Leaf
Leaves are arranged in a great many different ways on their stems. Here are three leaves together on…

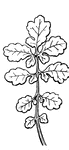
Leaf
Leaves are arranged in a great many different ways on their stems. Here the leaf-stem has three little…
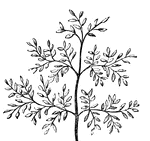
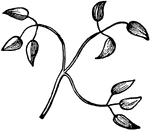
Leaf
Leaves are arranged in a great many different ways on their stems. On this leaf-stem are a great many…

Leaf
One of the three principal parts or organs of vegetation, generally flattened in shape, and greenish…
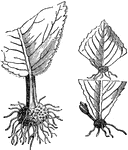
Leaf Cuttings
"Many plans may be propagated by planting their leaves or portions of their leaves as cuttings, as,…
Leaf Cuttings
"Many plans may be propagated by planting their leaves or portions of their leaves as cuttings, as,…

Leaf of Roman Diptych
An illustration of a roman diptych with gold leaf. A diptych is any object with two flat plates attached…
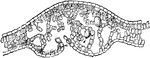
Blister Formed by Phytoptus Pyris by Leaf
In the middle of the blister, on its lower surface, is a small opening, which permits the gall mites…
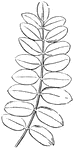
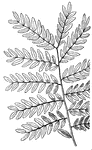
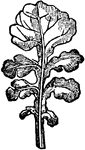
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a compound leaf. Pinnate leaves have their leaflets arranged along the sides of…
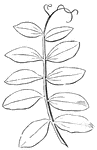
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a compound leaf. Pinnate leaves have their leaflets arranged along the sides of…
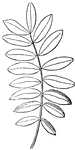
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a compound leaf. Pinnate leaves have their leaflets arranged along the sides of…
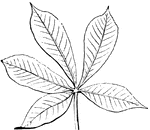
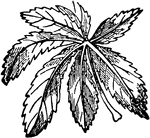
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a compound leaf. Palmate leaves have their leaflets arranged on the very end of…
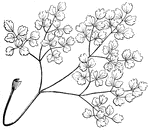
Compound Leaf
This is an example of a decompound leaf structure, meaning it is divided three or four times.
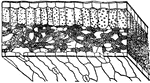
Cross-section of a leaf
Cross section of a leaf, showing the breathing pores and intercellular spaces. The small dots are grains…
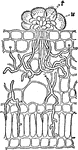
Diseased Leaf
"Transverse section of a diseased patch in the leaf showing the hyphae of the fungus pushing between…

Fork-Veined Leaf
"Fork-veined leaves are those in which the primary veins divide into two nearly equal secondary veins,…
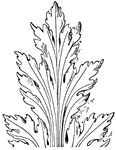
French Leaf Renaissance
The French Renaissance Leaf design tend to look more formal. This design was found in a church in Epernay…
Lanceolate Leaf
"Lanceolate, when it is three or more times as long as it is broad, and rounded at the base, and tapering…
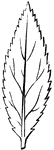
Lanceolate Leaf
Lanceolate leaves are lance or spear shaped. These leaves are narrowly elliptical, tapering to each…
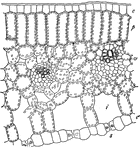
Lily Leaf
Cross section of leaf of lily, somewhat diagrammatic: e, upper epidermis,s, stomata in cross-section,…
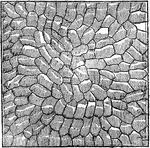
Microscopic view of a leaf
"The branch vascular bundles will be distinctly seen, resembling in some respects the arteries and veins…