The 1861-1865 Civil War Land Battles ClipArt gallery offers 270 illustrations of land battles that were fought between the Union and the Confederacy during the American Civil War.

Attack at Harrisonburg
"Gallant attack by 150 of the Pennsylvania Bucktails, led by Colonel Kane, upon a portion of General…

Attack at Harrisonburg
"Gallant attack by 150 of the Pennsylvania Bucktails, led by Colonel Kane, upon a portion of General…

Attack at Harrisonburg
"Gallant attack by 150 of the Pennsylvania Bucktails, led by Colonel Kane, upon a portion of General…

Attack at Harrisonburg
"Gallant attack by 150 of the Pennsylvania Bucktails, led by Colonel Kane, upon a portion of General…

Battle of Hatcher's Creek
"The army of the Potomac- Battle of Hatcher's Creek, Va., October 27th, 1864- the Second Corps, under…

Hooker's Battle
"The war in Tennessee. Hooker's Battle above the clouds, and capture of the Confederate position on…
!["Assault of the Second Louisiana [African American] Regiment on the Confederate works at Fort Hudson, May 27th, 1863. The Battle of Fort Hudson was a severe and well-fought action. The Federal troops displayed their usual bravery, and were well handled by General Banks, driving the enemy to his second line of works. Of the [African American] regiments General Banks, in his official report, says: 'They answered every expectation. Their conduct was heroic. No troops could be more determined or more daring. They made during the day three charges upon the batteries of the enemy, suffering very heavy losses, and holding their position at nightfall with the other troops on the right of our line. The highest commendation is bestowed upon them by all officers in command on the right. Whatever doubt may have existed heretofore as to the efficiency of organizations of this character, the history of this day proves conclusively to those who were in a condition to observe the conduct of these regiments that the Government will find in this class of troops effective supporters and defenders. The severe test to which they were subjected, and the determined manner with which they encountered the enemy leave upon my mind no doubt of their ultimate success. They require only good officers, commands of limited numbers, and careful discipline to make them excellent soldiers.'"— Frank Leslie, 1896](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/11800/11805/ft-hudson_11805_mth.gif)
Fort Hudson
"Assault of the Second Louisiana [African American] Regiment on the Confederate works at Fort Hudson,…

Jackson's Men Rush into the Federal Camp
Thomas J. (Stonewall) Jackson's men rush into the Federal camp at Chancellorsville

James Island
"Repulse of the Confederates at James Island, near Charleston, S. C., June 10th, 1862, in the attempt…

Kentucky Raid
"The Confederate raid into Kentucky- the fight at the Licking Bridge, Cynthiana, between the Federal…

Kentucky Raid
"The raid in Kentucky- the Confederate Morgan with his guerillas bivouacking in Courthouse Square, Paris,…

Captain Knapp
"Captain Knapp's Battery engaging the Confederates at the battle of Cedar Mountain, August 9th, 1862-…

Battleground of Little Round Top
Little Round Top is the smaller of two rocky hills south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. It was the site…

Battle of Lookout Mountain
"The Battle of Lookout Mountain, also known as the Battle Above the Clouds."—E. Benjamin Andrews…

Capture of Lost Mountain
"The war in Georgia. Capture of Lost Mountain by General Hooker, June 16th, 1864. On June 14th General…

War in Louisiana
"The war in Louisiana. The army of General Banks crossing Vermilion Bayou, October 10th, 1863. Our artist…

War in Louisiana
"The war in Louisiana- Battle of Mansfield, between General Banks and General Dick Taylor, April 8th,…

War in Louisiana
"The war in Louisiana. General Banks's army, in the advance on Shreveport, crossing Cane River, March…

Battle of Malvern Hill
"Battle of Malvern Hill, near Turkey Bend, James River, Va., fought Tuesday, July 1st, 1862. The battle…

Battle of Malvern Hill
"Battle of Malvern Hill, near Turkey Bend, James River, Va., fought Tuesday, July 1st, 1862. The battle…

Battle of Malvern Hill
"Battle of Malvern Hill, near Turkey Bend, James River, Va., fought Tuesday, July 1st, 1862. The battle…

Battle of Malvern Hill
"Battle of Malvern Hill, near Turkey Bend, James River, Va., fought Tuesday, July 1st, 1862. The battle…

Battle of Malvern Hill
"Battle of Malvern Hill, near Turkey Bend, James River, Va., fought Tuesday, July 1st, 1862. The battle…

Battle of Malvern Hill
"Battle of Malvern Hill, near Turkey Bend, James River, Va., fought Tuesday, July 1st, 1862. The battle…

Battle of Malvern Hill
The Battle of Malvern Hill, also known as the Battle of Poindexter's Farm took place on July 1, 1862,…

Invasion of Maryland
"The invasion of Maryland- General Kilpatrick repulsing the Confederate Stuart at Boonsborough, July…

Massachusetts Battery
Martin's Massachusetts Battery C opening fire on the Confederate fortifications commanding the approaches…

George McClellan at Battle of Antietam
George Brinton McClellan (December 3, 1826 – October 29, 1885) was a major general during the…

George McClellan
George Brinton McClellan (December 3, 1826 – October 29, 1885) was a major general during the…

Battle of Mechanicsville
The Battle of Beaver Dam Creek, also known as the Battle of Mechanicsville or Ellerson's Mill took place…
Battle of Middletown
"Battle of Middletown, on the afternoon of the 19th of October, 1864. Great victory won by Major General…

Battle of Mill Spring
"Battle of Mill Spring, on the Cumberland River, near Jamestown, between a confederate force, 8,000…

Battle of Mill Spring
"Battle of Mill Spring, on the Cumberland River, near Jamestown, between a confederate force, 8,000…

Battle of Mill Spring
"Battle of Mill Spring, on the Cumberland River, near Jamestown, between a confederate force, 8,000…

Battle of Mill Spring
"Battle of Mill Spring, on the Cumberland River, near Jamestown, between a confederate force, 8,000…

Gaine's Mill
Soldiers capturing a cannon. Depiction of the Battle of Gaine's Mill during the Civil War. It was the…

Battle of Missionary Ridge
The Battle of Missionary Ridge included in the Third Battle of Chattanooga was fought November 23–25,…

War in Mississippi
"The war in Mississippi. General McPherson's army crossing the Big Black at messenger's Ferry, Thursday,…

War in Mississippi
"The war in Mississippi- defeat of Wirt Adams's Confederate cavalry by the Second Wisconsin cavalry,…

Siege of Mobile
"The siege of Mobile- explosion of Fort Powell, at Grant's Pass, July 5th, 1864."— Frank Leslie,…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Battle of Munfordville
"Battle of Munfordville, Ky., Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the Confederates charging through the abatis…

Munson's Hill
"Skirmishing between the pickets of the two armies near Munson's Hill- the hill in the distance. Munson's…

Battle of Murfreesboro
The Battle of Stones River or Second Battle of Murfreesboro (in the South, simply the Battle of Murfreesboro),…

Battle of New Bern
Landing at the Battle of New Bern, also known as the Battle of New Berne or Battle of Newbern which…

Battle of New Berne
"The battle of Newberne- final and successful charge of the Federal troops under General Burnside, on…

Battle of New Berne
"Battle of New Berne- Lieutenant Hammond capturing Colonel Avery, of South Carolina, while he was endeavoring…
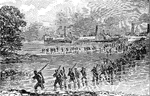
Troops Landing at Newbern
The Battle of New Bern was fought on 14 March 1862, near the city of New Bern, North Carolina, as part…

Old Church
"Desperate skirmish at Old Church, near Tunstall's Station, VA., between a squadron of the Fifth United…

Old Church
"Desperate skirmish at Old Church, near Tunstall's Station, VA., between a squadron of the Fifth United…

Old Church
"Desperate skirmish at Old Church, near Tunstall's Station, VA., between a squadron of the Fifth United…

Battle of Pea Ridge
The Battle of Pea Ridge, also known as Elkhorn Tavern, was fought on March 7th and 8th in 1862 during…

Battle of Pea Ridge
"Battle of Pea Ridge, Ark., fought March 6th, 7th and 8th, 1862, between the Federal forces, 13,000…




