The 1861-1865 Civil War Land Battles ClipArt gallery offers 270 illustrations of land battles that were fought between the Union and the Confederacy during the American Civil War.

Battle of Pea Ridge
"Battle of Pea Ridge, Ark., fought March 6th, 7th and 8th, 1862, between the Federal forces, 13,000…

Battle of Pea Ridge
"Battle of Pea Ridge, Ark., fought March 6th, 7th and 8th, 1862, between the Federal forces, 13,000…

Battle of Pea Ridge
"General Asboth and staff at the Battle of Pea Ridge, Ark., March 6th-8th, 1862. The gallantry displayed…

Battle of Perryville
The Battle of Perryville, also known as the Battle of Chaplin Hills, was fought on October 8, 1862,…

Siege of Petersburg
"The Siege of Petersburg, Va. Charge of the second division, Ninth Army Corps, into the crater, July…
!["Siege of Petersburg. The [African American] infantry bringing in captured guns and cheers of the Ohio troops. When the [African American] troops found themselves within the works of the enemy no words could paint their delight. Numbers of them kissed the guns they had captured with extravagant satisfaction, and a feverish anxiety was minfested to get ahead and charge some more of the Confederate works. A number of the [African American] troops were wounded and a few killed in the first charge. A large crowd congregated, with looks of unutterable admiration, about Sergeant Richardson and Corporal Wobey, of the Twenty-second United States [African American] regiment, who had carried the colors of their regiment and been the first men in the works. Our artist gives a sketch of this gallant action."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/11800/11801/petersburg_11801_mth.gif)
Siege of Petersburg
"Siege of Petersburg. The [African American] infantry bringing in captured guns and cheers of the Ohio…
!["Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine, July 30th, 1864. Immediately after the explosion of the mine a hundred cannons opened along the Federal front, and at half-past five the Ninth Corps charged, carrying the fort with a part of the line on each side. The Second Division, which was in the centre, advanced and carried the second line a short distance beyond the fort, and rested, holding ground with the utmost determination. It was at the time the [African American] Division, under General White, was pushed forward and ordered to charge and carry the crest of the hill, which would have decided the contest. The troops advanced in good order as far as the first line, where they received a galling fire, which checked them, and although quite a number kept on advancing, the greater number seemed to become utterly demoralized, part taking refuge in the fort, and the remainder running to the rear as fast as possible. They were rallied and again pushed forward, but without success, the greater part of the officers being killed or wounded."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/11800/11856/petersburg_11856_mth.gif)
Siege of Petersburg
"Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine,…
!["Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine, July 30th, 1864. Immediately after the explosion of the mine a hundred cannons opened along the Federal front, and at half-past five the Ninth Corps charged, carrying the fort with a part of the line on each side. The Second Division, which was in the centre, advanced and carried the second line a short distance beyond the fort, and rested, holding ground with the utmost determination. It was at the time the [African American] Division, under General White, was pushed forward and ordered to charge and carry the crest of the hill, which would have decided the contest. The troops advanced in good order as far as the first line, where they received a galling fire, which checked them, and although quite a number kept on advancing, the greater number seemed to become utterly demoralized, part taking refuge in the fort, and the remainder running to the rear as fast as possible. They were rallied and again pushed forward, but without success, the greater part of the officers being killed or wounded."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/13900/13915/petersburg_1_13915_mth.gif)
Siege of Petersburg
"Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine,…
!["Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine, July 30th, 1864. Immediately after the explosion of the mine a hundred cannons opened along the Federal front, and at half-past five the Ninth Corps charged, carrying the fort with a part of the line on each side. The Second Division, which was in the centre, advanced and carried the second line a short distance beyond the fort, and rested, holding ground with the utmost determination. It was at the time the [African American] Division, under General White, was pushed forward and ordered to charge and carry the crest of the hill, which would have decided the contest. The troops advanced in good order as far as the first line, where they received a galling fire, which checked them, and although quite a number kept on advancing, the greater number seemed to become utterly demoralized, part taking refuge in the fort, and the remainder running to the rear as fast as possible. They were rallied and again pushed forward, but without success, the greater part of the officers being killed or wounded."— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/13900/13917/petersburg_2_13917_mth.gif)
Siege of Petersburg
"Siege of Petersburg- the Ninth Corps charging on the enemy's works after the explosion of the mine,…

Battle of Pittsburg Landing
Recapture of artillery by the First Ohio and other regiments under General Rousseau, April 7, 1862.…

Pocotaligo Bridge
"The Federal troops under Generals Brannan and Terry driving the Confederates under beauregard across…

Battle of Poplar Spring Church
"Grant's movements south of the James- Battle of Poplar Spring Church- the Ninth Corps passing Poplar…

Battle of Poplar Spring
"Grant's movements south of the James- Battle of Poplar Spring Church- gallant charge of a part of the…

Battle at Potomac
"Engagement between the Federal troops and the Confederates on the Virginia side of the Potomac, opposite…

Battle of Ream's Station
"The Siege of Petersburg. Battle of Ream's Station- the attempt of the enemy to regain the Weldon Railroad…

Sixth Regiment
"Gallant charge of the Sixth Regiment, United States Regular Cavalry, upon the Confederate Stuart's…

Battle of Resaca
"Battle of Resaca, Ga., May 14th, 1864. Geary's Second Brigade charging up the mountain."— Frank…

Battle of Rich Mountain
"The battle of Rich Mountain, Beverly Pike, Va., between a division of Major General McClellan's command,…

Battle of Rich Mountain
The Battle of Rich Mountain took place on July 11, 1861, in Randolph County, Virginia as part of the…

Mission Ridge
Mission Ridge (or Missionary Ridge) was the site of the November 25, 1864 Civil War battle, the Battle…

Battle of Roanoke Island
"Battle of Roanoke Island, February 8th, 1862- decisive bayonet charge of the Ninth New York Volunteers…

Battle of Roanoke Island
"Battle of Roanoke Island, February 8th, 1862- decisive bayonet charge of the Ninth New York Volunteers…

Battle of Roanoke Island
"Battle of Roanoke Island, February 8th, 1862- decisive bayonet charge of the Ninth New York Volunteers…

Battle of Roanoke Island
"Battle of Roanoke Island, February 8th, 1862- decisive bayonet charge of the Ninth New York Volunteers…

Roemer's Battery
"The war in Virginia- Roemer's Battery, Third Division, Ninth Army Corps, shelling Petersburg. Our readers…

Engagement at Romney
"Engagement at Romney, VA., twenty miles from New Creek, Tuesday, June 11th, 1861- the Eleventh Indiana…

Battle of Savages Station
"Battle of Savages Station. Brigadier General Smith's division hotly engaged with the enemy, at noon,…

Battle of Secessionville
"Battle of Secessionville, James Island, S. C.- bayonet charge of Federal troops, commanded by General…

Shenandoah Valley
"The army of General Fremont on its march up the Shenandoah Valley- wounded and ragged soldiers. Fremont…

Valley of the Shenandoah
"Sheridan's campaign in the Valley of the Shenandoah- Battle of Summit Point, Sunday, August 21st, 1864."—…

Sheridan's Great Battle
"The war in Virginia- Sheridan's Great Battle with J. E. B. Stuart at Yellow Tavern, May 11th, 1864-…

Sherman's Campaign
"Sherman's Campaign in Georgia- the attack of the Fourteenth, Sixteenth and Twentieth Army Corps on…

Battle of Shiloh
"Battle of Shiloh, or Pittsburg Landing, left wing- the woods on fire during the engagement of Sunday,…

Battle of Shiloh
"Battle of Shiloh, or Pittsburg Landing, left wing- the woods on fire during the engagement of Sunday,…

Battle of Shiloh
"Battle of Shiloh, or Pittsburg Landing, left wing- the woods on fire during the engagement of Sunday,…

Siege of Corinth
The Siege of Corinth, also known as the First Battle of Corinth, was a Civil War battle fought from…

Battle of South Mountain
"Federal artillery taking up position at the Battle of South Mountain. The Federal movement was admirably…

Battle of South Mountain
The Battle of South Mountain (known in several early Southern accounts as the Battle of Boonsboro Gap)…

Battle of South Mountain
The Battle of South Mountain, also known as the Battle of Boonsboro Gap, fought on September 14, 1862…

Battle of Spottsylvania
"The war in Virginia. Battle of Spottsylvania Courthouse- opening of the fight at Alsop's Farm, May…
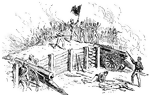
Fort Steadman
The Battle of Fort Steadman was one of the Confederacy's last attempts to besiege Petersburg, Virginia.…

Battle of Stone River
"Battle of Stone River, Tenn. The decisive charge of General Negley's division across the river- the…

Battle of Stone River
"Battle of Stone River, Tenn. The decisive charge of General Negley's division across the river- the…

Battle of Stone River
"Battle of Stone River, Tenn. The decisive charge of General Negley's division across the river- the…

Battle of Stone River
"Battle of Stone River, Tenn. The decisive charge of General Negley's division across the river- the…

Battle of Stone River
"Battle of Stone River, Tenn. Decisive charge and capture of Byrne's Confederate battery by the Seventy-eighth…

War in Tennessee
"The war in Tennessee. Federal pickets approached by Confederates in cedar bushes near Chattanooga.…

War in Tennessee
"The war in Tennessee. Capture of Mission Ridge, near Rossville, by General Thomas, November 25th, 1863.…

War in Tennessee
"The war in Tennessee- Lookout Mountain and its vicinity, from the position of the Eleventh Army Corps."—…

War in Tennessee
"The war in Tennessee- Confederate massacre of Federal troops after the surrender at Fort Pillow, April…
War in Texas
"The War in Texas. Brownsville, occupied by the army under Major General N. P. Banks, in 1863. The sudden…

Little Round Top
A war council at the top of Little Round Top in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. It was the site where the…