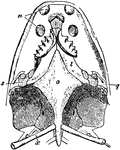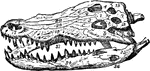
Acrodont
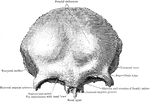
"Skull of lizard with Acrodont Dentition. One of those lizards which have the edge of the jaw, without…
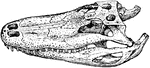
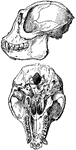
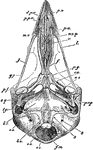
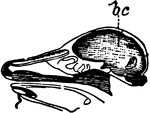
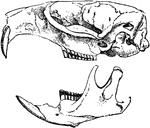
Alligator Skull
"Skull of a member of the family Alligatoridæ, or some American member of the Crocodilidæ."-Whitney,…
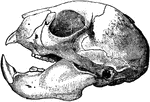
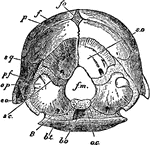
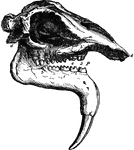
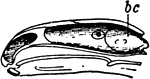
Aye-Aye Skull
"Skull of the Aye-aye (Chiromys madagascariensis)." —The Encyclopedia Britannica, 1910
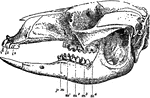
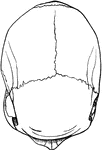
Bennett's Kangaroo
"Skull and teeth of Bennett's Kangaroo (Macropus bennettii). i1, i2, i3, first second and third upper…
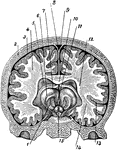
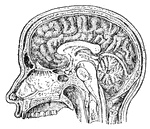
Brain
A cross section of the brain from left to right. Labels: 1, thalamus; 2, skull; 3, cerebral membrane;…
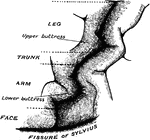
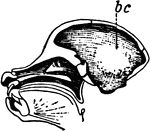
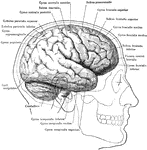
Precentral Gyrus in the Brain
The convolutionary projections of the precentral gyrus, and their relationship to motor areas.
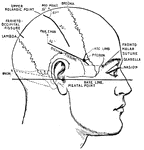
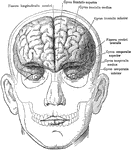
Principle Fissures of the Brain
Showing the lines which indicate the position of the principal fissures of the brain.
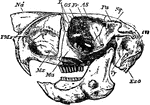
Cape Jumping Hare
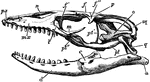
"Side view of skull of Cape Jumping Hare. Pmx, premaxilla; Mx, maxilla; Ma, malar; Fr, frontal; L, lachrymal;…
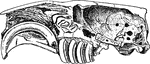
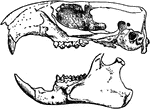
Castor Fiber
"Vertical and Longitudinal section through skull of Castor Fiber, showing the cerebral cavity, the greatly-developed…

St. Jerome In His Cell
St. Jerome in his Cell is an engraving that was created by German artist Albrecht Dürer in 1514.…
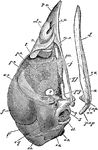
Ripe Chick's Skull Profile
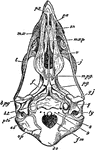
"Ripe chick's skull, longitudinal section, vied inside, x 3 diameters; after Parker. px, premaxillary;…
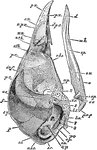
Ripe Chick's Skull
"Ripe chick's skull, longitudinal section, vied inside, x 3 diameters; after parker. In the mandible…
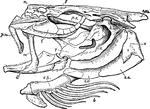
Cod Skull
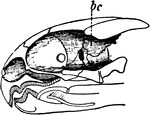
"The skull of a cod. b, branchiostegal rays born on c.h., the ceratohyal bone; d, dentary portion of…
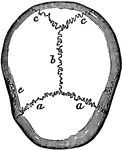
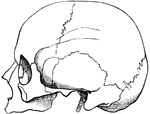
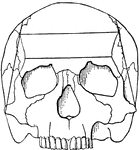
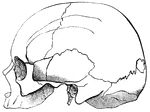
Cranial Sutures
The bones of the top of the head are fastened together by what are called sutures which are locked together…
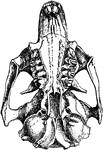
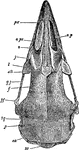
Cynomys Ludovicianus
"Under Side of Skull of Cynomys Ludovicianus." —The Encyclopedia Britannica, 1903

The Arms of Death
The Arms of Death is an engraving that was created by German artist Albrecht Dürer in 1503. It…
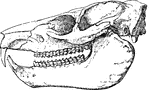
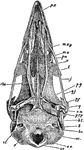
Dendrohyrax Dorsalis
"Skull and Dentition of Dendrohyrax Dorsalis." —The Encyclopedia Britannica, 1903
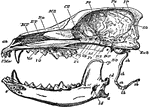
Dog Skull
"Longitudinal and Vertical section of the skull of a dog, with mandible and hyoid arch. an, anterior…
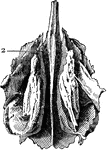
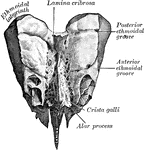
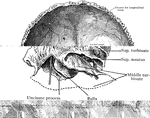
Ethmoid Bone of the Human Skull
Ethmoid bone, posterior surface. The ethmoid bone is an exceedingly light, spongy bone, placed between…
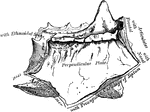
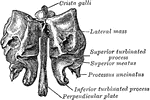
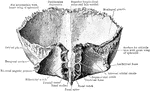
Perpendicular Plate of Ethmoid
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid, shown by removing the right lateral mass.
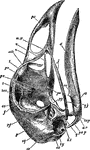
Fowl Skull
The skull of an adult fowl. Here the temporal fossa is bridged over by the junction of the post-frontal…
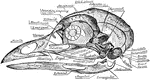
Skull of a Common Fowl
"Fig. 62 Skull of common fowl, enlarged. from nature by Dr. R.W. Shufeldt, U.S.A. The names of bones…
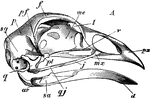
Skull of Common Fowl
"Typical Skull of Common Fowl (Galliformes). A, side view: sa, surangular bone of mandible; ar, articular…
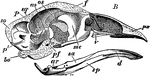
Skull of Common Fowl
"Typical Skull of Common Fowl (Galliformes). B, vertical longitudinal section: sa, surangular bone of…
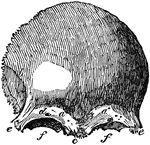
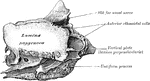
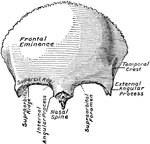
Frontal Bone
A front view of the frontal bone; a,a, frontal sinuses; b, the temporal arch, beneath which lies the…
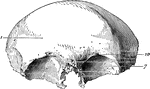
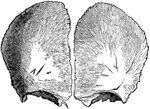
Frontal Bone of the Human Skull
Frontal bone of the human skull, outer surface. The frontal bone forms the forehead, roof of the orbital…
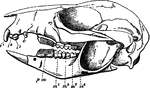
Gray's Rat Kangaroo
"Skull and teeth of Gray's Rat Kangaroo (Bellongia grayii). c, upper canine tooth. i1, i2, i3, first,…