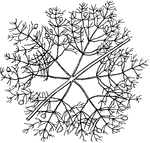
Banyan
The banyan is actually a variety of a fig plant that germinates in the branches of trees. It sends down…

Camphor
The camphor plant is known for its essential oil that gives it its characteristic odor. The oil is distilled…

Lemur
The lemur (Latin, lemures, ghosts) get their name from the fact that their movements are noiseless,…

Kinkajou
The kinkajou lives in S. America and spends most of its life in trees. It hunts at night for insects…
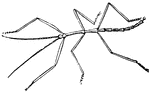
Walking Stick
Walking sticks lead a sluggish life among the branches of shrubs, living on the young shoots. Their…

Leaf Insect
Walking Sticks and Leaf Insects lead a sluggish life among the branches of shrubs, living on the young…

Chameleon
This type of lizard lives on trees, clinging to the branches by their feet and prehensile tails. They…

Leaf
Leaves are arranged in a great many different ways on their stems. Here the leaf-stem has three little…

Magnolia Seed
This is the cucumber-tree, Magnolia acuminata fruit discharging its seed", (Keeler, 1915).
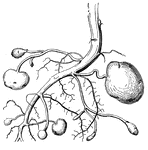
Potato Root
This shows real roots of the potato, as well as several branches of the stem, with potatoes forming…
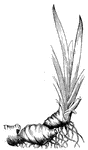
Solomon's Seal Root
In some perennial herbs, prostrate stems or branches underground are thickened with this store of nourishment…
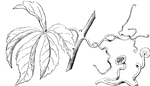
Tendrils
Tendrils, such as these of the Virginia Creeper, are very slender, leafless branches, used to enable…
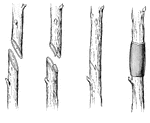
Grafting
(a) the two branches to be joined; (b) a tounge cut in each; (c) how fitted together; (d) method of…

77th Pennsylvania Regiment
"Captain Muller's Battery Company of the Seventy-seventh Pennsylvania Regiment making fascines and gabions…

Monk Saki
"The monkeys of this genus are marked by a short head, an angular muzzle, and a non-prehensile tail.…

Satanic Saki
"The monkeys of this genus are marked by a short head, an angular muzzle, and a non-prehensile tail.…

Masquerade of War
"The Masquerade of War. Ingenious method of disguising the masts and hulls of Commodore Porter's morter…

Waterhouse's Battery
"Waterhouse's Battery, Sherman's Corps, before Vicksburg. The interior view of Waterhouse's battery,…

War in Georgia
"The war in Georgia- Stevenson, Ala., depot for General Rosecrans's Army. The campaign of General Rosecrans…

Fruitful cotton plant
An early, rapid fruiting, productive type of cotton plant, with low fruit limbs, short joints and continuous…

Continental Bills
Fac-simile of the Continental Bills. The paper on which these bills were printed was quite thick, and…

Liberty Tree
"Liberty Tree. I am indebted to the Hon. David Sears, of Boston, for this sketch of the 'Liberty Tree,'…

Jamestown Island
"Distant view of Jamestown Island. This view is from the north side of what was once a marsh, but now…

Nelson Mansion
"The Nelson Mansion. This view is from the street looking northwest. A long wooden building, with steep…

Banyan Tree
"The Banyan Tree is a species of the genus ficus. It is regarded as a sacred tree by the Hindus. Its…

Breadfruit
"The breadfruit is a large, globular fruit of a pale-green color, about the size of a child's head,…

Breadfruit Fruit
"The breadfruit is a large, globular fruit of a pale-green color, about the size of a child's head,…

Walnut
"Walnut is a genus comprising seven or eight species of beautiful trees. The common walnut is a native…

Green Woodpecker
"Woodpecker is the popular name of the old Linnæan genus Picus, now greatly divided. Woodpeckers…
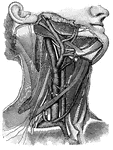
Blood vessels of the neck
"Showing the carotid artery and jugular vein on the right side, with some of their main branches; also…

Arteries
"The Right Axillary and Branchial Arteries, with Some of their Main Branches." — Blaisedell, 1904
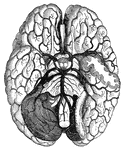
Blood vessels of the brain
"Arteries and their Branches at the Base of the Brain." — Blaisedell, 1904
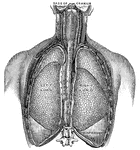
Lungs
"Relative Postion of the Lungs, the Heart, and Some of the Great Vessels belonging to the latter. A,…
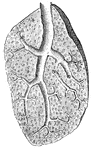
Lobule of a Lung
"Showing the structure of a lobule of the lung. The lobule has been injected with mercury, afterwards…

Lake Dwellings
"The earliest account of lake dwellings is to be found in Herodotus, who describes a Thracian tribe…
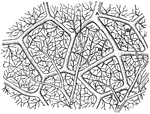
Capillaries of the Air Sac
"Diagram showing the capillary network of the air sacs and origin of the pulmonary veins.. A,…
Nerve Cells
"Nerve tissue is really made up of a great number of distinctive units called nerve cells.…
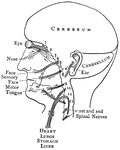
Distribution of the Cranial Nerves
"The cranial nerves are thus arranged in pairs: 1, olfactory nerves, special nerves of smell; 2, optic…
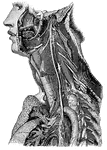
Trunk of the Pneumogastric Nerve
"Showing its distribution by its branches and ganglia to the larynx, pharynx, heart, lungs, and other…
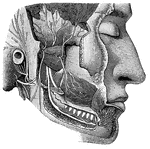
Cranial Nerves
"Dental Branch of One of the Divisions of the Fifth Pair of Cranial Nerves, supplying the Lower Teeth.…
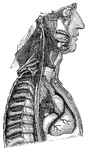
Sympathetic nerve
"The Cervical and Thoracic Portions of the Sympathetic Nerve and their Main Branches. In the center…
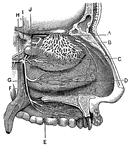
Cranial Nerves
"Dental Branches of One of the Divisions of the Fifth Pair of Cranial Nerves, supply the Upper Teeth."…

Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Crural) and its branches on the Front of the Thigh. The femoral artery with its cut…
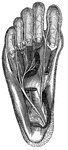
Great Nerve
"A Great Nerve (Plantar) and its Branches which supply the Bottom of the Feet. Note the cut tendons…
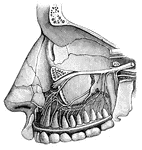
Nerves of the Nostril
"A, branches of the nerves of smell; B, nerves of touch to the nostrils; E, F,…

Orang Outang
"The Orang Outang is the Mias of the Dyaks; also known as the 'wild man of the wood.' It is a dull,…
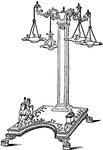
Candelabrum
"Originally a candlestick, but afterwards the name of a stand for supporting lamps, in which signification…

Seventeen Year Locust
The Seventeen Year Locust (Cicada septendecim) spends seventeen years underground feeding on the roots…

Giant Sloth
"Sloth is the popular name for any individual of the Edentate group Tardigrada, from their slow and…
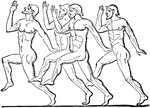
Foot-race
"The Olympic games were of greater efficacy than the Amphictyonic Council in promoting the spirit of…
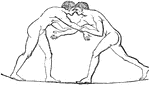
Wrestling
"The Olympic games were of greater efficacy than the Amphictyonic Council in promoting the spirit of…
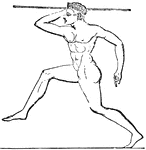
Hurling the javelin
"The Olympic games were of greater efficacy than the Amphictyonic Council in promoting the spirit of…