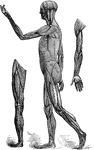Clipart tagged: ‘muscles’
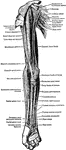
Muscles on the Front of the Arm and Forearm
Superficial muscles on the front of the arm and forearm.
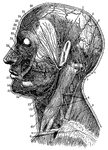
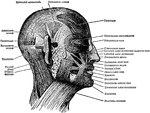
Arteries and Nerves
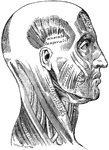
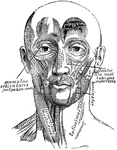
"Superficial arteries and nerves of the face and neck. 1, Temporal artery; 2, artery behind the ear;…
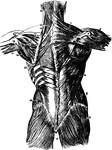
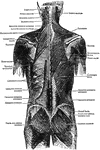
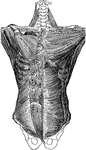
Muscles of the Back
Second layer of muscles of the back. Labels: 1, trapezius; 2, a portion of the ten dinous ellipse formed…

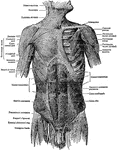
Superficial Muscles of the Body
"A single muscle rarely or never contracts alone, but always in harmony with a number of other muscles.…
Muscles of the Forearm
Outer layer of muscle on the back of the forearm. Labels: 1, biceps flexor; brachialis internus; 3,…
Muscles of the Forearm
Outer layer of muscles on the front of the forearm. Labels: 1, biceps flexor cubiti; 2, brachialis internus;…
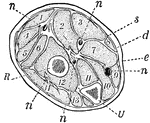
Forearm, Section of
A section across the forearm a short distance below the elbow-joint. R and U, its two supporting bones,…
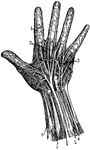
Hand Nerves
"Nerves of the had. 1, Nerves of the skin; 2, tendons; 3, arteries of the palm of the hand; 4, elbow…
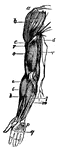
Arm Muscle
A,b,c, deltoid muscle; d, coracobrachialis muscle; r,r, triceps;e,i, extensors of the hand; km, flexor…

Muscles
A frontal view of the human muscles. The right half shows superficial muscles and the left half shows…
Muscles
Diagram illustrating the muscles (drawn in thick black lines) which pass before and behind the joints,…

Forms of Muscles and Tendons
Forms of muscles and tendons. Labels: A, adductor of thigh; B, biceps of arm; D, deltoid, G, gastrocnemius;…

Muscles of Different Forms
Diagrams illustrating, A, typical muscle with a central belly and two terminal tendons; B, a penniform…

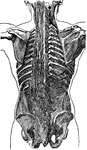
Back View of the Muscles of the Body
Muscle of the body, back view: The fascia is left upon the left limbs, removed from the right.

Front View of the Muscles of the Body
Muscle of the body, front view: On the right half, the superficial muscles; left half, deep-seated muscles.
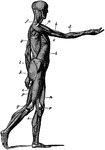
Side View of the Muscles of the Body
Side view of the muscles of the body, showing those that lie directly under the skin. Other deeper muscles…
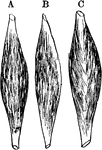
Typical Muscles
Diagrams of typical muscles with a central belly and two terminal tendons. Labels: b, a penniform muscle;…
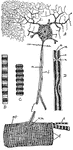
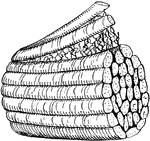
Muscular Tissue
This illustration shows a diagram of nervous and cross-striate muscular tissue, showing the mode of…
Nervous System
Element of Nervous System. a: Sensory fiber; b: Motor fiber; c: Center; f: End of sensory fiber; m:…
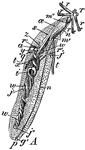
Peanut Worm - Interior Anatomy of Adult
Sipunculus nudus. A species of unsegmented marine worm, commonly called the peanut worm. "A, One fourth…
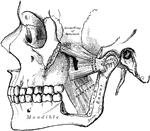
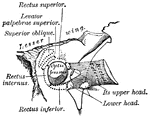
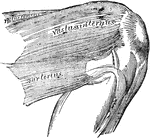
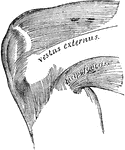
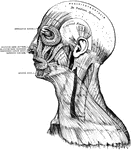
Pterygoid Muscles
The Pterygoid muscles, the zygomatic arch, and a portion of the ramus of the mandible have been removed.
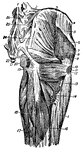
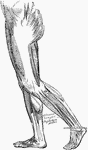
Rear Thigh Muscles
The muscles of the rear thigh. 1, fifth lumbar vertebra; 2, ilio-lumbar ligament; 3, crest of ilium;…
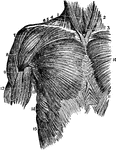
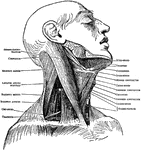
Muscles of the Upper Trunk
Superior muscles of the upper front of the trunk. Labels: 1, sterno-hyoid; 2, sterno-cleido-mastoid;…