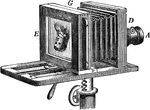
Bellows Camera
"The photographer's camera corresponds to the camera-obscura. A darkened box, adjustable in length,…
Catadioptric Holophote
"Catadioptric Holophote.—Part of the anterior hemisphere of rays is intercepted and at once parallelized…
Catadioptric Holophote
"Catadioptric Holophote.—Part of the anterior hemisphere of rays is intercepted and at once parallelized…
Convex Lens
"A modification of the simple kaleidoscope was introduced by Sir David Brewster, whereby the images…
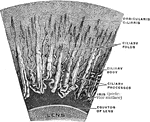
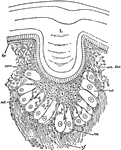
Magnified Corona Ciliaris
A portion of the corona ciliaris magnified. The ciliary processes and the ciliary folds.
Differential Lens
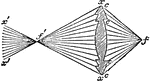
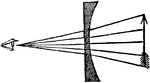
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
Differential Lens
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
Differential Lens
"Differential Lens.—Horizontal divergence may be obtained to any required amount by varying the radius…
Diffraction
"Throw a sunbeam through a very small opening in the shutter of a darkened room. Receive the beam upon…
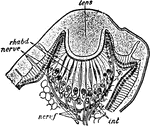
Euscorpius Italicus
"Section through the lateral eye of Euscorpius italicus. lens, Cuticular lens. nerv.c, Retinal cells…
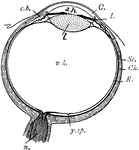
Eye
"Diagram of the eye. C., Cornea; a.h., aqueous humour; c.b., ciliary body; l., lens; I., iris; Sc.,…
Optical Position and Size of Image Through Lens in Front of Eye
The illustration of putting lenses in front of the eye. The focal point of the image is reflected into…
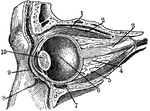
Eye Section
"Section through the left eye, closed. 1, lifting muscle; 2, upper straight muscle; 3, optic nerve;…
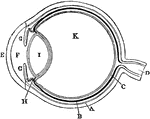
Diagram of the Eye
Plan of the eye seen in section. Labels: A, The Sclerotic Coat; B, The Choroid Coat; C, The Retina;…
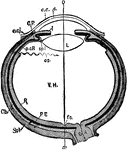
Human Eye
"Diagrammatic horizontal section of the eye of man. c, cornea; ch. choroid (dotted); C. P, ciliary processes;…

Lens of the Eye
Lens of the eye. The rays of light are brought nearer together by the lenses of the eye, just as they…
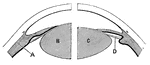
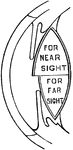
Lens of the eye
"Diagram showing the Change in the Lens during Accomadation. On the right the lens is arranged for distant…
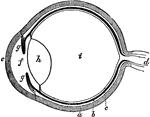
The Eye
The eye. Labels: a, sclerotica; e, cornea; b, choroid; d, optic nerve; f, aqueous humor; g g , iris;…
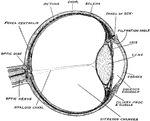
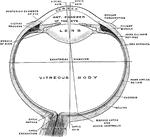
Eyeball
Horizontal section of the eyeball, showing the suspensory ligament of the lens, the aqueous and vitreous…
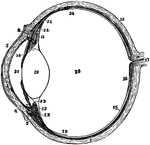
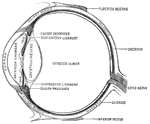
The Eyeball in Horizontal Section
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
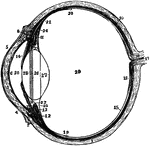
Section of Left Eyeball
The left eyeball in horizontal section from before back. Labels: 1, sclerotic; 2, junction of sclerotic…
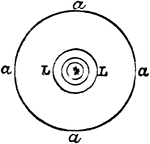
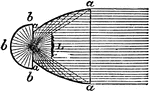
Holophotal Catadioptric
"Holophotal Catadioptric Apparatus Revolving round a Central Flame." —The Encyclopedia Britannica,…
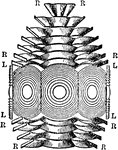
Holophotal Catadioptric
"Holophotal Catadioptric Apparatus Revolving round a Central Flame.—If in place of Fresnel's compound…
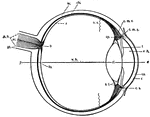
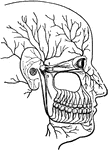
Human Eye
This diagram shows a side view of the right eye of man. a.c., central artery; a.h., aqueous humor; b.,…
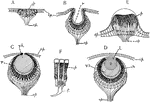
Invertebrate Simple Eye
"Diagrams showing some of the stages in the increasing complexity of the simple eye in Invertebrates.…
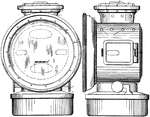
Lamp Body
This lamp body is used for a lighting fixture; an electrical device used to create artificial light.…
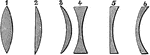
Lens
"A lens is a transparent body the two refracting surfaces of which are curved, or one of which is curved…

Upper Portion of Plant of Lens Esculenta
The common name of lens is lentils. Lens esculenta is the edible variety. The flowers are small and…
Lens of a Rabbit
Meridional section through the lens of a rabbit. Labels: 1, Lens capsule; 2, epithelium of lens; 3,…
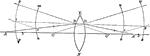
Refraction of Light through Bi Convex Lens
"...let LN represent a glass biconvex lens, with centres of curvature at C and C', and AB, the incident…
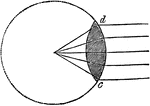
Double Convex Lens
"The shape of the double convex lens, d, c, is that of two plano-convex lenses, placed with their plane…
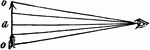
Double Convex Lens Magnifing an Arrow
"Double convex lenses are used in the eyeglasses for old people, becoming more spherical according to…
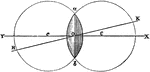
Double Convex Lens
"The double convex lens may be described as the part common to two spheres that intersect each other.…
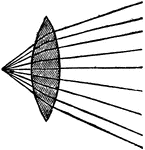
Converging Rays and a Double Convex Lens
"Thus the pencils of converging rays, are rendered still more convergent by their passage through the…
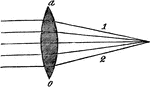
Diverging Rays from a Double Convex Lens
"If diverging rays fall on the surface of the same lens, they will, by refraction, be rendered less…
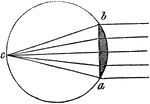
Plano Convex Lens
"If the whole circle be considered the circumfrence of a sphere, of which the plano-convex lens b, a,…
View of an Arrow Through a Plano Convex Lens
"View of an arrow through a plano convex lens will have the arrow appear smaller than it actually is."…
Section Through Lens
Section through the equator of the lens. Showing gradual transition of the epithelium into lens fibers.
Lenses of Various Forms
"a, prism; b, plane glass; c, spherical lens; d, double-convex; e, plano-convex, f, double-concave;…
Limulus
"Section through one of the central eyes of a young Limulus. L, Cuticular or corneous lens. hy, Epidermic…
Magnification of Image Beyond Axis with Lens
"The lens is spherically corrected for OO', but the sinecondition is not fulfilled. Hens the different…
Microscope
"A microscope consists of a lens or a combination of lenses used to observe small objects, often so…
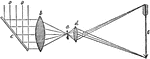
Solar Microscope
"This consists of two lenses, one of which is called the condesner, because it is employed to concentrate…
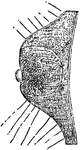
Ocellus
"Ocellus of a medusa (Lizzia Koellikeri). oc, pigmented ectodermal cells; l, lens." — Encyclopedia…
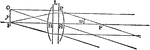
Optical Position and Size of Image Through Magnifying Glasses
"If y be the object the image appears to a normal eye situated behind the system L with passive accommodation…
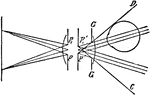
Optical Position of Diaphragms using Lens
"The intersection of the principal rays in this case lies in the middle of the entrance pupil or of…
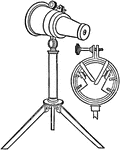
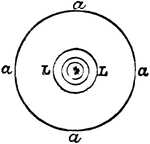
Polyangular Kaleidoscope
"Another form is called the polyangular kaleidoscope. The only essential difference in it is that the…
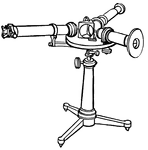
Prism Spectroscope from the Late 19th Century
"...a tube with a slit at the further end through which the light enters, and at the other end a collimating…
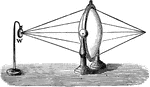
Sound Refraction
"Fill with carbon dioxide a large rubber toy balloon or other double-convex lens having easily flexible…
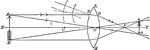
Object Refracted through Biconvex Lens
"Showing how an object is refracted through a biconvex lens." -Avery 1895
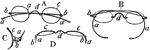
A Collection of Spectacles
"A, spectacles with bows hinged to the shoulders on the rims connected by the nose or bridge. B, spectacles…
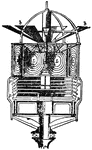
Stevensons Revolving Light
"In 1835 Mr. Stevenson, in a report to the Northern Lighthouse Board, proposed to add fixed reflecting…
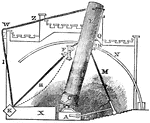
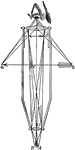
Telescope
"The following description of a section of Lord Rosse's telescope, though not so perfect as could be…