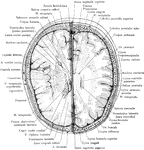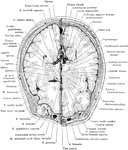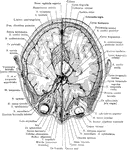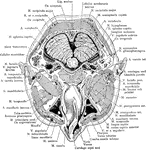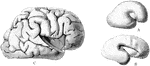
Cerebral Cortex
The most important association tracts of the brain. The fibers are projected upon the external surface…
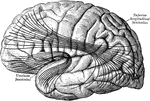
Cerebral Cortex
The most important association tracts of the brain. The fibers are projected upon the mesial (medial)…

Minute Structure of Cerebral Cortex
Diagram to illustrate minute structure of the cerebral cortex. Labels: A and B, neuroglia cells; C,…
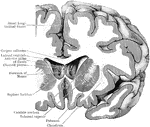
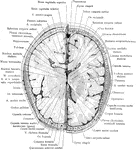
Coronal Section Through Cerebral Hemisphere
Coronal section through the right cerebral hemispheres as to cut through the anterior part (putamen)…
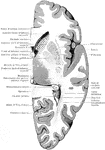
Section Through Cerebral Hemisphere
Horizontal section through the right cerebral hemisphere at the level of the widest part of the lenticular…
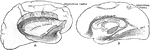
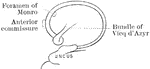
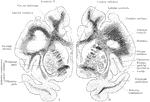
Association Bundles of the Cerebral Hemispheres
Diagram of the leading association bundles of the cerebral hemisphere. A, Outer aspect of hemisphere.…
Coronal Sections of the Cerebral Hemispheres
Two coronal sections through the cerebral hemisphere of an orangoutang, in the plan of the anterior…
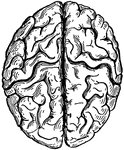
Cerebrum
"The Upper Surface of the Cerebrum. Showing its division into two hemispheres, and also of the convolutions."…
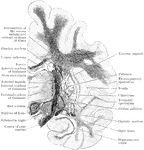
Coronal Section Through Cerebrum
Coronal section through the cerebrum of an orangoutang passing through the subthalamic tegmental region.
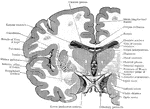
Coronal Section Through the Cerebrum
Coronal section through the cerebrum, so as to cut through the three divisions of the lenticular nucleus;…
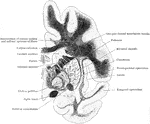
Coronal Section Through the Cerebrum
Coronal section through the left side of the cerebrum of an orangoutang. The section passes through…
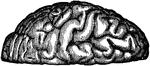
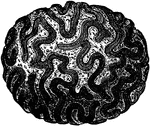
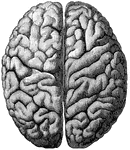
Convolutions of the Brain
View of the appearance of the tortuous elevations (convolutions) of the brain, seen from above.
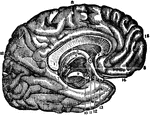
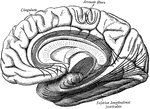
Corpus Callosum
Middle vertical section of the callous body (corpus callosum). The inner left side of the brain is also…
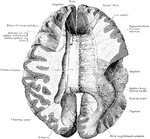
Corpus Collosum
The corpus callosum, exposed from above and the right half dissected to show the course taken by its…

Dissected Fish
"Dissected fish. a, air bladder; b, urinary bladder; b, urinary bladder; br, brain; c, spinal cord;…
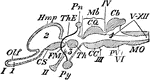
Encephalon
"Diagram of Vertebrate Encephalon ... in longitudinal vertical section. Mb, mid-brain; in front of it…
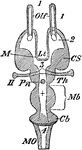
Encephalon
"Diagram of Vertebrate Encephalon ... in horizontal section. Mb, mid-brain; in front of it all is forebrain,…
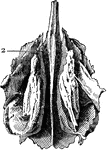
Ethmoid Bone of the Human Skull
Ethmoid bone, posterior surface. The ethmoid bone is an exceedingly light, spongy bone, placed between…
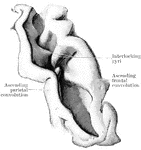
Fissure of Rolando
Fissure of Rolando fully opened up, so as to exhibit the interlocking gyri and deep annectant gyrus…

Section Through Forebrain of Human and Lepidosteus Embryos
Two cross sections through the forebrain. A. Through the forebrain of the early human embryo. B. Through…
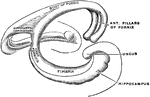
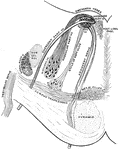
Fornix
The fornix is a paired structure consisting of bilaterally symmetrical halves composed of longitudinally…
Frontal Bone of the Human Skull
Frontal bone of the human skull, outer surface. The frontal bone forms the forehead, roof of the orbital…
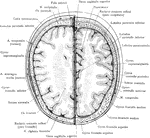
Cross Section of Head 3 cm above Supraorbital Border
Section of head 3 cm above supraorbital border.
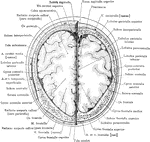
Cross Section of Head 4 cm above Supraorbital Border
Section of head 4 cm above supraorbital border.
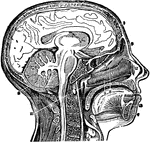
Head and Neck, Section of
Vertical middle section of head and neck showing the opening through the Eustachian tube, and its relations…
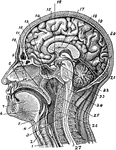
Section of the Head and Neck
Section of head and neck from front to back. Labels: 1, windpipe; 2, larynx; 3, spinal marrow; 4, pharynx;…
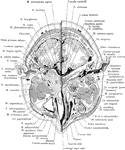
Cross Section of Head Exposing Maxillary Sinus
Section of the head immediately below the orbits, at the level of Reid's base line exposing the maxillary…
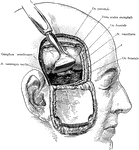
Incision of the Head Showing Gasserian Ganglion
Exposure of the Gasserian ganglion and middle meningeal artery though a flap incision of the scalp and…
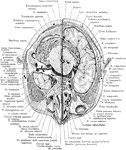
Cross Section of Head Through Lower Portion of Orbit
Section of the head through lower portion of orbit.
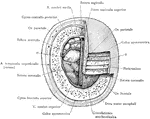
Cross Section of Head
Section two inches above supraorbital border. Upper surface. The (*) on right indicates subaponeurotic…
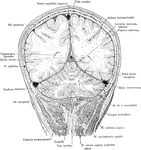
Frontal Section of the Head
Frontal section of the head passing through the parietal and occipital cerebral lobes and he cerebellar…
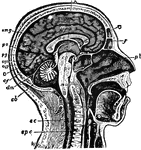
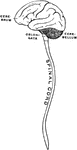
Human Brain
"The Brain is the encephalon, or center of the nervous system and the seat of consciousness and volition…
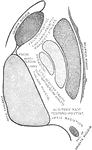
Internal Capsule
Diagrammatic representation of the internal capsule (as seen in horizontal section).
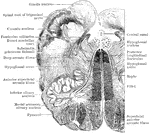
Section Through Medulla in Olivary Region
Transverse section through the human medulla in the lower olivary region.
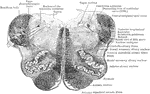
Section Through Medulla in Olivary Region
Transverse section through the the middle of the olivary region of the human medulla or bulb.
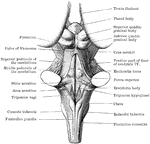
Back View of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Back view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
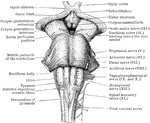
Front view of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Front view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
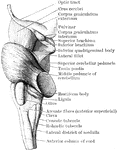
Lateral View of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Lateral view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
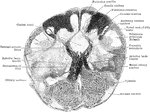
Transverse Section Through Closed Part of Medulla
Transverse section through the closed part of the human medulla immediately above the decussation of…
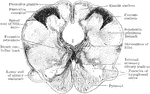
Transverse Section Through Closed Part of Fetal Medulla
Transverse section through the closed part of the fetal medulla immediately above the decussation of…

Transverse Section Through the the Medulla
Transverse section through the lower end of the medulla of a full term fetus.
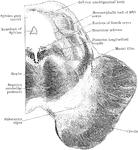
Section of Mesencephalon at Inferior Quadrigeminal Body
Transverse section through the mesencephalon at the level of the inferior quadrigeminal body.
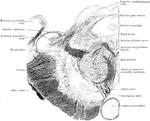
Section of Mesencephalon at Superior Quadrigeminal Body
Transverse section through the mesencephalon at the level of the superior quadrigeminal body.