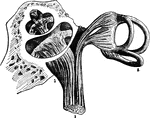
Auditory Nerve
"By anatomists, the auditory nerve is associated with the facial, and is the seventh in order of origin…

Aviz
"An order of knighthood in Portugal, instituted by Sancho, the first king of Portugal, in imitation…

Bacchus
"The god of wine, was the son of Zeus and Semele, the daughter of Cadmus. Before his birth, Semele fell…

Balm
"An erect, branching perennial, herbaceous plant of the natural order Labiatae, a native of the south…

Basil
"A genus of plants of the natural order Labiatae. The species are all natives of the tropics, or of…
Rock-Rose
"A genus of exogenous plants, which gives its name to the natural order Cistaceae; an order allied to…

Clematis
"A genus of plants of the natural order ranuculaceae having four colored sepals, no corolla, and fruit…

Cloves
"Cloves are the flower-buds of the Clove-tree. The genus to which this tree belongs is of the natural…
Colchicum
"A genus of plants of the natural order Melanthaceae. The species, which are few in number, are stemless,…
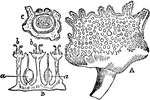
Contrayerva
"A medicine once in much repute against low fevers, and as a mild stimulant and diaphoretic, and still…
Copaiva Tree
"A valuable medicinal substance, consisting chiefly of a resin (Resin of Copaiva) and a volatile oil…
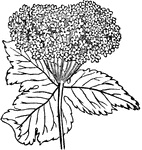
Cow Parsnip
"A genus of plants of the natural order Umbelliferae, having petals bent in at the middle, and flat…

Cress
"A name given to many plants, of which the foliage has a pungent, mustard-like taste, and is used as…

Crowberry
"A small procumbent shrub, of the natural order Empetraceae, a native of the northern parts of the world,…
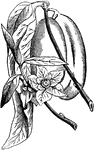
Custard Apple
"The name commonly given in the West Indies and other tropical countries to the fruits of certain species…

Daphne Mezereon
"A genus of plants of the natural order Thymeleaceae, having a 4-cleft, funnel-shaped perianth, the…

Day-lily
"A genus of plants of the natural order Liliaceae, having a perianth with bell-shaped limb, and sub-cylindrical…

Dielytra
"A genus of plants of the natural order Fumariaceae, in appearance and habit much resembling fumitories…
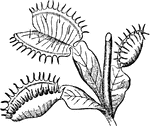
Dionaea
"A very curious and interesting genus of plants of the natural order Droseraceae, having a 5-partite…

Dittany
"A genus of plants of the natural order Rutaceae, having a short 5-partite calx, five some-what unequal…

Dragon Tree
"A tree of the natural order Liliaceae, remarkable for the size which it sometimes attains, rivalling…

Ebony
"A wood remarkable for its hardness, heaviness, and deep black color, is the heart-wood of different…
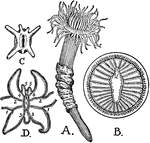
Cerianthus Solitarius
"A, Cerianthus solitarius. B, Transverse section of the stomodaeum, showing the sulculus, sl, and the…
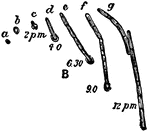
Bacillus Ramosus
"The various phases of germination of spores of Bacillus ramosus, as actually observed in hanging drops…
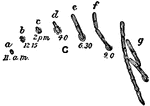
Bacillus Ramosus
"The various phases of germination of spores of Bacillus ramosus, as actually observed in hanging drops…
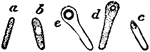
Spores
"Various stages in the development of the endogenous spores in a Clostridium — the small letters…
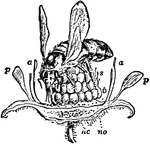
Raspberry Fertilization
"Raspberry (Rubus idaeus, order Rosaceae), being fertilized. A, Flower. p, p, Petals. a, a, Anthers.…
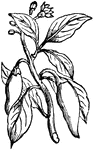
Capsicum
"A genus of annual, subshrubby plants, order Solanaceae, with a wheel-shaped corolla, projecting and…

Black Pepper
"A genus of order Piperaceae. The Piper nigrum, which furnishes the black pepper of commerse, is a native…

Myrrh
"Myrrh, is the name given to a gum resin which exudes from a shrub growing in Arabia and Abyssinia,…

Ipecacuanha Plant
"The root used in medicine under this name is obtained from Cephaelis Ipecacuanha, A. Rich, a small…

Jasmine
"Botanically Jasminum, a genus of shrubs or climbers constituting the principal part of the natural…

Center of Gravity
"Why does a person carrying a weight upon his back stoop forward? In order to bring the center of gravity…
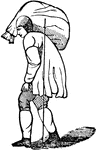
Center of Gravity
"Why does a person carrying a weight upon his back stoop forward? In order to bring the center of gravity…
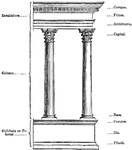
Elements of an Architectural Order
A diagram showing the titles for different types of architecture.
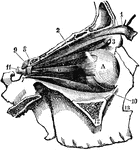
Eye Muscles
"The external bones of the temple are supposed to be removed in order to render visible the muscular…
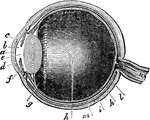
Eye
"Next in order is the aqueous humor, b, e, in the middle of which is the iris, d, c. Behind the pupil…
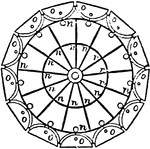
Revolving Light
"In order to produce, on the catoptric system, a fixed light showing all round the circle, a number…
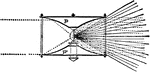
Parabolic Profile
"In order strictly to equalize a fixed light over the whole horizon, which could not possibly be done…
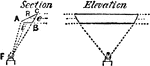
Reflecting Prism
"Fresnel next conceived the admirable improvement of employing the principle of "total" or internal…
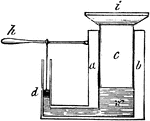
Hydraulic Press
"The pump barrel, a, b, is represented as divided lengthwise, in order to show the inside. The piston,…

Water Weighing
"Take a piece of ivory, or any other substance that will sink in water, and weigh it accurately in the…
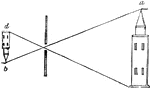
Camera Obscura
"Camera obscura strictly signifies a darkened chamber, because the room must be darkened, in order to…
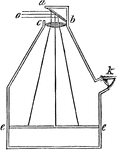
Camera Obscura
"Camera obscura strictly signifies a darkened chamber, because the room must be darkened, in order to…
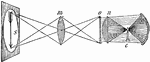
Magic Lantern
"Let a candle c, be placed on the inside of a box or tube, so that its light may pass through the plano-convex…
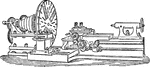
Break Lathe
"Break lathes can take in work of considerable length as well as of large diameter,—the treble-geared…
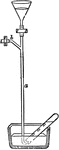
Air-Pump
"This was invented in 1865 by H. Sprengel. The instrument, in its original (simplest) form, consists…
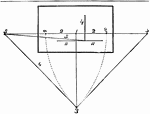
Angular Perspective
This figure comprises the whole of the points and lines preparatory to beginning a drawing in "angular…
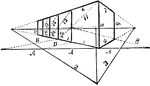
Angular Perspective
This cube has four additional cubes of equal dimensions. This is effected by first drawing the cube…

Oil palm
pinnate leaved palm that produces thick clusters of red flowers and fruit that produces high quality…

Sloughter Signing the Death-Warrant
Colonel Sloughter signing the order to execute two rebels. According to popular lore, Sloughter was…

Agricultural and Mechanical College of Texas
The basis for funding for the college was established by the Morrill Act, passed by the US Congress…

Coca
The coca plant is the source of the coca leaf used in medicine and in the production of cocaine

Seals and Walrus
Fur Seals make up one of the two distinct groups of mammals called "seals". Both the fur seals and the…

Offering of Isaac
"And they came to the place which God had told him of. And Abraham built the altar there, and laid the…
Three-ranked
Three-ranked arrangement, shown in a piece of the stalk of a Sedge, with the leaves cut off above their…
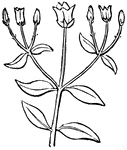
Opposite-Leaved
Diagram of opposite-leaved plant with a cyne of three flowers; a the first flower, of the main…
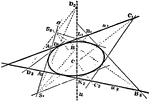
Second Order Curve
Five points are given, of which not three are in a line, a curve of second order may be drawn through…
