The Human Sensory Systems: Hearing ClipArt gallery offers 133 illustrations related to the human auditory sense. The structures within the ear also contribute to the sense of balance or equilibrium.
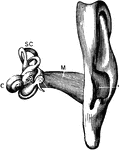
The Auditory Apparatus
The auditory apparatus with the surrounding bone removed. Labels: M, external auditory canal; SC, semicircular…
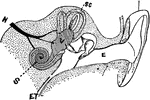
Diagram of the Auditory Apparatus
A diagram of a section of the auditory apparatus. Labels: E, external canal; M, in the middle ear; V,…
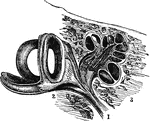
Auditory Nerve
"By anatomists, the auditory nerve is associated with the facial, and is the seventh in order of origin…
Auditory Nerve
"By anatomists, the auditory nerve is associated with the facial, and is the seventh in order of origin…
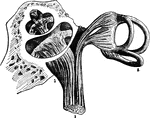
Auditory Nerve
"a, the osseous septum grooved for the passage of the cochlear nerve b, which terminates by a free end…
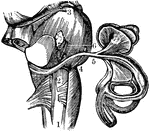
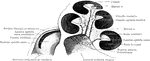
View of the Auditory Nerve
A view of the auditory nerve. Labels: 1, The spinal cord. 2, The medulla oblongata. 3, The lower part…
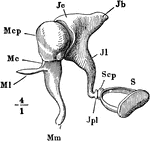
The Auditory Ossicles
The auditory ossicles of the right ear, seen from the front. Labels: M, malleus; J, incus; S, stapes;…
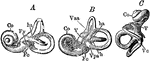
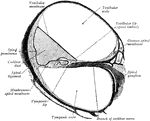
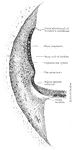
The Bony Labyrinth of the Ear
Casts of the bony labyrinth of the ear. Labels: A, left labyrinth see from the outer side; B, right…
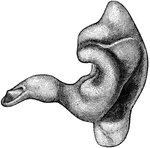
External auditory canal
"A Cast of the External Auditory Canal. The auditory canal is a passage in the solid potion of the temporal…
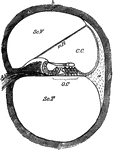
Cochlea
Diagram of a section of a coil of the cochlea of the ear. Labels: C.C, canal of the cochlea; mR, its…
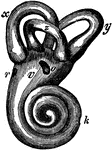
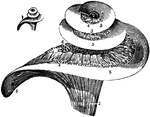
The Cochlea and Passages of the Ear
In this figure are shown the winding passages of the ear (the labyrinth of the ear). The middle part…
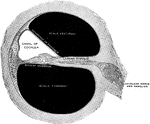
Cochlea in Transverse Section
The cochlea in transverse section. Observe especially the canals of the cochlea, which is a part of…
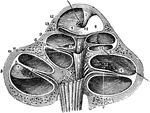
The Cochlea of the Ear
A vertical section of the cochlea, highly magnified, to show the arrangement and connection of its parts.
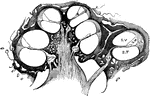
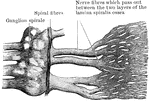
Longitudinal Section of the Cochlea
Longitudinal section of the cochlea, showing the relations of the scalae, the ganglion spirale, ect.…
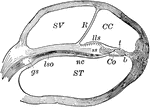
Cochlea, Section of
Section of one coil of the cochlea, magnified. Labels: SV, scala vestibuli; R, membrane of Reissner;…
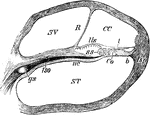
Section Through Coil of the Cochlea
Section through one of the coils of the cochlea. Labels: ST, scala tympani; SV, scala vestibuli; CC,…

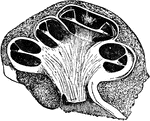
The Cochlea
The cochlea of the ear which is a spiral canal situated in the eburnated portion of the petrous bone,…
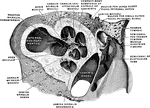
Vertical Section Through the Cochlea
Vertical section through the right cochlea, medial portion, viewed from the lateral side.
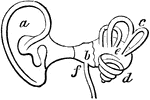
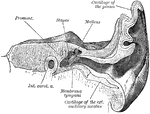
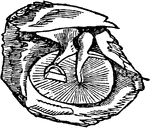
Ear
Interior of the ear. There is external to the head a wide-mouthed tube, or ear-trumpet (a), for catching…
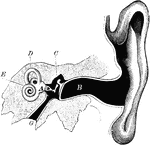
Ear
The human ear. Labels: A, vestibule or antechamber; B, auditory canal; C, the hammer, anvil, and the…
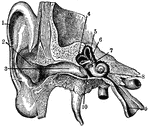
Ear
"Section through right ear. 1, helix; 2, concha; 3, outer passage; 4, 5, 6, semi-circular canals; 7,…
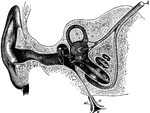
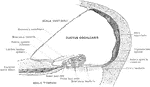
Ear and Auditory Canal
Semi-diagrammatic section through the right ear. Labels: M, concha; G, the external auditory canal;…
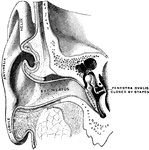
Ear Showing Auditory Canal and Tympanum
Vertical section through the external auditory canal and tympanum, passing in front of the fenestra…
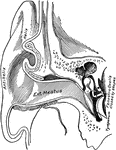
Ear Showing External Auditory Meatus
Vertical section through the external auditory meatus and tympanum, passing in front of the fenestra…
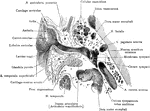
Auditory Apparatus of the Ear
Horizontal section through the right external acoustic canal viewed from above.
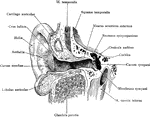
Auditory Canal of the Ear
Vertical section through the right external acoustic canal, viewed from in front.

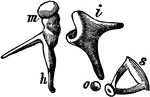
Bones of the Ear
Bones of the ear: Malleus, Incus and Orbiculare, Stapes. The bones of the area are connected with each…
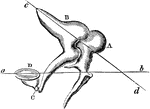
Bones of the Ear
A, the malleus, or mallet, with its long handle running down, to touch with its delicate extremity the…
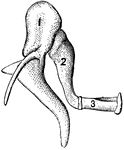
Bones of the Ear
"1, malleus, or hammer; 2, incus, or anvil; 3, stapes, or stirrup." — Blaisedell, 1904
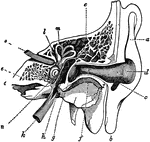
A Cross-Section of the Ear
Cross-section of the external and internal ear. a, b, and c: External ear. d: Entrance…
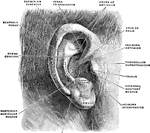
External Ear
The external ear consists of an expanded portion named pinna or auricula, and the auditory canal or…
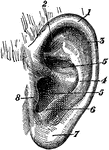
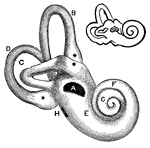
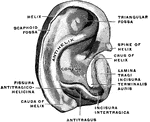
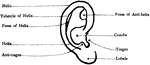
External Ear
"External Ear, or Pinna. 1, helix; 2, fossa of antihelix, or fossa triangularis; 3, fossa of helix,…
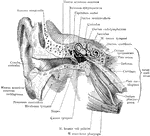
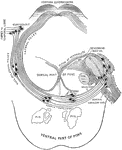
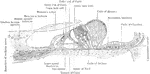
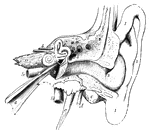
External Ear and Middle Ear
General view of the right external ear and middle. The external ear has been opened by a vertical section…
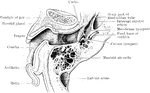
Horizontal Section of Ear
Horizontal section of right ear; upper half of section, viewed from below.
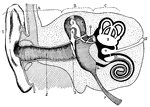
Human Ear
A diagram of the human ear. It is divided into the outer ear - A, middle ear - B, and inner ear - C.…
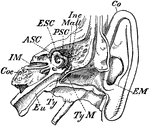
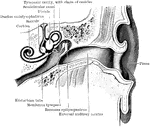
Inner Ear
"Transverse Section through Side Walls of Skull, showing the Inner Parts of the Ear. Co, concha or external…