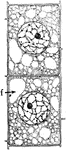
Onion Cells
"B, older (onion) cells farther back from the root tip. The cytoplasm is becoming vacuolate; f, vacuole."…
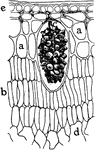
T. Zebrina Cell
In onion cells: "C, a cell from the epidermis of the mid-rib of Tradescantia zebrina, in its natural…
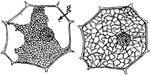
Plant Epidermis
"Two epidermal cells in cross section showing thickened outer wall differentiated into three layers,…
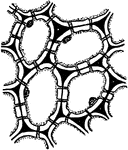
F. Elastica Epidermis
"Cross section of a portion of leaf of Ficus elastica showing the multiple epidermis from e to a inclusive;…

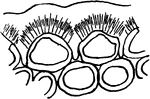
Stone Cells 1
First developmental stage of stone cells: "1, in the primary meristem condition." -Stevens, 1916
Stone Cells 2
Second developmental stage of stone cells: "2, the cells have enlarged and the walls have begun to thicken…
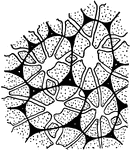
Stone Cells 3
Third and final developmental stage of stone cells: "3, The walls are completed. The primary wall is…

Bast Fibers 1 and 2
Developmental stages of bast fibers: "1 and 2, cross and longitudinal sections of primary meristem cells…
Bast Fibers 3 and 4
Developmental stages of bast fibers: 3 and 4, cross and longitudinal sections of meristem cells becoming…
Bast Fibers 5
Developmental stages of bast fibers: "5, longitudinal section of completed bast fibers. In 5 the stippling…
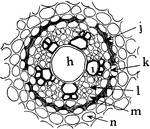
A. Ascalonicum Root
"Portion of a cross section of a root of Allium ascalonicum. h, large central, tracheal tube; i, xylem,…
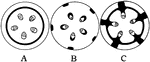
Bast Fibers
"Diagram to show different plans in the distribution of bast fibers. A, bast a continuous cylinder in…
Plant Cell Development 1
First developmental stage of sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma. "A, a and b, two rows…
Plant Cell Development 2
Second developmental stage of sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma. "B, c, companion…
Plant Cell Development 3
Third developmental stage of sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma. "The pits in the cross-walls…
Xylem Development 1
"Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. A, progressive steps in the development of…
Xylem Development 2
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "B, stages in the formation of tracheids from…
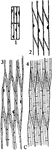
Xylem Development 3
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "C, steps in the development of wood fibers…
Xylem Development 4
Stages in the development of the elements of the xylem. "D, steps in the formation of wood parenchyma…