
Woodhull's Grave
"Woodhull's Grave. Nathaniel Woodhull was born at Mastic, Long Island, December 30, 1722. Agriculture…
Sowing
"Egyptian Sowing. The people were mainly agricultural, but employed rude methods of cultivation. In…

Miltiades
"The chief credit of the battle of Marathon belongs to Miltiades. But for his courage, the Athenians…

Caesar's Death
"The Death of Caesar. Naturaly such extraordinary success made him enemies, and though the city seemed…

William the Conqueror
"William the Conqueror (1066-1087), as represented on his seal. Although William really ruled 'as king…

Gustavus Adolphus
"Gustavus Adolphus entered Germany at the head of 16,000 men. Among some of the Protestants there was…

George III, King of England
"George III (1760-1815). The first two Hanoverian kings were ignorant of English politics and obliged…

Bastile
"The taking of the Bastile, July 14, 1789. The Parisian mob, not satisfied with the formation of the…

Napoleon
"France under Napoleon. The consulate was the form of government established after the overthrow of…

Garibaldi
"Garibaldi was a patriot who started up a revolt in Sicily and took possession of the island, then passed…

Dutch West India Flag
"Flag of the Dutch West India Company. When the rights of the company ceased, a new and more powerful…

Stamp Act
"Stamp from the Stamp Act. The first direct issue of importance between the colonies and England came…

Stamp Act
"Stamp from the Stamp Act. The first direct issue of importance between the colonies and England came…

John Brown
In 1859, John Brown collected a small body of men, white and black, in the mountains of Maryland. He…

Atlantic Cable
"Laying the Atlantic Cable. In 1866, a previous attempt in 1858 having failed, a telegraphic cable was…

Date Palm
"Date Palm is a genus of palms, the most important species of which is the common date palm, the palm…

Torque
"A Torque, in archæology, is a twisted collar of gold, or other metal, worn around the neck, in…

Statue of Liberty
"The Statue of Lberty is a colossal statue on Bedloe's Island, N.Y. On Oct. 28, 1886, after more than…

Egyptian Water Lily
"Lotus is a name given to various flowers, including several beautiful species of water lily, especially…

Theocritus
"The fame of Theocritus, the prince of bucolic poetry, depends on his faithful pictures of natural scenery…
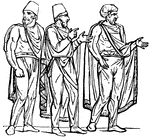
Bracae
"Trowsers, pantaloons, were common to all the nations which encircled the Greek and Roman population,…

Calceus
"A shoe or boot, anything adapted to cover and preserve the feet in walking. The use of shoes was by…
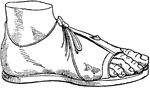
Calceus
"A shoe or boot, anything adapted to cover and preserve the feet in walking. The use of shoes was by…

Roller Skating
A group of people rollerskating indoors. The man in front is about to fall. All of the people are wearing…
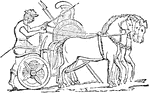
Greek Chariot
"In the battles, as depicted by Homer, the chiefs are the only important combatants, while the people…

Bust of Pericles
"The enormous influence which Pericles exercised for so long a period over an ingenious but fickle people…
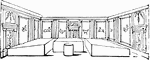
Banqueting room
"The Roman people reclined at their meals. On each couch there were commonly three persons. They lay…
Pons Cestius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
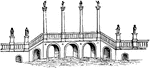
Pons Aelius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Ariminum
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Trajan
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…

Rostra
"The Beaks, was the name applied to the stage in the Forum, from which the orators addressed the people.…
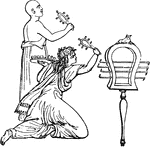
Sistrum
"The sistrum was an Egyptian instrument of music, used in certain ceremonies by that people, and especially…

Saxons
"In the eleventh century, the Anglo-Saxons, originally the fiercest nation of the North of Europe, had…

Peter the Hermit and followers
"Peter, a hermit of Picardy, on his return from a pilgrimage to Jerusalem, represented the condition…

Wine growing
"In Spain, Portugal, France, Italy, and elsewhere the manufacture of wine from grapes is an important…

German Street Corner
"Each is as big around as a hogshead, and about fifteen feet high; it is covered with printed manner,…

People of Odessa
"Odessa is the chief city of southern Russia, and men from all the countries about come here to trade."…

Drinking Tea in Russia
"The Russians drink more tea perhaps than any other people. The tea is served in glass tumblers, with…

Mowgli's Brothers
Baloo teaching Mowgli. "Thou has been with the Monkey People, the gray apes, the people without a Law,…

Mowgli's Brothers
Mowgli used to make little play-huts. The Monkey People considered these huts most wonderful.

Edward Lear's Rhymes
There was an old lady of Chertsey, who made a remarkable curtsey; She twirled round and round, till…

Edward Lear's Rhymes
There was an old person of Basing, whose presence of mind was amazing; He purchased a steed, which he…

Simple Simon
From a nursery rhyme, Simple Simon Met a Pieman. He went to ride a spotted cow that had a little…

Little Miss Fat
My Piggywig, Lulu, is fond of the sea. She looks a droll sight, but she doesn't mind that; Wither her…
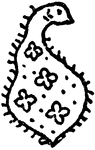
Rooster
The people of Shiraz personify the Devil in a form of a rooster, which they weave in some of their choicest…
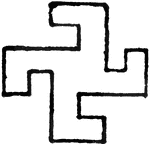
Swastika Design
"Derived from the Sanscrit word Svasti, which means good pretence. It dates bck three or four thousand…

Swastika Design
"Derived from the Sanscrit word Svasti, which means good pretence. It dates bck three or four thousand…
Swastika Design
"Derived from the Sanscrit word Svasti, which means good pretence. It dates bck three or four thousand…










