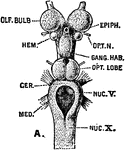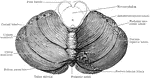
Brain of a Bird
In birds the hemispheres are not united as in humans; the cerebellum is proportionately larger than…
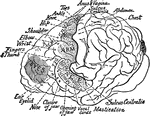
Motor Area of the Brain of a Chimpanzee
Location of the motor areas in the brain of a chimpanzee. The extent of the motor area is indicated…
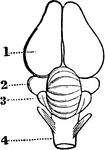
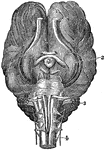
Brain of a Dog
Brain of dog, viewed from above and in profile. F, frontal fissure sometimes termed crucial sulcus,…
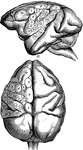
Brain of a Fish
The brain of fish are small, it does not fill the whole cranial cavity, there being found within it…
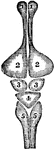
Base of Brain of a Horse
The base of brain of a horse. Labels: l, Cerebrum. 2, Ganglion of sight. 3, Cerebellum. 4, Medulla Oblongata…
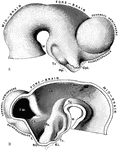
Brain of a Monkey to Show effects of Electric Stimulation
Diagrams of monkey's brain to show the effects of electric stimulation of certain spots. Labels: 1.…
Brain of an Alligator
In Amphibians the nervous system is but slightly developed. The cerebrum is small; the cerebellum is…
Brain of Embryo
The brain of a human embryo in the fifth week. A, Brain as seen in profile. B, Mesial section through…
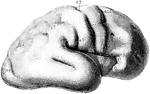
Brain of Fetus
The left cerebral hemisphere, from a fetus in the early part of the seventh month of development. Labels:…
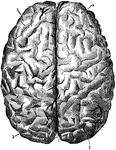
Brain Seen from Above
Labels: 1, longitudinal fissure separating the hemispheres; 2, frontal lobes of the cerebrum; 3, posterior…
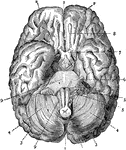
Brain Seen from Below
Labels: 1, longitudinal fissure separating the hemispheres; 2 and 3, front and posterior lobes of the…
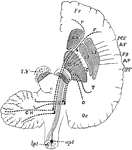
Brain Showing Connection of Frontal Occipital Lobe with Cerebellum
Diagram to show the connecting of the Frontal Occipital Lobes with the Cerebellum. The dotted lines…
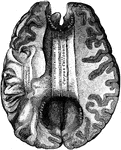
Brain Showing Corpus Callosum
Shown is the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum is a thick stratum of transversely directed nerve…
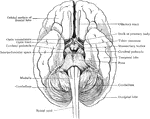
Relation of Brain Stem to Spinal Cord
Simplified drawing of brain as seen from below, showing relations of brain stem to spinal cord and cerebrum.
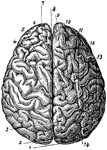
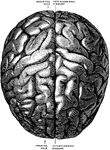
Brain Viewed from Above
The brain viewed from above. Labels: 1, occipital convolution; 2, occipital lobe; 3, inner parietal…
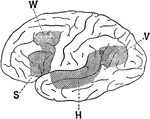
Association Area of the Brain
Lateral view of a brain hemisphere; cortical area V, damage to which produces "mind blindness" (word…
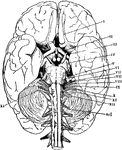
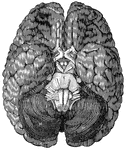
The Base of the Brain
The base of the brain. The cerebral hemispheres are seen overlapping all the rest. Labels: I, olfactory…
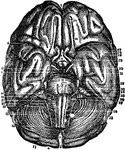
Base of the Brain
Base of the Brain. Labels: 1,2, longitudinal fissure; 3, anterior lobes cerebrum; 4, middle lobe; 5,…
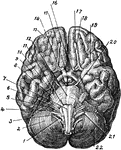
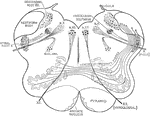
Base of Brain
The base of the brain. Labels: 1, eleventh or spinal accessory nerve; 2, right hemisphere of cerebellum;…
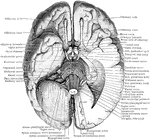
Base of the Brain
The base of the brain. The under part of the left temporal and occipital lobes has been sliced off so…
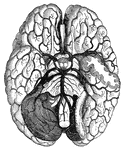
Blood vessels of the brain
"Arteries and their Branches at the Base of the Brain." — Blaisedell, 1904

Cerebellum of Dog's Brain
Vertical section of dog's cerebellum. Labels: p m, pia mater; p, corpuscles of Purkinje, which are branched…
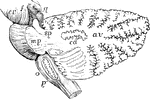
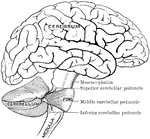
The Cerebellum of the Brain
Outline sketch of a section of the cerebellum, showing the corpus dentatum. The section has been carried…
The Cerebrum and Basic Ganglia of the Brain
Vertical section through the cerebrum and basic ganglia to show the relation of the latter. Labels:…
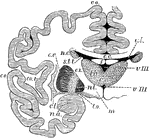
The Cerebrum and Fourth Ventricle of the Brain
The cerebellum in section and fourth ventricle, with the neighboring parts. Labels: 1, median groove…
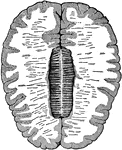
Cross-Section of the Brain
Cross-section of the brain. Here the upper half of the brain is cut off, and you see the upper cut surface…
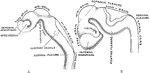
Development of Human Brain
Two stages in the development of the human brain. A. Brain of an human embryo of the third week. B.…
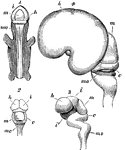
Development of the Brain
Early stages in development of human brain. 1, 2, 3, are from an embryo about seven weeks old; 4, about…
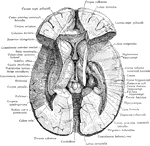
Dissection of the Brain
Dissection of the brain showing basal ganglia, third ventricle and adjacent structures viewed from above.
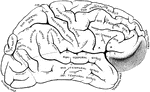
Gyri and Sulci on the Brain
Gyri and sulci, on the outer surface of the cerebral hemisphere. Labels: f1, sulcus frontalis superior;…
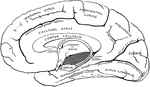
Gyri and Sulci on the Brain
The gyri and sulci on the mesial aspect of the cerebral hemisphere. Labels: r, fissure of Rolando; r.o,…
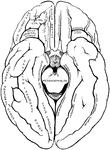
Gyri and Sulci on the Brain
The gyri and sulci on the tentorial and orbital aspects of the cerebral hemispheres.
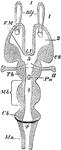
Horizontal Section of a Vertebrate Brain
Diagrammatic horizontal section of a vertebrate brain. Mb, midbrain: what lies in front of this is the…
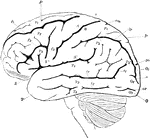
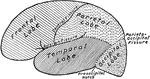
Lateral View of the Brain
Lateral view of the brain. F, Frontal lobe; P, Parietal lobe; O, Occipital lobe; T, Temporal lobe; S,…
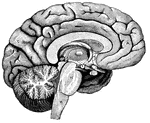
Left Half of the Brain
"A,frontal love of the cerebrum; B, parietal lobe; C, parieto-occipital lobe;…
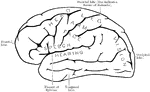
Motor Centers of the Brain
Diagram to indicate position of centers on the external surface of the brain.
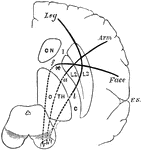
Motor Tracts of the Brain
Diagram to show the relative position of several motor tracts in their course from the cortex to the…
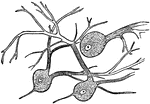
Nerve Cells of the Brain
"Wherever nerve cells are abundant, the nerve tissue has a gray color; in other places, it looks white.…
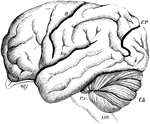
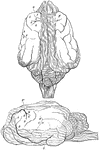
Brain of the Orangutan
Brain of the Orangoutang, showing arrangement of the convolutions. Sy, fissure of Sylvius; R, fissure…
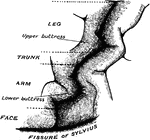
Precentral Gyrus in the Brain
The convolutionary projections of the precentral gyrus, and their relationship to motor areas.
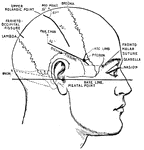
Principle Fissures of the Brain
Showing the lines which indicate the position of the principal fissures of the brain.
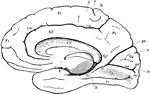
Right Hemisphere of the Brain
View of the right hemisphere in the median aspect. CC, corpus callosum longitudinally divided; Gf, gyrus…
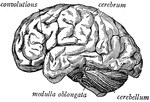
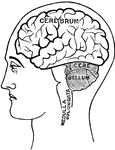
Side view of the brain
"The brain seen from the side, showing the three principal divisions." — Ritchie, 1918
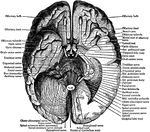
Under Surface of the Brain
View of the under surface of the brain, with the lower portion of the temporal and occipital lobes,…
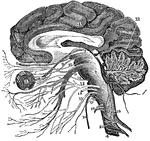
Vertical Section of the Brain
A vertical section of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata, showing the relation of the…
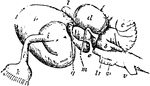
Carcharias Brain
"Brain of Carcharias. ae, nervus acousticus; b, corpus restiforme; c, cerebellum; d, lobus opticus;…
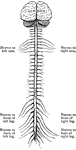
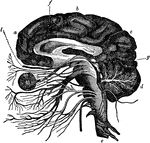
Central Nervous System
"Brain and spinal cord, with the thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves." — Tracy, 1888
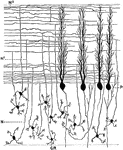
Sagittal Section Through Cerebellar Folium
Section through the molecular and granular layers in the long axis of a cerebellar folium. Labels: P,…
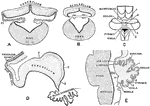
Development of Cerebellum
Showing the development of the cerebellum. A, Transverse section through the forepart of the cerebellum…
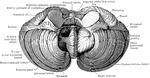
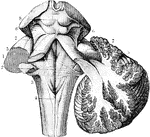
Lower Surface of Cerebellum
The lower surface of the cerebellum. The tonsil on the right side has been removed so at to display…
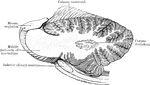
Sagittal Section Through Cerebellum
Sagittal section through the left lateral hemisphere of the cerebellum. Showing the "arbor vitae" and…